Vamidothion
Synonym(s):O,O-Dimethyl S-[2-(1-methyl-2-methylamino-2-oxoethylthio)ethyl] phosphorothioate
- CAS NO.:2275-23-2
- Empirical Formula: C8H18NO4PS2
- Molecular Weight: 287.34
- MDL number: MFCD00055442
- EINECS: 218-894-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
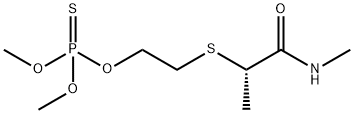
What is Vamidothion?
Description
Vamidothion is a colorless crystalline substance,. It is readily soluble in water (4 kg/L) and most organic solvents except aliphatic hydrocarbons. Log Kow = 0.12. It decomposes in strong alkaline and acidic media.
The Uses of Vamidothion
Vamidothion is a systemic insecticide used to control Homoptera in cotton, fruit and rice.
The Uses of Vamidothion
Vamidothion is a phosphorothioic insecticide for apples and potatoes.
What are the applications of Application
Vamidothion solution is an acaricidal component of some pesticides
Definition
ChEBI: An organic thiophosphate that is N-methyl-2-[(2-sulfanylethyl)sulfanyl]propanamide in which the thiol group has been converted to the corresponding O,O-dimethyl thiophoshate. Formerly used as an inse ticide and acaricide, it is no longer approved for use within the European Union.
Pharmacology
Pyriproxyfen formulations demonstrate persistent efficacy. For example, a water-based 5.3% pyriproxyfen spot-on formulation applied to cats was reported to completely prevent the hatching of flea eggs for at least 46 days after treatment and continued to provide greater than 96% control until day 60 (57). Because pyriproxyfen is efficacious at very low concentrations, trace amounts of the chemical, when transferred from treated pets to their environments, are sufficient to inhibit the development of larvae.
Metabolic pathway
Vamidothion is mainly metabolised via oxidation to its sulfoxide; further oxidation to the corresponding sulfone has been observed in houseflies but occurs much less readily than with other thioether-containing organophosphates (e.g. phorate). The sulfoxide is then hydrolysed via P-S and C-S bond cleavage to give the thiol or hydroxyl derivatives and dimethyl phosphate and O,O-dimethyl phosphorothioate respectively. O-Demethylation apparently occurs as a major degradation process in plants but has not been observed in soil or in animals. N-Demethylation and hydrolysis to the corresponding carboxylic acid, such as occurs with dimethoate, does not apparently happen in the case of vamidothion.
Degradation
Vamidothion is decomposed in strongly acidic or alkaline media (PM). Barceld et al. (1993) examined the photolysis of vamidothion in water containing 2-4% methanol and 5% acetone as a photosensitiser irradiated by a xenon arc (suntest) lamp. Metabolites were analysed and characterised by HPLC, thermospray MS and UV (diode array) spectra. The main degradation product identified was vamidothion sulfoxide (2). This product of vamidothion photolysis is shown in Scheme 1.
Toxicity evaluation
The acute oral LD50 for rats is 64–105 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats is 1.73 mg/L air. ADI is 8 μg/kg b.w.
Properties of Vamidothion
| Melting point: | 35.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 72.8°C |
| Density | 1.240±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 9×10-6 Pa (est.) |
| Flash point: | 2 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| Water Solubility | 4,000,000 mg l-1 |
| pka | 15.22±0.46(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 2275-23-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phosphorothioic acid, o,o-dimethyl s-[2-[[1-methyl-2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]thio]ethyl] ester(2275-23-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Vamidothion (2275-23-2) |
Safety information for Vamidothion
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Vamidothion
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1