HAFNIUM CARBIDE
Synonym(s):HF516010
- CAS NO.:12069-85-1
- Empirical Formula: CHf
- Molecular Weight: 190.5
- MDL number: MFCD00016126
- EINECS: 235-114-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 15:08:38
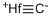
What is HAFNIUM CARBIDE?
Chemical properties
dark, gray, brittle solid; fcc, a=0.4640 nm; high cross section for absorption of thermal neutrons; resistivity 8.8μohm· cm; most refractory binary material known; hardness 2300kgf/mm2; used in control rods of nuclear reactors; can be prepared by heating HfO2 with lampblack under H2 at 1900°C–2300°C; used in crucible form for melting hafnium oxide, other oxides [KIR80] [HAW93] [CER91]
Physical properties
Dark gray brittle solid, most refractory binary material known. Controls rods in nuclear reactors, crucible container for melting HfO and other oxides. 2 Corrosion resistant to liquid metals such as Nb, Ta, Mo, and W. Severe oxidation in air above 1100–1400°C and stable up to 2000°C in helium.
The Uses of HAFNIUM CARBIDE
Hafnium carbide (HfC) with a melting point over 3890°C is a refractory binary compound. HfC and NbC can also be used as refractory coatings in nuclear reactors. The mixed carbide Ta4HfC5 possesses the highest melting point of any currently known compound at 4215°C.
The Uses of HAFNIUM CARBIDE
Used for preparation of ultra-high temperature ceramics 1 Reactant in synthesis of hafnium-containing organometallic polymers 2 Additive in alloys 3 Used in coatings 4
The Uses of HAFNIUM CARBIDE
It is an ideal metal in the manufacture of control rods for nuclear reactors.
Production Methods
Hafnium carbide is a dark gray, brittle solid. It can be
prepared by heating a mixture of the elements or by reacting
hafnium tetrachloride with methane at 2100 C. Sufficient
quantities of hafnium oxide or hafnium metal sponge are
obtained during the large-scale production of pure zirconium
for nuclear reactors. On an industrial scale, hafnium carbide
can be produced from the hydrided hafnium sponge at
1500–1700 ℃ or from hafnium oxide at 2000–2200 ℃ by
carburization in vacuo in the presence of hydrogen.
The resulting carbide contains almost the theoretical quantity
of carbon (6.30% °C) and a maximum of 0.1% free carbon
(219). The hafnium carbide obtained is not a true
stoichiometric compound as much as a solution of carbon
at specific interstitial sites of a face-centered cubic hafnium
lattice.
Hafnium carbide is inert to most reagents at room temperature
but is dissolved by hydrofluoric acid solutions.
Hafnium carbide reacts exothermally with halogens at
250–500 ℃to form hafnium tetrahalide, and to form hafnium
oxide with oxygen above 500℃. In the presence of hydrogen,
hafnium carbide slowly loses some of its carbon at higher
temperatures.
Properties of HAFNIUM CARBIDE
| Melting point: | 2930 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 12.2 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| RTECS | MG4620000 |
| form | Powder |
| color | Gray |
| Resistivity | 45.0 (ρ/μΩ.cm) |
| Water Solubility | it is insoluble in water. |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, NaCl Structure |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 50 mg/m3; TWA 0.5 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 12069-85-1 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hafnium carbide (HfC) (12069-85-1) |
Safety information for HAFNIUM CARBIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. |
Computed Descriptors for HAFNIUM CARBIDE
| InChIKey | NVDNLVYQHRUYJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
BOC-L-4-HYDROXYPROLINE 2-nitro 3-hydroxy pyridine 2,6-Dichloropyridin-4-amine 2,3 Diamino pyridine 5-Iodo-2-(1-methylethyl)-3(2H)-pyridazinone 1-Azetidinecarboxylic acid, 3-[(3S)-1-(trans-3-carboxy-3-methylcyclobutyl)-3-piperidinyl]-, 1-(1,1-dimethylethyl) ester Tert-Butyl N-[3-(dimethylcarbamoyl)prop-2-en-1-yl]carbamate 1-(difluoromethyl)-N-methylcyclobutan-1-amine 2-(4-Methyl-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1H-benzimidazole 6-(4-iodophenyl)-1-oxa-6-azaspiro[3.3]he Trimethyl(phenylthio)silane Polycaprolactone(2000)-PEG(20000)-Polycaprolactone(2000) Diacrylate Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, PolyoxyethyleneOleylCetylEtherSulfosuccinate Ascorbyl Tetraisopalmitate or Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate Castor Oil, Ethoxylated, Cremophor EL or PEG-35 Castor Oil Tween 20 or Polysorbate 20 Acetone-d6 (R)-2-Mercaptobutanoic acid 3-iodo-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine 3-(naphthalen-1-ylsulfonyl)-1H-indazol-5-amine methyl 5-amino-3-(1,1-dioxidotetrahydro-2H-1,2-thiazin-2-yl)-2-fluorobenzoate 7-methoxy-8-(2-morpholinoethoxy)-4-((3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)amino)benzo[g]quinoline-3-carbonitrile Dimethylaluminum isopropoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
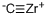



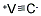
You may like
-
 Hafnium(IV) carbide, <1.25 μm CAS 12069-85-1View Details
Hafnium(IV) carbide, <1.25 μm CAS 12069-85-1View Details
12069-85-1 -
 Hafnium(IV) carbide, 99.8% CAS 12069-85-1View Details
Hafnium(IV) carbide, 99.8% CAS 12069-85-1View Details
12069-85-1 -
 Hafnium carbide CASView Details
Hafnium carbide CASView Details -
 Hafnium(IV) carbide CAS 12069-85-1View Details
Hafnium(IV) carbide CAS 12069-85-1View Details
12069-85-1 -
 5721-91-5 98%View Details
5721-91-5 98%View Details
5721-91-5 -
 Calcium 11% clear solution 98%View Details
Calcium 11% clear solution 98%View Details -
 Sodium Croscarmellose 98%View Details
Sodium Croscarmellose 98%View Details
74811-65-7 -
 16455-61-1 98%View Details
16455-61-1 98%View Details
16455-61-1
