Trifluoroacetic acid
Synonym(s):TFA;TFA in H2O/ACN;TFA solution;Trifluoroacetic acid solution;Trifluoroacetic acid ZerO2
- CAS NO.:76-05-1
- Empirical Formula: C2HF3O2
- Molecular Weight: 114.02
- MDL number: MFCD00004169
- EINECS: 200-929-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:50
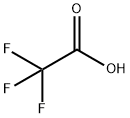
What is Trifluoroacetic acid?
Description
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is an important organic reagent, commonly employed as an additive for the separation of amino acids, peptides, and proteins. The excellent solubility of peptides in TFA, its minimal side effects during deprotection, and its mild nature render it suitable not only for the removal of temporary protecting groups but also for the final deprotection step. Moreover, it is one of the most economical fluorinated building blocks, frequently used in nucleophilic trifluoromethylation reactions.
Chemical properties
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is an analogue of acetic acid with the three hydrogen atoms replaced by three fluorine atoms. It has a vinegar-like odor and is a strong acid, a good solvent and has excellent reactive properties. Due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the fluorine atom, acetic acid exhibits significantly greater acidity than AcOH. The pKa of TFA is 0.23, whereas that of AcOH is 4.76. The specific gravity of liquid TFA is 1.48 and it boils at 72 °C.
The Uses of Trifluoroacetic acid
Trifluoroacetic acid is an important building block in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and performance products. It is a precursor to many fluorinated compounds, and widely used in peptide synthesis and other organic transformations involving deprotection of t-BOC group. The combination of properties like solubility in most of the solvents, volatility, catalytic property, and strong acidity with non-oxidizing nature makes it a widely used reagent in organic synthesis. Trifluoroacetic acid can use as an ion pairing agent in liquid chromatography, as a solvent in NMR spectroscopy and as a calibrant in mass spectrometry. It is used as a catalyst in esterification reaction and condensation reaction and a protective agent for hydroxyl and amino.
What are the applications of Application
Trifluoroacetic acid is a strong non-oxidizing acid
Definition
ChEBI: Trifluoroacetic acid is a monocarboxylic acid that is the trifluoro derivative of acetic acid. It has a role as a reagent and a human xenobiotic metabolite. It derives from an acetic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a trifluoroacetate.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 26, p. 923, 1961 DOI: 10.1021/jo01062a068
General Description
Trifluoroacetic acid appears as a colorless fuming liquid with a pungent odor. Soluble in water and denser than water. Corrosive to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Used to make other chemicals and as a solvent.
Air & Water Reactions
Fumes in air. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Trifluoroacetic acid is a strong acid; attacks many metals [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 935]. A 30% solution of hydrogen peroxide in Trifluoroacetic acid is often used to destructively oxidize aromatic rings in preference to the side chains. Explosions have occurred, if the excess peroxide is not catalytically destroyed, prior to removal of solvent, [Tetrahedron Lett., 1977, 1703-1704]. The reduction of amides of Trifluoroacetic acid with lithium aluminum hydride are dangerous at all phases of the process, explosions have occurred, [Chem. Eng. News, 1955, 33, 1368].
Health Hazard
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a highly corrosive acid that is extremely destructive to the upper respiratory tract, eyes, and skin.
Fire Hazard
Trifluoroacetic acid is not combustible. Nevertheless, the presence of trifluoroacetic acid at the site of a fire would be of great concern because of its high vapor pressure and extreme corrosiveness. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Trifluoroacetic acid?(TFA) is mainly preferred as an internal chemical shift referencing agent in?19F NMR.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by intravenous route. Mildly toxic by inhalation. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of F-. Used as a strong organic acid catalyst.
Storage
trifluoroacetic acid should be stored in an acid cabinet away from other classes of compounds. Because of its high vapor pressure, fumes of trifluoroacetic acid can destroy labels on other bottles if the container is not tightly sealed.
Purification Methods
The purification of trifluoroacetic acid, reported in earlier editions of this work, by refluxing over KMnO4 for 24hours and slowly distilling has resulted in very SERIOUS EXPLOSIONS on various occasions, but not always. This apparently depends on the source and/or age of the acid. The method is NOT RECOMMENDED. Water can be removed by adding trifluoroacetic anhydride (0.05%, to diminish water content) and distilling. [Conway & Novak J Phys Chem 81 1459 1977]. It can be refluxed and distilled from P2O5. It is further purified by fractional crystallisation by partial freezing and again distilled. Highly TOXIC vapour. Work in an efficient fume hood. [Beilstein 2 IV 458.]
Incompatibilities
Mixing trifluoroacetic acid and water evolves considerable heat.
Waste Disposal
Trifluoroacetic acid and waste material containing this substance should be placed in an appropriate container, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines.
Properties of Trifluoroacetic acid
| Melting point: | -15.4 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 72.4 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.489 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.9 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 97.5 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | None |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | Miscible with ether, acetone, ethanol, benzene, hexane, and CCl<sub>4</sub> |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| pka | -0.3(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.480 |
| color | Colorless |
| Odor | Sharp, pungent odor |
| PH Range | 1 |
| PH | 1 (10g/l, H2O) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.9 λ: 270 nm Amax: 0.10 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 290 nm Amax: 0.04 λ: 300 nm Amax: 0.03 λ: 320 nm Amax: 0.025 |
| Merck | 14,9681 |
| BRN | 742035 |
| Dielectric constant | 23.7(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with combustible material, strong bases, water, strong oxidizing agents. Non-combustible. Hygroscopic. May react violently with bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 76-05-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetic acid, trifluoro-(76-05-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetic acid, 2,2,2-trifluoro- (76-05-1) |
Safety information for Trifluoroacetic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Trifluoroacetic acid
| InChIKey | DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Trifluoroacetic acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
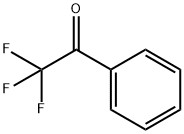
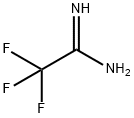
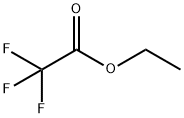
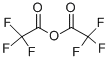
![(1S,4S)-2-CYCLOPROPYLMETHYL-2,5-DIAZA-BICYCLO[2.2.1]HEPTANE DI-TRIFLUOROACETIC ACID](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure20/GIF/CB8825100.gif)
You may like
-
 Trifluoroacetic acid 98%View Details
Trifluoroacetic acid 98%View Details -
 Trifluoroacetic acid CAS 76-05-1View Details
Trifluoroacetic acid CAS 76-05-1View Details
76-05-1 -
 TRIFLUOROACETIC ACID 99%View Details
TRIFLUOROACETIC ACID 99%View Details -
 Trifluoroacetic Acid CASView Details
Trifluoroacetic Acid CASView Details -
 Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) for molecular biology CAS 76-05-1View Details
Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) for molecular biology CAS 76-05-1View Details
76-05-1 -
 Trifluoroacetic Acid CASView Details
Trifluoroacetic Acid CASView Details -
 Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) extrapure AR CAS 76-05-1View Details
Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) extrapure AR CAS 76-05-1View Details
76-05-1 -
 Trifluoroacetic Acid, Purity: 99%, 25 kg DrumView Details
Trifluoroacetic Acid, Purity: 99%, 25 kg DrumView Details
76-05-1
