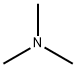
Triethylamine
Synonym(s):TEA;Triethylamine;acid;Degassed and low oxygen triethylamine;N,N-Diethylethanamine, (Diethylamino)Ethane
- CAS NO.:121-44-8
- Empirical Formula: C6H15N
- Molecular Weight: 101.19
- MDL number: MFCD00009051
- EINECS: 204-469-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:52
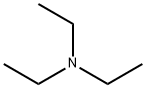
What is Triethylamine?
Description
Triethylamine (TEA) is a very commonly used organic base. Diisopropylethylamine (DIEA) is a closely related organic base. DIEA is more sterically hindered than TEA therefore is less prone to quaternization when used with highly reactive alkylation agents. TEA has a boiling point of 89 C, making it easier to remove via rotovap distillation. DIEA has a boiling point of 127 C, making it more useful for reactions that are over 90 C. In most situations TEA and DIEA can be used interchangably. However, for certain situations one is a better choice than the other.
Chemical properties
Triethylamine is a colorless to yellowish liquid with a strong ammonia to fish-like odor. It is a base commonly used in organic chemistry to prepare esters and amides from acyl chlorides. Like other tertiary amines,it catalyzes the formation of urethane foams and epoxy resins.
The Uses of Triethylamine
Triethylamine is a base used to prepare esters and amides from acyl chlorides as well as in the synthesis of quaternary ammonium compounds. It acts as a catalyst in the formation of urethane foams and epoxy resins, dehydrohalogeantion reactions, acid neutralizers for condensation reactions and Swern oxidations. Triethylamine is used in accelerating activators for rubber; as a corrosion inhibitor for polymers; a propellant; wetting, penetrating, and waterproofing agent of quaternary ammonium compounds.
Definition
ChEBI: Triethylamine is a tertiary amine that is ammonia in which each hydrogen atom is substituted by an ethyl group.
Production Methods
Triethylamine is prepared by a vapor phase reaction of ammonia with ethanol or reaction of N,N-diethylacetamide with lithium aluminum hydride. It may also be produced from ethyl chloride and ammonia under heat and pressure or by vapor phase alkylation of ammonia with ethanol.
Aroma threshold values
High strength odor, fishy type; recommend smelling in a 0.01% solution or less.
Reactivity Profile
Triethylamine reacts violently with oxidizing agents. Reacts with Al and Zn. Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Health Hazard
Vapors irritate nose, throat, and lungs, causing coughing, choking, and difficult breathing. Contact with eyes causes severe burns. Clothing wet with chemical causes skin burns. Triethylamine may also be irritating to skin and mucous membranes (Windholz et al 1983).
Fire Hazard
Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Triethylamine is known to drive polymerization reaction. It acts as a source of carbon and nitrogen for bacterial cultures. Triethylamine is used in pesticides. Triethylamine can serve as an organic solvent.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. Mildly toxic by inhalation. Human systemic effects: visual field changes. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. A skin and severe eye irritant. Can cause kidney and liver damage. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. Complex with dinitrogen tetraoxide explodes below 0°C when undduted with solvent. Exothermic reaction with maleic anhydride above 150°C. Can react with oxidzing materials. Incompatible with N2O4. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical, alcohol foam. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Potential Exposure
Triethylamine is and aliphatic amine used as a solvent; corrosion inhibitor; in chemical synthesis; and accelerator activators; paint remover; base in methylene chloride or other chlorinated solvents. TEA is used to solubilize 2,4,5-T in water and serves as a selective extractant in the purification of antibiotics. It is used to manufacture quaternary ammonia compounds and octadecyloxymethyltriethylammonium chloride; an agent used in textile treatment.
Carcinogenicity
TEA was not mutagenic in bacterial assays, but it did cause aneuploidy and chromosome aberrations in rats.
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. Low et al. (1991) reported that the photooxidation of aqueous tertiary amine
solutions by UV light in the presence of titanium dioxide resulted in the formation of ammonium
and nitrate ions.
Chemical/Physical. Triethylamine reacted with NOx in the dark to form diethylnitrosamine. In
an outdoor chamber, photooxidation by natural sunlight yielded the following products:
diethylnitramine, diethylformamide, diethylacetamide, ethylacetamide, diethylhydroxylamine,
ozone, acetaldehyde, and peroxyacetyl nitrate (Pitts et al., 1978).
Metabolism
There have been few studies on the metabolism of industrially important aliphatic amines such as triethylamine. It is generally assumed that amines not normally present in the body are metabolized by monoamine oxidase and diamine oxidase (histaminase).
Ultimately ammonia is formed and will be converted to urea. The hydrogen peroxide formed is acted upon by catalase and the aldehyde formed is thought to be converted to the corresponding carboxylic acid by the action of aldehyde oxidase (Beard and Noe 1981).
Shipping
UN1296 Triethylamine, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid, 8-Corrosive material.
Incompatibilities
A strong base. Violent reaction with strong acids; halogenated compounds; and strong oxidizers. Attacks some forms of plastics, rubber and coatings. Corrosive to aluminum, zinc, copper, and their alloys in the presence of moisture. Reaction with nitrosating agents (e.g., nitrites, nitrous gases, and nitrous acid) capable of releasing carcinogenic nitrosamines.
Waste Disposal
Controlled incineration (incinerator equipped with a scrubber or thermal unit to reduce nitrogen oxides emissions).
Properties of Triethylamine
| Melting point: | -115 °C |
| Boiling point: | 90 °C |
| Density | 0.728 |
| vapor density | 3.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 51.75 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 4246 | TRIETHYLAMINE |
| Flash point: | 20 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | water: soluble112g/L at 20°C |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| pka | 10.75(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.725 (20/4℃) |
| color | Clear |
| Odor | Strong ammonia-like odor |
| Relative polarity | 1.8 |
| PH | 12.7 (100g/l, H2O, 15℃)(IUCLID) |
| explosive limit | 1.2-9.3%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.0054ppm |
| Water Solubility | 133 g/L (20 ºC) |
| JECFA Number | 1611 |
| Merck | 14,9666 |
| BRN | 1843166 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.79 at 25 °C (Christie and Crisp, 1967) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: IDLH 200 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 25 ppm (100 mg/m3); ACGIH
TLV: TWA 1 ppm, STEL 3 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 5.0(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Extremely flammable. Readily forms explosive mixtures with air. Note low flash point. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, ketones, aldehydes, halogenated hydrocarbons. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 121-44-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Triethylamine(121-44-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Triethylamine (121-44-8) |
Safety information for Triethylamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Triethylamine
| InChIKey | ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Triethylamine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Tri Ethyl Amine 99%View Details
Tri Ethyl Amine 99%View Details -
 Tri Ethyl Amine 99%View Details
Tri Ethyl Amine 99%View Details -
 Triethylamine CAS 121-44-8View Details
Triethylamine CAS 121-44-8View Details
121-44-8 -
 Triethylamine CAS 121-44-8View Details
Triethylamine CAS 121-44-8View Details
121-44-8 -
 Triethylamine CASView Details
Triethylamine CASView Details -
 Tri Ethyl Amine LR Grade, Purity: 99%, 25 Liter CarboyView Details
Tri Ethyl Amine LR Grade, Purity: 99%, 25 Liter CarboyView Details
121-44-8 -
 Tri ethyl amine 99 %View Details
Tri ethyl amine 99 %View Details
102-71-6 -
 Tri Ethyl Amine (TEA), For Pharma, LiquidView Details
Tri Ethyl Amine (TEA), For Pharma, LiquidView Details
102-71-6
