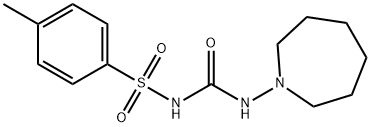
TOLAZAMIDE
Synonym(s):1-(Hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)-3-(p-toluenesulfonyl)urea
- CAS NO.:1156-19-0
- Empirical Formula: C14H21N3O3S
- Molecular Weight: 311.4
- MDL number: MFCD00083504
- EINECS: 214-588-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
What is TOLAZAMIDE?
Absorption
Rapidly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Toxicity
Overdosage of sulfonylureas can produce hypoglycemia. Severe hypoglycemic reactions with coma, seizure, or other neurological impairment occur infrequently, but constitute medical emergencies requiring immediate hospitalization.
Description
Tolazamide is a first generation sulfonylurea that inhibits sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) linked to the inwardly rectifying potassium channel (KIR6.2; IC50 = 4.2 μM in HEK293 cells transfected with the human receptor). It has no effect on glucose uptake in L6 rat skeletal muscle cells when used at a concentration of 0.6 mg/mL but enhances glucose uptake two-fold when used in combination with insulin. In vivo, tolazamide (128 mg/kg) reduces glomerulosclerosis and albumin excretion in a rat model of insulin-dependent diabetes induced by streptozotocin . Formulations containing tolazamide have been used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Tolinase,Upjohn,Italy,1964
The Uses of TOLAZAMIDE
Labelled Tolazamide, an antidiabetic.
The Uses of TOLAZAMIDE
This drug is also a derivative of first generation of sulfonylurea, and it possesses stimulatory action on β-cells in pancreas, as well as the same range of action as all other drugs of the group of examined compounds. Tolazamide is used for non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus without expressed microvascular complications.
What are the applications of Application
Tolazamide is sulphonylurea hypoglycemic agent with actions and uses similar to those of chlorpropamide
Background
A sulphonylurea hypoglycemic agent with actions and uses similar to those of chlorpropamide.
Indications
For use as an adjunct to diet to lower the blood glucose in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (Type II) whose hyperglycemia cannot be satisfactorily controlled by diet alone.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-sulfonylurea that is 1-tosylurea in which a hydrogen attached to the nitrogen at position 3 is replaced by an azepan-1-yl group. A hypoglycemic agent, it is used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Manufacturing Process
1-Nitrosohexamethyleneimine: A solution of 89.5 grams of
hexamethyleneimine, 75 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 36 ml of
water was heated to 70°C on a steam bath. The solution was made acidic by
adding 5 ml of 2 N hydrochloric acid. While maintaining the reaction mixture
at 70° to 75°C, a solution of 67 grams of sodium nitrite in 95 ml of water was
added with stirring over a period of 1 hour. The mixture was then stirred at
70°C for 2 hours, and then cooled. The upper oily layer was separated and
the aqueous layer was then extracted with ether. The combined ether extract
and oil was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and concentrated to
dryness. Upon distillation of the residue there was obtained 1-
nitrosohexamethyleneimine as a yellow oil, boiling at 136° to 138°C/34 mm.
1-Aminohexamethyleneimine: To a mixture of 15.18 grams of lithium
aluminum hydride and 400 ml of anhydrous ether was added about 10% of a
solution of 51.27 grams of 1-nitrosohexamethyleneimine in 100 ml of
anhydrous ether. The mixture was refluxed until the reaction started. The
remainder of the solution was added at such a rate as to maintain gentle
reflux. Refluxing was continued for 2 hours more, followed by the successive
addition of 16 ml of water, 12 ml of 20% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution
and 56 ml of water. The inorganic precipitate was removed by filtration and
washed with ether. The filtrate and ether washes were dried and the ether
was removed by evaporation. Upon distillation of the residue there was
obtained 25.46 grams (56%) of 1-aminohexamethyleneimine as a colorless
liquid boiling at 94° to 96°C/55 mm.
N-(4-Methylbenzenesulfonyl)-N'-Hexamethyleneiminourea Free Base: A
mixture of 11.42 grams of 1-aminohexamethyleneimine and 24.33 grams of
4-methylbenzenesulfonylurethane was heated at 130°C (oil-bath temperature)
for 2 hours. The resulting ethanol and unreacted amine were removed at 15
mm pressure for 2 hours while keeping the oil bath at 130°C. The residue was
cooled and recrystallized from methanol, giving 16.73 grams (54%) of N-(4-
methylbenzenesulfonyl)-N'-hexamethyleneiminourea free base melting at 163°
to 166°C. After a second recrystallization from methanol, the melting point
was 163.5° to 166.5°C.
Therapeutic Function
Oral hypoglycemic
General Description
White to off-white crystalline powder. Odorless or with a slight odor.
General Description
Tolazamide is N-[[(hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide; or 1-(hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea; or 1-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-3-(hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)urea (generic).Tolazamide incorporates a fully saturated azepine moietythat is but weakly basic, with a pKa of~3.32 The pKa of thesulfonylurea group lies within the typical range; thus, inareas of the duodenum wherein the pH falls within the rangeof 4 to 5, the uncharged form of the drug is the predominantspecies, and its lipophilicity lends to rapid absorption bypassive diffusion.
General Description
Tolazamide, 1-(hexahydro-1Hazepin-1-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea (Tolinase), is an analogof tolbutamide and is reported to be effective, in general,under the same circumstances in which tolbutamide is useful.Tolazamide, however, appears to be more potent than tolbutamideand is nearly equal in potency to chlorpropamide. Instudies with radioactive tolazamide, investigators found that85% of an oral dose appeared in the urine as metabolites thatwere more soluble than tolazamide itself.
Air & Water Reactions
TOLAZAMIDE may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to air. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
TOLAZAMIDE is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx). TOLAZAMIDE is incompatible with acids. .
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for TOLAZAMIDE are not available; however, TOLAZAMIDE is probably combustible.
Pharmacokinetics
Tolazamide is an oral blood glucose lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Tolazamide appears to lower the blood glucose acutely by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, an effect dependent upon functioning beta cells in the pancreatic islets. The mechanism by which tolazamide lowers blood glucose during long-term administration has not been clearly established. With chronic administration in Type II diabetic patients, the blood glucose lowering effect persists despite a gradual decline in the insulin secretory response to the drug. Extrapancreatic effects may be involved in the mechanism of action of oral sulfonylurea hypoglycemic drugs. Some patients who are initially responsive to oral hypoglycemic drugs, including tolazamide, may become unresponsive or poorly responsive over time. Alternatively, tolazamide may be effective in some patients who have become unresponsive to one or more other sulfonylurea drugs. In addition to its blood glucose lowering actions, tolazamide produces a mild diuresis by enhancement of renal free water clearance.
Synthesis
Tolazamide is 1-hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)-3-(p-toluenesulfonyl)urea (26.2.8). By maintaining structural similarities with first-generation drugs, this drug differs from the other drugs examined in that it has a semicarbazide group instead of a urea residue, and an azepine group instead of a cyclohexyl group. It is synthesized by reacting with ethyl-(p-toluenesulfonyl)carbamate (26.2.7), which is made from p-toluenesulfonamide and ethylchloroformate, with 1-aminoazepine.

Metabolism
Tolazamide is metabolized to five major metabolites ranging in hypoglycemic activity from 0 to 70%.
Properties of TOLAZAMIDE
| Melting point: | 162-164°C |
| Boiling point: | 300°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2228 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6740 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in chloroform; soluble in acetone; slightly soluble in ethanol (96%). |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 3.6(at 25℃) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 65.4mg/L(30 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1156-19-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tolazamide (1156-19-0) |
Safety information for TOLAZAMIDE
Computed Descriptors for TOLAZAMIDE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Tolazamide CAS 1156-19-0View Details
Tolazamide CAS 1156-19-0View Details
1156-19-0 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1