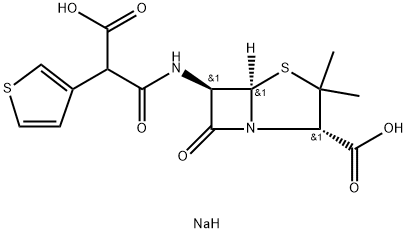
Ticarcillin
- CAS NO.:34787-01-4
- Empirical Formula: C15H16N2O6S2
- Molecular Weight: 384.43
- MDL number: MFCD00864998
- EINECS: 252-213-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2022-12-21 16:56:50
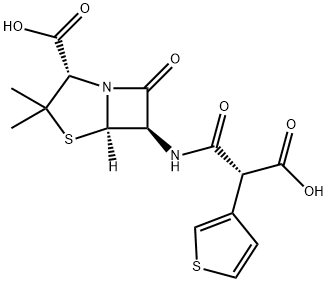
What is Ticarcillin?
Toxicity
As with other penicillins, neurotoxic reactions may arise when very high doses of ticarcillin are administered, especially in patients with impaired renal function.
Description
Temocillin disodium is a broad-spectrum, β-lactamase resistant, injectable penicillin. High serum levels and a five hour half-life allow once or twice-daily dosing.
Originator
Beecham (United Kingdom)
The Uses of Ticarcillin
Ticarcillin is a carboxypenicillin belonging to the beta-lactam class of antibiotics. Ticarcillin is an injectable antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by gram-negative bacteria, part icularly Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The Uses of Ticarcillin
Ticarcillin (SB) is a significant penicillin antibiotic that incorporates the thiophene ring system.
The Uses of Ticarcillin
Ticarcillin is a carboxypenicillin belonging to the beta-lactam class of antibiotics. Ticarcillin is an injectable antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by gram-negative bacteria, particularly Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Indications
For the treatment of bacterial infections.
Background
An antibiotic derived from penicillin similar to carbenicillin in action.
Definition
ChEBI: A penicillin compound having a 6beta-[(2R)-2-carboxy-2-thiophen-3-ylacetyl]amino side-group.
brand name
TEMOPEN
Antimicrobial activity
Because it is hydrolyzed less rapidly than ampicillin, non-β- lactamase-producing strains of N. gonorrhoeae, ampicillin-susceptible H. influenzae and some Enterobacteriaceae are susceptible. Most aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive bacteria are susceptible, with the exception of E. faecalis and β-lactamase-producing Staph. aureus. Anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria including B. fragilis are usually susceptible. Bactericidal synergy with aminoglycosides is demonstrable against Ps. aeruginosa and enterobacteria.
Acquired resistance
Ticarcillin is generally cross-resistant with carbenicillin. It is somewhat stable to hydrolysis by AmpC-mediated β-lactamases of Gram-negative bacilli, but can be hydrolyzed by most other chromosomally and plasmid-mediated enzymes unless protected by a β-lactamase inhibitor.
Pharmacokinetics
Ticarcillin is a semisynthetic antibiotic with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Ticarcillin is, however, susceptible to degradation by ?-lactamases, and therefore, the spectrum of activity does not normally include organisms which produce these enzymes.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: Negligible
Cmax 1 g intramuscular: 35 mg/L after 1 h
Plasma half-life: 1.3 h
Volume of distribution: 0.21 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: 50–60%
Absorption and distribution
It is not orally absorbed. On parenteral co-administration
with gentamicin, the plasma concentration of ticarcillin is
unaffected, but the concentration of gentamicin is lowered. It
enters the serous fluids, providing concentrations up to 60%
of those of the plasma. It does not cross the normal meninges
but levels of up to 50% of those of the plasma can be found
in meningitis.
Metabolism and excretion
Up to 15% is excreted as penicilloic acid, a higher percentage
than for carbenicillin (up to 5%). Some is excreted in
the bile, producing levels 2–3 times those in the plasma, but
the main route of excretion is through the kidneys (80%),
principally as unchanged drug, appearing in the urine in the
first 6 h. It is more rapidly eliminated in children with cystic
fibrosis.
Clinical Use
Serious infection, including septicemia, respiratory tract infections, genitourinary tract infections and skin and soft-tissue infections caused by susceptible bacteria
Side Effects
As with all penicillins, hypersensitivity reactions may occur, but are less frequent and severe than those associated with benzylpenicillin. Rashes and eosinophilia occur; reversible abnormalities of liver function can develop. Since large doses of the drug have to be used, convulsions can occur, as with other penicillins, and being a disodium salt, electrolyte disturbances can result from the sodium load and from loss of potassium.
Synthesis
Ticarcillin, [2S-(2|á,5|á,6|?)]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[2-carboxy-2-(3-thienyl) acetamido]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]-heptan-2-carboxylic acid (32.1.1.34), is synthesized by direct acylation of 6-APA in the presence of sodium hydroxide, but with 3-thienylmalonic acid chloride (32.1.1.33), which gives ticarcillin.

Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Ticarcillin
| Boiling point: | 768.3±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.62±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| pka | pKa 2.89±0.05(H2O
t=25.0
I=0.15 (KCl)) (Uncertain);3.28±0.04 (Uncertain) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 34787-01-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Ticarcillin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P342+P311:IF experiencing respiratory symptoms: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Ticarcillin
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Ticarcillin Supplement CAS 34787-01-4View Details
Ticarcillin Supplement CAS 34787-01-4View Details
34787-01-4 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1