Dimethyl phthalate
Synonym(s):Dimethyl phthalate;DMP;Phthalic acid dimethyl ester
- CAS NO.:131-11-3
- Empirical Formula: C10H10O4
- Molecular Weight: 194.18
- MDL number: MFCD00008425
- EINECS: 205-011-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:41
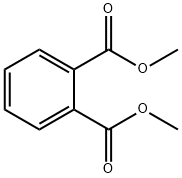
What is Dimethyl phthalate?
Description
Phthalates are plasticizers, and increase the flexibility of plastics. They are also found in deodorant formulations, perfumes, emollients and insect repellents.
Chemical properties
colourless oily liquid
Chemical properties
Dimethyl phthalate occurs as a colorless, or faintly colored, odorless, viscous, oily liquid.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless, odorless, moderately viscous, oily liquid
History
Screened during World War II, this repellent is exceptionally effective against A. aegypti, lasting 196 d on cloth. Tests have been run against the newer pests A. albopictus and A. aegypti, including five repellents containing DEET (test standard), a controlled release formulation containing DEET, two dosages of DEET in ethanol, and Avon Skin-So- Soft. On the skin, the repellent chemicals provide significant protection from biting; however, A. albopictus is more sensitive to repellents than A. aegypti.
The Uses of Dimethyl phthalate
Dimethyl Phalate is the methyl ester of phthalic acid. Dimethyl phthalate is an ectoparasiticide and has many other uses, including in solid rocket propellants, plastics, and insect repellents.
The Uses of Dimethyl phthalate
It is used as insect repellent.
The Uses of Dimethyl phthalate
Solvent and plasticizer for cellulose acetate and cellulose acetate-butyrate compositions. Insect repellent for personal protection against biting insects.
The Uses of Dimethyl phthalate
Dimethyl phthalate is used as an insect repellant. It has also been employed as a solvent for cellulose acetate.
What are the applications of Application
Dimethyl phthalate is an ectoparasiticide
Production Methods
Dimethyl phthalate is produced industrially from phthalic anhydride and methanol.
Definition
ChEBI: Dimethyl phthalate is a phthalate ester, a diester and a methyl ester.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 37, p. 6375, 1996 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(96)01351-2
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 35, p. 3205, 1970 DOI: 10.1021/jo00835a002
General Description
A water-white liquid without significant odor. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Hence sinks in water. Flash point 300°F. Eye contact may produce severe irritation and direct skin contact may produce mild irritation. Used in the manufacture of a variety of products including plastics, insect repellents, safety glass, and lacquer coatings.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Dimethyl phthalate reacts with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing with alkali metals and hydrides. Can generate electrostatic charges by swirling or pouring [Handling Chemicals Safely, 1980. p. 250].
Health Hazard
Symptoms unlikely from any exposure.
Health Hazard
The acute toxicity of dimethyl phthalate intest animals was found to be very low.Ingestion may produce irritation of the gas trointestinal tract, somnolence, hypotension,and coma. The oral LD50 value in miceis 6800 mg/kg. Animal studies have shownthat administration of this compound causeddevelopmental toxicity, having effects on fer tility. Maternal toxicity in Sprague-Dawleyrats was observed at a dietary treatmentlevel of 5% (Field 1989). There was noeffect on average litter size, fetal bodyweight, or the incidence of skeletal or vis ceral malformations.
Fire Hazard
Dimethyl phthalate is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Dimethyl phthalate is used in pharmaceutical applications as a solvent and plasticizer for film-coatings such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, cellulose acetate and cellulose acetate–butyrate mixtures.
In addition to a number of industrial applications, dimethyl phthalate is also widely used as an insect repellent with topical preparations typically applied as a 40% cream or lotion; it has also been applied as a tent fabric treatment.
Contact allergens
Phthalates are plasticizers and increase the flexibility of plastics. They are also found in deodorant formulations, perfumes, emollients, and insect repellents.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mldly toxic by inhalation. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. An eye irritant. A pesticide and insect repellent. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ESTERS.
Safety
In pharmaceutical applications, dimethyl phthalate is used in film coating and as a topically applied insect repellent.Acute exposure to the eyes and mucous membranes can cause irritation, although dimethyl phthalate is considered less irritant than diethyl phthalate. Inhalation of dimethyl phthalate can cause irritation of the respiratory tract; oral ingestion can cause a burning sensation in the mouth, vomiting, and diarrhea. Owing to the low water solubility and relatively high lipid solubility, dimethyl phthalate may accumulate in body tissues after chronic exposure, which may cause central nervous system depression.
Although some animal studies have suggested that high concentrations of dimethyl phthalate may be teratogenic or cause mutagenic effects with bacteria,(5,6) other studies have shown no adverse effects.(7) There are no confirmed reports of human reproductive or developmental effects, and the compound is not generally regarded as a carcinogenic material.
LD50 (chicken, oral): 8.5g/kg
LD50 (guinea pig, oral): 2.4g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): 1.38g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 6.8g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, oral): 4.40g/kg
LD50 (rat, IP): 3.38g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 6.80g/kg
Potential Exposure
AgriculturalChemical; Mutagen; Reproductive Effector; PrimaryIrritant. Dimethyl phthalate is used as a solvent, dye carrier,plasticizer for cellulose ester plastics, and as an insectrepellent.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Source
May leach from plastic products (e.g., tubing, containers) used in laboratories during chemical analysis of aqueous samples.
Environmental Fate
Biological. In anaerobic sludge, degradation occurred as follows: monomethyl phthalate to phthalic acid to protocatechuic acid followed by ring cleavage and mineralization (Shelton et al., 1984). In a static-culture-?ask screening test, dimethyl phthalate showed significant biodegradation with rapid adaptation. The ester (5 and 10 mg/L) was statically incubated in the dark at 25°C with yeast extract and settled domestic wastewater inoculum. After 7 days, 100% biodegrada-tion was achieved (Tabak et al., 1981).
Photolytic. An aqueous solution containing titanium dioxide and subjected to UV light (λ >290 nm) yielded mono- and dihydroxyphthalates as intermediates (Hustert and Moza, 1988).
Chemical/Physical. Hydrolyzes in water forming phthalic acid and methyl alcohol (Wolfe et al., 1980).
Storage
Dimethyl phthalate is sensitive to prolonged exposure to light and it should therefore be stored in a cool, dark, dry, well-ventilated area that is protected from physical damage, and isolated from incompatible substances. Containers of dimethyl phthalate may be hazardous when empty as they may retain product residues such as vapors and liquids. There is a slight fire hazard when exposed to heat, and above the flash point explosive vapor–air mixtures may be formed.Carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide are released when dimethyl phthalate is heated to decomposition. Solutions of dimethyl phthalate in acetone, dimethyl sulfoxide, ethanol (95%), and water are stable for 24 hours under normal laboratory conditions.
Shipping
The name of this material is not in the DOT listof materials for label and packaging standards. However,based on regulations, it may be classified as anEnvironmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s. It fallsin Hazard Class 9 and Packing Group III.[20,
Incompatibilities
Dimethyl phthalate is incompatible with strong acids or bases, nitrates, and strong oxidizing agents. As with other phthalates, contact with plastics should be avoided.
Regulatory Status
Dimethyl phthalate is included in a number of topical pharmaceutical formulations. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral tablets, sustained action). As from 1992, dimethyl phthalate is no longer registered for use as a pesticide in California.
Properties of Dimethyl phthalate
| Melting point: | 2 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 282 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.19 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.008 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 295 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 4.0g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear |
| Specific Gravity | 1.194 (20/4℃) |
| Odor | sl. aromatic odor |
| Relative polarity | 0.309 |
| PH | 7 (H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 20 ºC |
| Merck | 14,3255 |
| BRN | 1911460 |
| Henry's Law Constant | At 25 °C: 235, 246, 230, 214, 168, 127, and 118 at pH values of 3.00, 3.37, 5.88, 6.18, 7.62, 8.91,
and 8.99, respectively (Hakuta et al., 1977). |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA air 5 mg/m3 (ACGIH, MSHA,
and OSHA). |
| Dielectric constant | 8.1(45℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases, nitrates. Sensitive to prolonged exposure to light. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 131-11-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Dimethyl phthalate(131-11-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dimethyl phthalate (131-11-3) |
Safety information for Dimethyl phthalate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Dimethyl phthalate
| InChIKey | NIQCNGHVCWTJSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Dimethyl phthalate manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Di Methyl Phthalate (DMP) 99%View Details
Di Methyl Phthalate (DMP) 99%View Details -
 Dimethyl phthalate 98%View Details
Dimethyl phthalate 98%View Details -
 Dimethyl phthalate 99%View Details
Dimethyl phthalate 99%View Details -
 Dimethyl phthalate 95% CAS 131-11-3View Details
Dimethyl phthalate 95% CAS 131-11-3View Details
131-11-3 -
 Dimethyl phthalate CAS 131-11-3View Details
Dimethyl phthalate CAS 131-11-3View Details
131-11-3 -
 Dimethyl phthalate, puriss CAS 131-11-3View Details
Dimethyl phthalate, puriss CAS 131-11-3View Details
131-11-3 -
 Dimethyl Phthalate CAS 131-11-3View Details
Dimethyl Phthalate CAS 131-11-3View Details
131-11-3 -
 Dimethyl Phthalate CASView Details
Dimethyl Phthalate CASView Details
