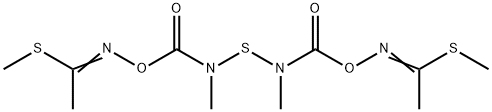
Thiodicarb
- CAS NO.:59669-26-0
- Empirical Formula: C10H18N4O4S3
- Molecular Weight: 354.47
- MDL number: MFCD00145401
- EINECS: 261-848-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
What is Thiodicarb?
Description
Thiodicarb, 3,7,9,13-tetramethyl-5,11- dioxa-2,8,14-trithia-4,7,9,12-tetra-azapentadeca-3,12-di ene-6,10-dione (IUPAC), consists of colorless crystals, which are sparingly soluble in water, readily soluble in dichloromethane, acetone, methanol, and xylene. Thiodicarb is produced by reaction of N,N -thiobis(methylcarbamic acid fluoride) with 2-methylthioacetaldoxim in the presence of a base.
The Uses of Thiodicarb
Thiodicarb is used as an insecticide.
The Uses of Thiodicarb
Thiodicarb is an oxime carbamate insecticide and ovicide with both oral and contact activities against major Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera and Hemiptera pests in/on cotton, maize, fruits, soyabeans and vegetables.
General Description
Colorless to pale tan crystals. Non corrosive. Used as an insecticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzed by strong acid or base.
Reactivity Profile
A carbamate derivative. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Molluscicide, Ovicide: Not approved for use in EU countries. Registered for use in the U.S. Thiodicarb is used primarily on cotton, sweet corn, and soybeans. The remaining usage is spread among leafy vegetables, cole crops, ornamentals, and other minor use sites. Thiodicarb acts as an ovicide against cotton bollworms and budworms.
Trade name
CGA® 45156; CHIPCO[C]; DICARBOSULF®; DICARBASULF®; LARVIN®; LEPICRON®; SEMEVIN®; NIVRAL®; UC-51762®; UC 51769®; UC 80502®
Environmental Fate
Soil. Under aerobic and anaerobic soil conditions, thiodicarb degrades to methomyl and methomyl oxime (Hartley and Kidd, 1987). The reported half-life in various soils is 3–8 days (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Metabolic pathway
The initial metabolic reaction of thiodicarb in soils, plants and animals is the hydrolytic or thiolytic cleavage of the N-S bond to methomyl. The subsequent metabolic pathway of methomyl involves hydrolysis / elimination reactions to yield S-methyl-N-hydroxythioacetimidate and ultimately acetonitrile and CO2 as the major terminal products. The metabolic pathways of thiodicarb are presented in Scheme l. See also the methomyl entry.
Degradation
Thiodicarb (1) is susceptible to alkaline hydrolysis (Feung and Heinzelmann,
1989). Thiodicarb was stable between pH 5 and 6, but it degraded
rapidly in alkaline conditions (pH 9) with a DT50 of less than one day. The
DT50 values of thiodicarb at pH 3 and 7 were 9 and 13 days, respectively.
The initial degradation product of thiodicarb was methomyl (2) which
was further hydrolysed to S-methyl-N-hydroxytoacetimidate (3) in
alkaline solution (pH 9).
Photolysis of thiodicarb in water was not significant (Andrawes
and College, 1977). The photolytic DT50 of thiodicarb was approximately
81 days. The major photolytic degradation product was methomyl(2).
Properties of Thiodicarb
| Melting point: | 168-172°C |
| Boiling point: | 433.8±28.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.4000 |
| vapor pressure | 5.1×10-3 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C
|
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | -1.79±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 35 mg l-1(25 °C) |
| Merck | 13,9403 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 59669-26-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thiodicarb (59669-26-0) |
Safety information for Thiodicarb
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for Thiodicarb
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Thiodicarb CAS 59669-26-0View Details
Thiodicarb CAS 59669-26-0View Details
59669-26-0 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1