Sulfurous Acid
Synonym(s):Sulfurous acid;Sulfurous anhydride
- CAS NO.:7782-99-2
- Empirical Formula: H2O3S
- Molecular Weight: 82.08
- MDL number: MFCD00011335
- EINECS: 231-973-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
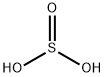
What is Sulfurous Acid?
Description
Sulfurous Acid is a weak and unstable inorganic acid, which is considered an aqueous solution of sulfur dioxide in water. It is formed theoretically by burning sulfur to produce sulfur dioxide, which is then reacted with water. However, there is no evidence that sulfurous acid exists in solution, while the molecules of which has been detected in the gas phase, since the reaction is reversible and the acid readily decomposes back into the reactants. Sulfurous acid is not usually available in its acid form, but more commonly prepared as its sodium or potassium salts.
Sulfurous acid and its salts are commonly applied as powerful reducing agents and disinfectant agents due to its strong reducibility. It is also considered as a mild bleaching agent especially for applications having chlorine sensitive materials. Besides, Sulfurous acid is a food additive listed on the EAFUS food Additive Database (Jan. 2001).
Chemical properties
colourless liquid
Chemical properties
SULFUROUS ACID, colorless liquid, prepared by dissolving SO2 in H2O. Reagent grade H2SO3 contains approximately 6% SO2 in solution
The Uses of Sulfurous Acid
Sulfurous acid (H2SO3) can be produced by burning sulfur to form sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas and by then dissolving the gas in water to form sulfurous acid. This is the acid produced by burning coal that has a high sulfur content; the gaseous sulfur dioxide by-product of combustion then combines with atmospheric water to form “acid rain.”
The Uses of Sulfurous Acid
Dental bleach.
The Uses of Sulfurous Acid
As a bleaching agent, sulfurous acid is used for whitening wool, silk, feathers, sponge, straw, wood, and other natural products. In some areas, its use is permitted for bleaching and preserving dried fruits. The salts of sulfurous acid are sulfites.
Definition
A weak acid found only in solution, made by passing sulfur(IV) oxide into water. The solution is unstable and smells of sulfur(IV) oxide. It is a reducing agent, converting iron(III) ions to iron(II) ions, chlorine to chloride ions, and orange dichromate(VI) ions to green chromium(III) ions.
General Description
Sulfurous acid, H2S03, is an unstable, water-soluble, colorless liquid with a pungent burning sulfur odor. Corrosive to metals and tissue. It is derived from absorption of sulfur dioxide( S02) in water.Reagent grade sulfurous acid contains about 6% sulfur dioxide in solution. Sulfurous acid is a strong reducing agent.It is readily oxidized to sulfuric acid and is itself reduced to hydrogen sulfide by zinc and dilute sulfuric acid. Sulfurous acid is used in the synthesis of medicines and chemicals, in the manufacture of paper and wine, in brewing, in metallurgy, in ore flotation, as a bleach and analytical reagent, and for refining of petroleum products.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water with release of heat.
Reactivity Profile
Colorless, corrosive, moderately toxic liquid. When heated to decomposition SULFUROUS ACID emits toxic fumes of oxides of sulfur [Lewis, 3rd ed., 1993, p. 1196].
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, strong irritant to tissue.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Industrial uses
Sulfurous acid (H2SO3) is usually marketed as liquid SO2. The bulk of SO2 is produced from off-smelter gases. Although handling of SO2 liquid requires special equipment, it is frequently used as a pH regulator and depressant, primarily during the treatment of complex sulfide ores. SO2 is largely used in North American operations as a pyrite depressant and for the depression of galena during copper/lead separation.
Safety Profile
A poison by ingestion and inhalation. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: nausea or vomiting, hypermotility, diarrhea, and othergastrointestinal effects. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes ofSOx.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sulfurous_acid
http://printwiki.org/Sulfurous_Acid
http://www.softschools.com/formulas/chemistry/sulfurous_acid_uses_properties_structure_formula/242/
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Sulfurous_acid#section=Top
http://www.chemistrylearner.com/sulfurous-acid.html
Properties of Sulfurous Acid
| Density | 1.03 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.3 (vs air) |
| solubility | solution of SO2 in H2O |
| pka | 1.92(at 25℃) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| Water Solubility | Miscible with water. |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8976 |
| Dielectric constant | 15.6(0℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7782-99-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sulfurous acid (7782-99-2) |
Safety information for Sulfurous Acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sulfurous Acid
| InChIKey | LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 7782-99-2 Sulfurous acid 98%View Details
7782-99-2 Sulfurous acid 98%View Details
7782-99-2 -
 Sulphur Dioxide 99%View Details
Sulphur Dioxide 99%View Details -
 Sulfurous acid, 6.0% SO<sub>2</sub> min. CAS 7782-99-2View Details
Sulfurous acid, 6.0% SO<sub>2</sub> min. CAS 7782-99-2View Details
7782-99-2 -
 Sulfurous Acid, 6.0% SO<sub>2</sub> min. CAS 7782-99-2View Details
Sulfurous Acid, 6.0% SO<sub>2</sub> min. CAS 7782-99-2View Details
7782-99-2 -
 Sulphurous acid, GR solution app. 5.6% CAS 7782-99-2View Details
Sulphurous acid, GR solution app. 5.6% CAS 7782-99-2View Details
7782-99-2 -
 SULPHUR DIOXIDE AQUEOUS SOLUTION 5-6% Extra Pure CAS 7782-99-2View Details
SULPHUR DIOXIDE AQUEOUS SOLUTION 5-6% Extra Pure CAS 7782-99-2View Details
7782-99-2 -
 Sulfur dioxide solution CAS 7782-99-2View Details
Sulfur dioxide solution CAS 7782-99-2View Details
7782-99-2 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
