Aluminum sulfate
Synonym(s):Aluminum sulfate hydrate;Aluminum sulfate octahydrate
- CAS NO.:10043-01-3
- Empirical Formula: Al2O12S3
- Molecular Weight: 342.15
- MDL number: MFCD00003423
- EINECS: 233-135-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:32
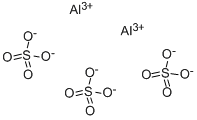
What is Aluminum sulfate?
Absorption
The degree of aluminum absorption depends on a number of factors, such as the aluminum salt ingested, pH (for aluminum speciation and solubility), bioavailability, as well as dietary conditions .
These facts should be taken into consideration during tissue dosimetry and response assessment to aluminum sulfate. It can be concluded that the use of currently available animal studies to develop a guideline value is inappropriate at this time due to the above specific toxicokinetic/dynamic factors that may affect results .
Toxicity
Aluminum Sulfate, Hydrated (ACS & FCC): ORAL (LD50):
Acute: >9000 mg/kg in the mouse . >9000 mg/kg in the rat .
Acute Toxicity
There is little indication that aluminum is acutely toxic by oral exposure despite it is widely found in foods, drinking water, and many antacid preparations . In 1988, a population of about 20 000 citizens of Camelford, England, was exposed to increased levels of aluminum for 5 days. The aluminum was accidentally ingested by the population from a water supply facility using aluminum sulfate for water treatment .
Some adverse effects observed were nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mouth ulcers, skin ulcers, skin rashes, and arthritis-type pain were observed. It was concluded in one study that the adverse effects of aluminum sulfate were primarily mild and transient. No long-lasting effects on health could be attributed to the exposures from aluminum in the drinking water during this period .
Chronic Toxicity
In humans, excess exposure to aluminum via dialysis water (aluminum sulfate) is a known etiological factor in several pathological conditions in patients treated with hemodialysis. Clinical symptoms and signs of aluminum toxicity include hypercalcemia, anemia, vitamin D refractory osteodystrophy, and a dialysis encephalopathy. Bone pain, pathological fractures, and proximal myopathy may occur. Aluminum has also been suggested as an etiology of several neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer senile and pre-senile dementia, as well amyotrophic sclerosis. Despite this, the most recent investigations have failed to confirm this hypothesis. A study in man has verified a number of possible deleterious interactions of aluminum salts with phosphorous metabolism, especially in long-term ingestion of aluminum-containing antacids .
It has been suggested that aluminum exposure is a risk factor for the development or acceleration of onset of Alzheimer disease (AD) in humans. The world health organization has completed a meta-analysis of 20 epidemiological studies done to test the hypothesis that aluminum in drinking-water is a risk factor for Alzheimer disease. Six studies on populations in Norway were considered of sufficiently high quality to meet the general criteria for exposure and outcome assessment and the adjustment for at least some confounding variables .
Of six studies that examined the relationship between aluminum in drinking- water and dementia, three found a positive relationship, but three did not. However, each of the studies had significant deficiencies in the study design (e.g. ecological exposure assessment; failure to consider aluminum exposure from all sources and to control for important confounders, such as education, socioeconomic status, and family history; the use of surrogate outcome measures for AD; and selection bias) .
In general, the relative risks determined were less than 2, with large confidence intervals, when the total aluminum concentration in drinking-water was 0.1 mg/L or higher. Due to the pathogenesis of AD and knowledge obtained from studies, it was concluded that the present epidemiological evidence does not support a causal association between AD and aluminum in drinking-water .
In addition to the epidemiological studies that examined the relationship between AD and aluminum in drinking-water, two studies studied cognitive dysfunction in elderly populations in relation to the levels of aluminum in drinking water. The results proved conflicting. A study of 800 male subjects, age 80-89, drinking water containing aluminum concentrations up to 98 μg/L found no relationship. The second study used “any evidence of mental impairment” as an outcome measure and found a relative risk of 1.72 at aluminum drinking-water concentrations above 85 μg/L in 250 males. Such data are insufficient to show that aluminum is a cause of cognitive impairment in the elderly .
Note on possible risk of breast cancer
Widespread concern has been raised regarding the exposure to aluminum in deodorant/antiperspirant products, with inconclusive results , , , . Results from a more recent case-control study suggest an association between underarm cosmetic use and aluminum concentration in breast tissue and breast cancer. The observed association of underarm cosmetic use with breast cancer was, however, limited to women who report using the products multiple times a day before age of 30 .
Chemical properties
Aluminum sulfate is a white powder, often used in water solution. The solution is a strong acid
Physical properties
White powder; refractive index 1.47; density 2.71 g/cm3; mp 770°C (decomposes); hygroscopic; readily soluble in water (31% at 0°C; solubility increases with temperature 98% in boiling water); soluble in dilute mineral acids; slightly soluble in alcohol.
Occurrence
It occurs in nature in minerals; alunite, KAl3(SO4)2(OH)6and natroalunite, NaAl3(SO4)2(OH)6. The anhydrous salt is used in food applications.
The Uses of Aluminum sulfate
Aluminum sulfate acts as a flocculating agent in the purification of drinking water, and in waste water treatment plants. It acts as a mordant in dyeing, printing, textiles and also used in paper manufacturing. It is a waterproofing agent and accelerator in concrete. Further, it is used as a foaming agent in fire fighting foam, photographic film and in photochemicals. It is also used in styptic pencils, pain relief and in dentistry for gingival retraction cords.
The Uses of Aluminum sulfate
Sizing paper, lakes, alums, dyeing mordant foaming agent in fire foams, cloth fireproofing, white leather tannage, catalyst in manufacturing ethane, p H control in paper industry, waterproofing agent for concrete, clarifier for fats and oils, lubricating compositions, deodorizer and decolorizer in petroleum refining, sewage precipitating agent and for water purification, food additive.
Indications
Solutions containing 5 to 10% aluminum sulfate have been used as local applications to ulcers and to arrest foul discharges from mucous surfaces. Aluminum sulfate is also used in the preparation of aluminum acetate ear drops . It is often purchased over the counter and is available in solid stick or powder form for minor cuts and abrasions after shaving , . Aluminum sulfate is also used as an adjuvant in vaccines .
Background
Aluminum (Al), also spelled aluminum, chemical element, a lightweight, silvery-white metal of main Group 13 (IIIa, or boron group) of the periodic table .
It is a chemical agent used in water purification, the pH regulation of garden soil, and other commercial or industrial applications. Medically, it is primarily used as a coagulating agent in minor cuts and abrasions as well as deodorant .
Aluminum (Al) is ubiquitous and represents the third most common element in the Earth’s crust. It most commonly exists in a combined state with various other elements. Al is found in materials used in the pharmaceutical industry, and in manufactured foodstuffs, cosmetics, and tap water. By overcoming the body barriers, Al may infiltrate into the blood and lead to toxic effects in liver, bone and the central nervous system .
Definition
ChEBI: An aluminium sulfate that contains no water of crystallisation.
Definition
alunogenite: A mineral form of hydrated aluminium sulphate, Al2(SO4)3.18H2O.
Preparation
The anhydrous salt may be obtained by slow and progressive heating of commercial hydrated salt, Al2(SO4)3 ?18H2O. Most water molecules are lost at heating between 250 to 420°C. The last three water molecules are lost between 250 to 420°C at a heating rate of 10°C/min.
General Description
Anhydrous aluminum sulfate is a white crystalline solid. Aluminum sulfate is also obtained as an 18-hydrate Al2(SO4)3.18H2O. Both forms are soluble in water, noncombustible, and nontoxic. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Aluminium sulfate is used in paper making, in firefighting foams, and in sewage treatment and water purification.
Air & Water Reactions
Dissolves in water with evolution of some heat. creates acidic solutions.
Reactivity Profile
Aqueous solutions of ALUMINUM SULFATE are acidic. The solid may corrode metals in presence of moisture.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust irritates nose and mouth. Ingestion of large doses causes gastric irritation, nausea, vomiting, and purging. Dust irritates eyes and skin.
Agricultural Uses
Alunogenite is a naturally occurring form of hydrated aluminum sulphate Al2(SO4)318 H2O.
Industrial uses
Aluminum chloride (AlCl3) can be obtained by reacting carbon dioxide and chlorine with kaolin at high temperatures. It is highly hygroscopic with a specific gravity of 2.3. It is highly soluble in water and in organic solvents. Similar to aluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride is used as a co-depressant for calcite, fluorite and dolomite.
Pharmacokinetics
Aluminum sulfate may be used as a deodorant, as well as an astringent . Aluminum sulfate is also known as an astringent. Astringents are substances that cause contraction or shrinkage of tissues and that dry up secretion .
Used as a post-shaving treatment, it can eliminate bleeding from superficial wounds , .
It has also shown in vitro anti-microbial activity .
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. Hydrolyzes to form sulfuric acid, whch irritates tissue, especially lungs. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx,.
Potential Exposure
Widely used in the paper industry, in waste and water treatment and treating sewage; in antiperspirants, deodorants; in flame-retardants; in tanning leather, sizing paper; mordant in dyeing, purifying water, waterproofing cloth, clarifying oils and fats; in agricultural pesticides; manufacturing aluminum salts and others
Metabolism
Not Available
Shipping
UN3264 Corrosive liquid, acidic, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
It crystallises from hot dilute H2SO4 (l mL/g) on cooling in ice. When a solution of alumina (Al2O3) in conc H2SO4 is slowly cooled, Al2SO4 17 or 18H2O deposits as a crystalline mass. Al2SO4 17H2O is the stable form in equilibrium with its saturated aqueous solution at 25o [Smith J Am Chem Soc 64 41 1942]. This is purified by dissolving it in a small volume of H2O and adding EtOH until the sulfate readily crystallises from the oily supersaturated solution. It forms Al2O3 16H2O between 0-112o. On gradual heating, the hydrate melts, giving the anhydrous salt at ca 250o. Several hydrates up to 27H2O have been described. Further heating to red heat (~ 600-800o) causes decomposition to Al2O3 + SO3 + SO2 and O2 [Cobb J Soc Chem Ind 29 250 1910]. The ACS reagent is Al2O3 18H2O (98+%).
Incompatibilities
In aqueous solution, aluminum sulfate forms sulfuric acid; reacts with bases and many other substances. Corrodes metals, some plastics and body tissues, especially in the presence of moisture.
Waste Disposal
Pretreatment involves hydrolysis followed by neutralization with NaOH. The insoluble aluminum hydroxide formed is removed by filtration and can be heated to decomposition to yield alumina which has valuable industrial applications. The neutral solution of sodium sulfate can be discharged into sewers and waterways as long as its concentration is below the recommended provisional limit of 250 mg/L
Properties of Aluminum sulfate
| Melting point: | 770 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 759.71°C (estimate) |
| Density | 2.71 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0-0.001Pa at 20-25℃ |
| solubility | Soluble in cold water, freely soluble in hot water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| pka | 3.6[at 20 ℃] |
| form | Powder and/or Chunks |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.71 |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,366 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: TWA 2 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.6(Ambient) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10043-01-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Aluminum sulfate (10043-01-3) |
Safety information for Aluminum sulfate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P390:Absorb spillage to prevent material damage. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Aluminum sulfate
Aluminum sulfate manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 ALUMINIUM SULPHATE 99%View Details
ALUMINIUM SULPHATE 99%View Details -
 Aluminium Sulphate 99%View Details
Aluminium Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Aluminum sulfate 98%View Details
Aluminum sulfate 98%View Details -
 Aluminum sulfate, Anhydrous CAS 10043-01-3View Details
Aluminum sulfate, Anhydrous CAS 10043-01-3View Details
10043-01-3 -
 Aluminum sulfate, 98% 99%View Details
Aluminum sulfate, 98% 99%View Details -
 Aluminium Sulphate CASView Details
Aluminium Sulphate CASView Details -
 Aluminum sulfate CAS 10043-01-3View Details
Aluminum sulfate CAS 10043-01-3View Details
10043-01-3 -
 Aluminium Sulfate, 50Kg BagView Details
Aluminium Sulfate, 50Kg BagView Details
10043-01-3
