STRONTIUM IODIDE
Synonym(s):Strontium diiodide
- CAS NO.:10476-86-5
- Empirical Formula: I2Sr
- Molecular Weight: 341.43
- MDL number: MFCD00049557
- EINECS: 233-972-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
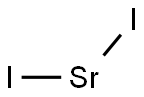
What is STRONTIUM IODIDE?
Description
Strontium iodide (SrI2) is an ionic, water-soluble, deliquescent
compound that has been used in medicine as
a substitute for potassium iodide. Strontium iodide crystals
are colorless, transparent, hexagonal in structure,
and have a bitter, saline taste. Soluble in 0.6 part of water
at 15°C, they are also soluble in alcohol.
Strontium iodide can be prepared by reacting strontium
carbonate with hydroiodic acid:
SrCO3+2HI→SrI2+H2O+CO2
Strontium iodide turns yellow when exposed to air
due to the formation of iodine at the surface of the crystals.
At high temperatures (when in the presence of air),
strontium iodide completely decomposes to form strontium
oxide and free iodine.
Several hydrates are known including SrI2·6H2O.
This salt is a white crystalline substance composed of
small plates. It decomposes in moist air due to its deliquescence.
Its specific gravity varies from 4.415 g/cm3
to 4.549 g/cm3, depending upon how the crystals are
formed. It loses water at 78°C and the anhydrate forms
above 200°C. The melting point of SrI2 is 507°C and its boiling point is 645°C where it decomposes to the
oxide and iodine.
Chemical properties
White to yellowish white crystalline powder
The Uses of STRONTIUM IODIDE
Strontium iodide is a yellowish granular powder made by treating strontium carbonate with hydriodic acid. It is soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. Strontium iodide was occasionally used to increase contrast in collodion emulsions.
The Uses of STRONTIUM IODIDE
Medicine (source of iodine), intermediate.
The Uses of STRONTIUM IODIDE
Strontium iodide (SrI2) is made by treating strontium carbonate with hydrochloric acid. It is used as a medicinal source of iodine.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation.
Properties of STRONTIUM IODIDE
| Melting point: | 515 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1773 °C/1 atm (lit.) |
| Density | 4.55 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| form | beads |
| color | White to pale yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 4.55 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water and ethanol. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8844 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10476-86-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Strontium iodide (SrI2) (10476-86-5) |
Safety information for STRONTIUM IODIDE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for STRONTIUM IODIDE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Strontium iodide, Anhydrous CAS 10476-86-5View Details
Strontium iodide, Anhydrous CAS 10476-86-5View Details
10476-86-5 -
 Strontium iodide, Anhydrous CAS 10476-86-5View Details
Strontium iodide, Anhydrous CAS 10476-86-5View Details
10476-86-5 -
 Strontium iodide, Anhydrous CAS 10476-86-5View Details
Strontium iodide, Anhydrous CAS 10476-86-5View Details
10476-86-5 -
 Strontium iodide, anhydrous, 99.995% CAS 10476-86-5View Details
Strontium iodide, anhydrous, 99.995% CAS 10476-86-5View Details
10476-86-5 -
 Strontium iodide 95% CAS 10476-86-5View Details
Strontium iodide 95% CAS 10476-86-5View Details
10476-86-5 -
 Strontium iodide CAS 10476-86-5View Details
Strontium iodide CAS 10476-86-5View Details
10476-86-5 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1