Strontium carbonate
Synonym(s):Strontium carbonate (SrCO);Strontium monocarbonate 3;Strontium(II) carbonate
- CAS NO.:1633-05-2
- Empirical Formula: CO3Sr
- Molecular Weight: 147.63
- MDL number: MFCD00011250
- EINECS: 216-643-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-05-20 17:08:58
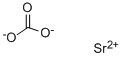
What is Strontium carbonate ?
Description
Strontium carbonate has the formula of SrCO3 and the molecular weight of 147.6326 g/mol. Strontium carbonate occurs in nature as the mineral “strontianite”. The name strontianite comes from a famous location for the mineral, Strontian, Scotland. Strontianite is strontium carbonate as found naturally. It occurs as white or slightly gray orthorhombic crystals with a refractive index of 1.518. The unit-cell parameters are: a = 5.107 ? , b = 8.414 ? , c = 6.029 ? , Z = 4; V = 259.07 ? 3, Den(Calc) = 3.78. The crystal system is orthorhombic with space group Pmcn and point group 2/m, 2/m, 2/m. Strontium carbonate has only one stable form (aragonite-type structure) and temperature of precipitation has no effect on crystal form, unlike that of calcium or magnesium carbonates.
Chemical properties
Strontium carbonate is a milky white free flowing powder. It is little more insoluble (Ksol=10-8.8) than calcium carbonate (Ksol=10-8.07), so it should not be surprising that under appropriate conditions Sr2+ can be precipitated by biogenic carbonate.
Chemical properties
Heating strontium carbonate up from 1000°C to 1300°C causes the compound to undergo a decomposition reaction which results in the capture of thermal energy, shown here as the peak in the black curve occurring between Time = 20 and Time = 40 minutes. Cooling the system back down to 1000°C leads to reconstitution of the starting material in a carbonation reaction thereby releasing the stored thermal energy, a process shown as the valley in the black curve between Time = 50 and Time = 80 minutes.
Physical properties
White orthorhombic crystals; refractive index 1.518; hygroscopic; hardness 3.5 Mohs; density 3.5 g/cm3; insoluble in water; soluble in dilute acids with liberation of carbon dioxide.
Occurrence
Strontium carbonate occurs in nature as mineral strontianite. The compound is used in pyrotechnics and ceramic ferrites. It also is used in making iridescent glass for color television tubes. Other uses are in refining sugar and preparing other strontium salts.
The Uses of Strontium carbonate
Strontium carbonate (SrCO3) is used to make radiation-resistant glass and TV picture tubes, as well as pyrotechnics.
The Uses of Strontium carbonate
Used in the preparation of?iridescent glass, luminous paints, strontium oxide or strontium salts and in refining sugar and certain drugs
The Uses of Strontium carbonate
Used for electronic applications. It is used for manufacturing CTV to absorb electrons resulting from the cathode
The Uses of Strontium carbonate
The compound, SrCO3, is used in pyrotechnics and ceramic ferrites. It is also used in making iridescent glass for color television tubes. Other uses are in refining sugar and preparing other strontium salts. The most common use is as an inexpensive fireworks colorant. Strontium and its salts emit a brilliant red color in flame. Its ability to neutralize acid is also very helpful in pyrotechnics. Another similar application is in road flares. Strontium carbonate is used for electronic applications. It is used for manufacturing glass colortelevision tubes to absorb X-rays resulting from the bombardment of the cathode rays on the glass enclosure of the cathode-ray gun. SrCO3 is used in the preparation of iridescent glass, strontium oxide or strontium salts and in refining sugar.It is widely used in the ceramics industry as an ingredient in glazes. It acts as a flux and also modifies the color of certain metallic oxides. It is also used in the manufacturing of strontium ferrites for permanent magnets that are used in loudspeakers and door-magnets. Strontium carbonate can be used to produce many different strontium compounds by simply dissolving it in the corresponding acid. Strontium bicarbonate has not been isolated.
Definition
strontianite: A mineral form ofstrontium carbonate, SrCO3.
Definition
strontium carbonate: A whitesolid, SrCO3; orthorhombic; r.d. 3.7;decomposes at 1340°C. It occurs naturallyas the mineral strontianite andis prepared industrially by boiling celestine(strontium sulphate) with ammoniumcarbonate. It can also beprepared by passing carbon dioxideover strontium oxide or hydroxide orby passing the gas through a solutionof strontium salt. It is a phosphor,used to coat the glass of cathode-rayscreens, and is also used in the refiningof sugar, as a slagging agent incertain metal furnaces, and to providea red flame in fireworks.
Production Methods
Strontium carbonate, formed (1) by reaction of strontium salt solution and sodium carbonate or bicarbonate solution, (2) by reaction of strontium hydroxide solution and CO2. Strontium carbonate decomposes at 1,200 °C (2,192 °F) to form strontium oxide and CO2, and is dissolved by excess CO2, forming strontium bicarbonate, Sr(HCO3)2, solution.
Preparation
Strontium carbonate occurs in nature as strontianite and can be mined from its deposit. It is, however, usually made commercially from the mineral “celestite”. Celestite is fused with sodium carbonate at elevated temperatures or boiled with a solution of ammonium carbonate.Strontium carbonate is insoluble in water. It precipitates from the product mixture in the second reaction. If fused with sodium carbonate, the product mixture is leached with water. Insoluble carbonate separates from the water-soluble sodium sulfate.
General Description
Strontium carbonate is insoluble in water. It is used predominantly in producing other strontium salts.
General Description
Strontianite is a strontium carbonate mineral (SrCO3). It is the original and principal source of strontium. It often occurs in white masses of radiating fibres, although pale green, yellow, or gray colours are also known. Strontianite forms soft, brittle crystals that are commonly associated with barite, celestine, and calcite in low-temperature veins. Strontianite is used in pyrotechnics to impart a red colour and in sugar refining as a clarifying agent.
Properties of Strontium carbonate
| Melting point: | 1494 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 3.7 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | dilute aqueous acid: slightly soluble(lit.) |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 3.7 |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ammonium chloride. Slightly soluble in ammonia and water. |
| Merck | 14,8838 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 9.25 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1633-05-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carbonic acid, strontium salt (1:1) (1633-05-2) |
Safety information for Strontium carbonate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. |
Computed Descriptors for Strontium carbonate
| InChIKey | LEDMRZGFZIAGGB-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Strontium carbonate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Zama Chemical
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Strontium carbonate 98%View Details
Strontium carbonate 98%View Details -
 Strontium carbonate CAS 1633-05-2View Details
Strontium carbonate CAS 1633-05-2View Details
1633-05-2 -
 Strontium carbonate, (metals basis) CAS 1633-05-2View Details
Strontium carbonate, (metals basis) CAS 1633-05-2View Details
1633-05-2 -
 Strontium carbonate, 99%, Ba 1% CAS 1633-05-2View Details
Strontium carbonate, 99%, Ba 1% CAS 1633-05-2View Details
1633-05-2 -
 Strontium carbonate CAS 1633-05-2View Details
Strontium carbonate CAS 1633-05-2View Details
1633-05-2 -
 Strontium carbonate CAS 1633-05-2View Details
Strontium carbonate CAS 1633-05-2View Details
1633-05-2 -
 Strontium carbonate CAS 1633-05-2View Details
Strontium carbonate CAS 1633-05-2View Details
1633-05-2 -
 Strontium Carbonate PowderView Details
Strontium Carbonate PowderView Details
1633-05-2
