Squaric acid
Synonym(s):Squaric acid
- CAS NO.:2892-51-5
- Empirical Formula: C4H2O4
- Molecular Weight: 114.06
- MDL number: MFCD00001334
- EINECS: 220-761-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
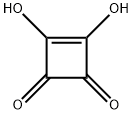
What is Squaric acid?
Chemical properties
Squaric acid (3,4-dihydroxycyclobut-3-ene-1,2-dione), also known as quadratic acid, has the fascinating structure, and is a vinylogous carboxylic acid. The parent compound is a white,crystalline powder which melts at~300℃. It is highly acidic (pKa 1.5 for the first proton and 3.4 for the second) due to resonance stabilization of the anion and exhibits IR resonances indicative of strong hydrogen bonding [2326cm-1 (OH),1818 cm-1 (C=O), and 1639cm-1 (C=C)].The UV absorption spectrum suggests that the acid is essentially completely ionized. Squaric acid is freely soluble in water but has poor solubility in many organic solvents.Solutions give an intense purple color with iron(III) chloride, and are also known to decolorize bromine water, cerium(IV) nitrate, and permanganate solutions.As the carbonyl groups are similar to those of carboxylic acids rather than those of ketones, squaric acid does not react in the phenylhydrazine test.The squarate dianion is thought to be completely symmetrical (unlike squaric acid itself), with all C-C and C-O bond lengths being, respectively, identical, as the negative charges are equally distributed between allthe oxygen atoms.The IR spectrum of dipotassium squarate (dipotassium 3,4-dioxocy-clobut-1-ene-1,2-diolate) differs greatly from that of squaric acid, with the loss of the car-bonyl (C=O) and alkene(C=C) absorptions seen in the protonated form, and supportsthe proposed symmetrical structure.
The Uses of Squaric acid
Squaric acid used as intermediate for squaraine dyes and heterocycles. Squaric acid is an immunotherapy used to treat common warts. This treatment is non-toxic, and easy to use. The treatment activated your immune system to combat the warts and therefore it may cause an allergic reaction , similar to poison oak. This reaction can be managed with a topical cortisone cream. Blistering and lightening of the skin may occur, but rarely.
Squaric acid derivatives – synthetic targets for ring expansion reactions
The Uses of Squaric acid
3,4-Dihydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione is used to produce diethoxy-cyclobutenedione by heating, pharmaceutical intermediates, squarylium dyes, and photoconducting squaraines; The dibutylester is used as a contact sensitizer in the treatment of alopecia and warts.
The Uses of Squaric acid
3,4-Dihydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione can be used:
- In fluorescence detection in immunoassays, hybridization assays, enzymatic reactions, and other analytical procedures.
- To form diffraction quality crystals.
- To synthesize a squarate dianion, which is used as a building block to create uncharged polymeric networks. These ordered structures are used in catalysis, nonlinear optics, electrical conductivity, molecular recognition, and molecular sieves.
Definition
ChEBI: A carbon oxoacid that consists of 1,2-diketocyclobut-3-ene bearing two enolic hydroxy substituents at positions 3 and 4.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 88, p. 1533, 1966 DOI: 10.1021/ja00959a040
Tetrahedron Letters, 18, p. 4437, 1977
General Description
3,4-dihydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2 dione, commonly known as squaric acid, is widely used in bioorganic and medicinal chemistry. It is an inhibitor of glyoxylase, semiqauric acid, pyruvate dehrogenase, and transketolase. It is used as a replacement for phosphate in a peptide-based ligand for an SH2 domain. Its derivatives are high-affinity ligands for excitatory amino acid receptors. These derivatives are also used as dyes for fluorescence detection of small biological molecules.
Biotechnological Applications
squaric acid is widely used in bioorganic and medicinal chemistry. It is an inhibitor of glyoxylase, semiqauric acid, pyruvate dehrogenase, and transketolase. It is used as a replacement for phosphate in a peptide-based ligand for an SH2 domain. Its derivatives are high-affinity ligands for excitatory amino acid receptors. These derivatives are also used as dyes for fluorescence detection of small biological molecules.
squaric acid can be used:
In fluorescence detection in immunoassays, hybridization assays, enzymatic reactions, and other analytical procedures.
To form diffraction quality crystals.
To synthesize a squarate dianion, which is used as a building block to create uncharged polymeric networks. These ordered structures are used in catalysis, nonlinear optics, electrical conductivity, molecular recognition, and molecular sieves.
Purification Methods
Purify squaric acid by recrystallisation from H2O — this is quite simple because the acid is ~ 7% soluble in boiling H2O and only 2% at room temperature. It is not soluble in Me2CO or Et2O; hence it can be rinsed with these solvents and dried in air or a vacuum. It is not hygroscopic and gives an intense purple colour with FeCl3. It has IR max at 1820 (C=O) and 1640 (C=C) cm-1, and UV max at 269.5nm ( 37K M-1cm -1). [Cohn et al. J Am Chem Soc 81 3480 1959, Park et al. J Am Chem Soc 84 2919 1962] See also pKa values of 0.59 ±0.09 and 3.48 ±0.023 [Scwartz & Howard J Phys Chem 74 4374 1970]. [Schmidt & Reid Synthesis 869 1978, Beilstein 8 IV 2701.]
Properties of Squaric acid
| Melting point: | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 250.96°C |
| Density | 1.82 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.5800 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 190 °C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | 20g/l |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 1.5??(at 25℃) |
| color | White to beige |
| PH | 1 (1g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 20 g/L (30 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,8769 |
| BRN | 774275 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 2892-51-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 3-Cyclobutene-1,2-dione, 3,4-dihydroxy-(2892-51-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 3-Cyclobutene-1,2-dione, 3,4-dihydroxy- (2892-51-5) |
Safety information for Squaric acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Squaric acid
| InChIKey | PWEBUXCTKOWPCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Squaric acid CAS 2892-51-5View Details
Squaric acid CAS 2892-51-5View Details
2892-51-5 -
 3,4-Dihydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione CAS 2892-51-5View Details
3,4-Dihydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione CAS 2892-51-5View Details
2892-51-5 -
 3,4-Dihydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione CAS 2892-51-5View Details
3,4-Dihydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione CAS 2892-51-5View Details
2892-51-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1