Sotalol
- CAS NO.:3930-20-9
- Empirical Formula: C12H20N2O3S
- Molecular Weight: 272.36
- MDL number: MFCD00242936
- EINECS: 227-541-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-04-01 13:12:09
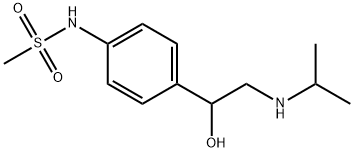
What is Sotalol?
Absorption
Sotalol is 90-100% bioavailable. When taken with a meal, adsorption is lowered by 18%. In patients with a creatinine clearance >80mL/min, the maximum concentration is 6.25±2.19.
Toxicity
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with bradycardia, congestive heart failure, hypotension, bronchospasm, and hypoglycemia. Larger intentional overdoses may present as hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac asystole, prolonged QT interval, torsade de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and premature ventricular complexes. Stop administering sotalol and observe the patient until the QT interval returns to normal and the heart rate rises above 50 beats per minute. Hemodialysis may help lower plasma concentrations of sotalol as it is not bound to plasma proteins. Bradycardia and cardiac asystole may be treated with atropine, other anticholinergic drugs, beta adrenergic agonists, or transvenous cardiac pacing.. Second or third degree heart block may be treated with a transvenous cardiac pacemaker. Hypotension may be treated with epinephrine or norepinephrine. Bronchospasm may be treated with aminophylline or a beta-2 agonist, possibly at higher than normal doses. Torsade de pointes may be treated with DC cardioversion, transvenous cardiac pacing, epinephrine, or magnesium sulfate.
The oral LD50 for rats is 3450mg/kg, intraperitoneal LD50 for rats is 680mg/kg, oral LD50 for mice is 2600mg/kg, and intraperitoneal LD50 for mice is 670mg/kg.
Pregnant rabbits given 6 times the maximum recommended human dose showed an increase in fetal death and maternal toxicity, while rats given 18 times the maximum recommended human dose had an increased number of fetal resorptions. Sotalol is present in human breast milk so patients taking sotalol should not breast feed.
Sotalol has not been found to be carcinogenic. No studies have been performed regarding mutagenicity or clastogenicity. In animal studies, sotalol was not associated with a reduction in fertility aside from smaller litter sizes.
Further information regarding adverse reactions can be found here.
Originator
Sotagard,Glaxo
Indications
Sotalol is indicated to treat life threatening ventricular arrhytmias and maintain normal sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation or flutter. There are also oral solutions and intravenous injections indicated for patients requiring sotalol, but for whom a tablet would not be appropriate.
Background
Sotalol is a methanesulfonanilide developed in 1960. It was the first of the class III anti arrhythmic drugs. Sotalol was first approved as an oral tablet on 30 October 1992. A racemic mixture of sotalol is currently formulated as a tablet, oral solution, and intravenous injection indicated for life threatening ventricular arrhythmias and maintaining normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation or flutter.
Definition
ChEBI: A sulfonamide that is N-phenylmethanesulfonamide in which the phenyl group is sustituted at position 4 by a 1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl group. It has both beta-adrenoreceptor blocking (Vaughan Williams Class II) and ardiac action potential duration prolongation (Vaughan Williams Class III) antiarrhythmic properties. It is used (usually as the hydrochloride salt) for the management of ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias.
Manufacturing Process
As a resulting of reaction of methansulfonylchloride reacted with aniline
methansulfonanilide was obtained. The methansulfonanilide reacted with
bromacetylbromide at the presence of AlCl3 and CS2 and 4-(bromacetyl)-
methansulfonanilide was prepeared.
Then to the 4-(bromacetyl)-methansulfonanilide isopropylamine was added to
give 4-(1-oxo-2-isopropylaminoethyl)methansulfonanilide.The 4-(1-oxo-2-isopropylaminoethyl)methansulfonanilide was reduced by
hydrogenesation in the presence of Pd-C catalyst and sodium borohydride. So
4-(1-hydroxy-2-isopropylaminoethyl)methansulfonanilide was obtained.
The 4-(1-hydroxy-2-isopropylaminoethyl)methansulfonanilide hydrochloride
may be prepared by treatment of base with hydrochloric acid.
Therapeutic Function
Beta-adrenergic blocker, Antiarrhythmic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Sotalol is a non-selective?-adrenoreceptor antagonist. It should be noted that when stopping sotalol the dose should be reduced gradually.
General Description
Sotalol, 4'[1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl]methylsulfonanilide (Betapace), is a relatively new antiarrhythmicdrug, characterized most often as a class IIIagent, and although it has effects that are related to the classII agents, it is not therapeutically considered a class II antiarrhythmic.It contains a chiral center and is marketed as theracemic mixture. Because of its enantiomers, its mechanismof action spans two of the antiarrhythmic drug classes. Thel(-) enantiomer has both β-blocking (class II) and potassiumchannel-blocking (class III) activities. The d(+) enantiomerhas class III properties similar to those of the (-) isomer,but its affinity for the -adrenergic receptor is 30 to 60 timeslower.
Biological Activity
sotalol hydrochloride is an adrenergic beta-antagonist that is used in the treatment of life-threatening arrhythmias.
Mechanism of action
Sotalol acts as an antiarrhythmic by β- receptor blockade as well as by prolonging the action potential duration in atrium and ventricle and the refractory period in atrium and AV node . Activity against supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmiaswas demonstrated.
Pharmacokinetics
Sotalol is a competitive inhibitor of the rapid potassium channel. This inhibition lengthens the duration of action potentials and the refractory period in the atria and ventricles. The inhibition of rapid potassium channels is increases as heart rate decreases, which is why adverse effects like torsades de points is more likely to be seen at lower heart rates. L-sotalol also has beta adrenergic receptor blocking activity seen above plasma concentrations of 800ng/L. The beta blocking ability of sotalol further prolongs action potentials. D-sotalol does not have beta blocking activity but also reduces a patient's heart rate while standing or exercising. These actions combine to produce a negative inotropic effect that reduces the strength of contractility of muscle cells in the heart. Extension of the QT interval is also adversely associated with the induction of arrhythmia in patients.
Hyperglycemia is a greater risk for non insulin dependant diabetics than insulin dependant diabetics. Beta blockers inhibit insulin secretion which may cause hyperglycemia in type II diabetes mellitus. The risk of hypoglycemia is higher in insulin dependant diabetes than non insulin dependant diabetics. Beta blockers decrease secretion of insulin, which may mask hypoglycemia in an insulin dependant patient. Beta blockers also increase glucose uptake into cells which may prolong or potentiate hypoglycemia.
Further information regarding adverse reactions can be found here.
Clinical Use
The sotalol enantiomers produce different effects onthe heart. Class III action of d-sotalol in the sinus node isassociated with slowing of sinus heart rate, whereas -adrenergicblockade contributes to the decrease in heart rate observedwith 1- or d,1-sotalol. Sotalol is not metabolized, noris it bound significantly to proteins. Elimination occurs byrenal excretion, with more than 80% of the drug eliminatedunchanged. Sotalol is characteristic of class III antiarrhythmicdrugs, in that it prolongs the duration of the action potentialand, thus, increases the effective refractory period of myocardialtissue. It is distinguished from the other class III drugs(amiodarone and bretylium) because of its -adrenergicreceptor–blocking action.
Side Effects
Side effects of sotalol include those attributed to both β-adrenoceptor blockade and proarrhythmic effects. This arrhythmia is a serious threat, as it may lead to ventricular fibrillation. Adverse effects attributable to its β- blocker activity include fatigue, dyspnea, chest pain, headache, nausea, and vomiting.
Drug interactions
Drugs with inherent QT interval–prolonging activity (i.e., thiazide diuretics and terfenadine) may enhance the class III effects of sotalol.
Metabolism
Sotalol is not metabolized.
Precautions
The contraindications that apply to other β-adrenoceptor blocking agents also apply to sotalol. In addition, hypokalemia and drugs known to prolong the QT interval may be contraindicated, as they enhance the possibility of proarrhythmic events.
Properties of Sotalol
| Melting point: | 206.5-207 °C |
| Boiling point: | 443.3±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.298 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly, Heated), Methanol (Slightly, Sonicated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pK1 8.2, pK2 9.8(at 25℃) |
| color | Pale Yellow to Light Yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C12H20N2O3S/c1-9(2)13-8-12(15)10-4-6-11(7-5-10)14-18(3,16)17/h4-7,9,12-15H,8H2,1-3H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 3930-20-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Methanesulfonanilide, 4'-(1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl)-(3930-20-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Methanesulfonamide, N-[4-[1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl]phenyl]- (3930-20-9) |
Safety information for Sotalol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sotalol
| InChIKey | ZBMZVLHSJCTVON-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CS(NC1=CC=C(C(O)CNC(C)C)C=C1)(=O)=O |
Sotalol manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![[2H6]-Sotalol](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20211123/GIF/1246912-17-3.gif)

You may like
-
 Sotalol 95% CAS 3930-20-9View Details
Sotalol 95% CAS 3930-20-9View Details
3930-20-9 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
