Isopropylamine
Synonym(s):2-Aminopropane;Isopropylamine
- CAS NO.:75-31-0
- Empirical Formula: C3H9N
- Molecular Weight: 59.11
- MDL number: MFCD00008082
- EINECS: 200-860-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:35
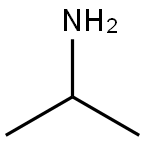
What is Isopropylamine?
Description
Isopropylamine (propan-2-amine, IUPAC) is a colorless, volatile liquid. It is highly flammable, with a flammable range of 2%–10.4% in air. Boiling point is 93°F (33°C), flash point is ?15°F (?26°C), and ignition temperature is 756°F (402°C).
It is miscible with water, with a specific gravity of 0.69, which is lighter than water. Vapor density is 2.04, which is heavier than air. In addition to flammability, isopropylamine is a strong irritant to tissue and has a TLV of 5 ppm in air. The four-digit UN identification number is 1221. The NFPA 704 designation for isopropylamine is health 3, flammability 4, and reactivity 0. Primary uses for isopropylamine are pharmaceuticals, dyes, insecticides, and as a dehairing agent.
Chemical properties
Isopropylamine is a colorless, flammable liquid. Isopropylamine is miscible with water, alcohol, and ether.The odor threshold reportedly ranges from 0.21 to 0.70 ppm; the pungent, ammoniacal odor becomes irritating at 24mg/m3 (110).
Physical properties
Colorless liquid with a penetrating, ammonia-like odor. Experimentally determined detection and recognition odor threshold concentrations were 500 μg/m3 (210 ppbv) and 1.7 mg/m3 (700 ppbv), respectively (Hellman and Small, 1974). An odor threshold concentration of 25 ppbv was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
Occurrence
Not reported found in natu
The Uses of Isopropylamine
Isopropylamine is used as a dehairing agentand as an intermediate in the preparation ofmany organics.
The Uses of Isopropylamine
Solvent, intermediate in synthesis of rubber accelerators, pharmaceuticals, dyes, insecticides, bactericides, textile specialties, and surface-active agents, dehairing agent, solubilizer for 2,4-D acid.
The Uses of Isopropylamine
Isopropylamine is an organic compound is a widely used for the synthesis of pharmaceutical and agricultural goods such as glyphosphate herbicides and as an additive for petroleum industry. such as bentazon (BASF), Roundup (Monsanto), imazapyr (ACC) and the triazines ametryne (Novartis), atrazine (Novartis), desmetryn (Novartis), prometryn (Novartis), pramitol (Novartis), dipropetryn (Novartis), and propazine. Other applications encompass the nematicide fenamiphos (Bayer), the fungicide iprodione (Rho?ne-Poulenc), insecticides, pharmaceuticals, and surfactants.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of alkylamines that is propane carrying an amino group at position 2.
Production Methods
Isopropylamine can be produced from the corresponding alcohol by reacting with ammonia in the presence of a dehydrating catalyst, or from the chloride by reacting with ammonia under pressure. It is also reported that this amine can be produced from acetone and ammonia or from the acetone oxime (HSDB 1989).
Aroma threshold values
High strength odor; fishy type; recommend smelling in a 0.10% solution or less.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Flash point -35°F. Boiling point 90°F. Less dense than water Vapors heavier than air. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Used as a solvent and to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Isopropylamine is a colorless, alkaline liquid, very volatile, moderately toxic, highly flammable. Dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, sparks, or strong oxidizers. When heated to decomposition Isopropylamine emits toxic fumes of oxides of nitrogen [M. K.]. A mixture of Isopropylamine and perchloryl fluoride resulted in an uncontrolled oxidation and/or explosion, [J. Org. Chem., 1980, 45, 4036]. The reaction of 1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane and the amine and most probably other nitrogen bases, yields a violent exotherm, [Chem. & Ind., 1971, 994].
Hazard
Highly flammable, dangerous fire risk. Strong irritant to tissue.
Health Hazard
Isopropylamine is a strong irritant to theeyes, skin, and respiratory system. A shortexposure to 10–20 ppm can cause irritationof the nose and throat in humans (Procturand Hughes 1978). Prolonged exposure tohigh concentrations may lead to pulmonaryedema. Skin contact can cause dermatitisand skin burns. Exposure to 8000 ppm for4 hours was lethal to rats.
LD50 value, oral (mice): 2200 mg/kg.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reactions; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Industrial uses
Isopropylamine can be used as a dehairing agent and as a solvent. It also finds use as an intermediate in the production of insecticides, herbicides and bactericides and in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes and rubber accelerators (HSDB 1989).
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. Low et al. (1991) reported that the photooxidation of aqueous primary amine
solutions by UV light in the presence of titanium dioxide resulted in the formation of ammonium
and nitrate ions.
Chemical/Physical. Releases toxic nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and
Lewis, 1987). Forms water-soluble salts with acids.
Metabolism
One would expect isopropylamine to be readily absorbed from the gut and respiratory tract. Shorter chain aliphatic amines such as isopropylamine also are efficiently absorbed through the skin (Beard and Noe 1981). When administered intravenously, isopropylamine distributed rapidly into tissue compartments with tissue/plasma ratios ranging from 1.8 in the atrium to 16.7 in the renal medulla (Privitera et al 1982). During the elimination phase, a half-life of 146 min was observed in plasma. There do not appear to be any definitive metabolic studies with this compound, however through a comparison with other substrates, one might expect oxidation to acetone and ammonia through the action of monoamine oxidase (Tipton 1980).
Properties of Isopropylamine
| Melting point: | -101 °C |
| Boiling point: | 32-35 °C
33-34 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.688 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.04 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 9.2 psi ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 4238 | ISOPROPYLAMINE |
| Flash point: | −26 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 1000g/l |
| form | Crystalline Powder, Needles or Crystals |
| pka | 10.63(at 25℃) |
| color | APHA: ≤50 |
| Odor | Strong ammoniacal; pungent, irritating, typical amine. |
| PH | 13 (700g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 2-10.4%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.025ppm |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| JECFA Number | 1581 |
| Merck | 14,5209 |
| BRN | 605259 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 5 ppm (~12 mg/m3) (ACGIH,
MSHA, and OSHA); TLV-STEL 10 ppm(~24 mg/m3) (ACGIH); IDLH 4000 ppm
(NIOSH). |
| Dielectric constant | 5.5(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Extremely flammable - note low boiling point and low flash point. Readily forms explosive mixtures with air. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, perchloryl fluoride. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-31-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Propanamine(75-31-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isopropylamine (75-31-0) |
Safety information for Isopropylamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H224:Flammable liquids H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Isopropylamine
Isopropylamine manufacturer
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Monoisopropylamine 70% CASView Details
Monoisopropylamine 70% CASView Details -
 Isopropylamine CAS 75-31-0View Details
Isopropylamine CAS 75-31-0View Details
75-31-0 -
 Isopropylamine 99% CAS 75-31-0View Details
Isopropylamine 99% CAS 75-31-0View Details
75-31-0 -
 Mono Isopropyl Amine Mipa 70, IndustrialView Details
Mono Isopropyl Amine Mipa 70, IndustrialView Details
75-31-0 -
 Monoisopropylamine MipaView Details
Monoisopropylamine MipaView Details
75-31-0 -
 Mono Isopropyl Amine Mipa 70, IndustrialView Details
Mono Isopropyl Amine Mipa 70, IndustrialView Details
75-31-0 -
 MONO ISOPROPYLAMINE 70 % (MIPA), IndustrialView Details
MONO ISOPROPYLAMINE 70 % (MIPA), IndustrialView Details
75-31-0 -
 Mono Isopropylamine Liquid ChemicalView Details
Mono Isopropylamine Liquid ChemicalView Details
75-31-0
