SODIUM DICHROMATE
- CAS NO.:10588-01-9
- Empirical Formula: Cr2Na2O7
- Molecular Weight: 261.97
- MDL number: MFCD00003483
- EINECS: 234-190-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
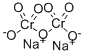
What is SODIUM DICHROMATE?
Chemical properties
Red or red-orange deliquescent crystals.Decomposes at 400C, loses 2H 2 O on prolonged heating at 100C. Soluble in water; insoluble in alcohol. Noncombustible.
Chemical properties
Sodium chromate, including the hexahydrate, is yellow crystalline solids that can also be used in solution. Disodium dichromate (10588-01-9):
The Uses of SODIUM DICHROMATE
Sodium dichromate is red solid, soluble, powerful oxidizing agent, and consequently a fire hazard with dry carbonaceous materials. Formed by acidifying sodium chromate solution, and then evaporating. Used (1) in matches and pyrotechnics, (2) in leather tanning and in the textile industry, (3) as a source of chromate, cheaper than potassium dichromate.
The Uses of SODIUM DICHROMATE
Colorimetry (copper determination), complex- ing agent, oxidation inhibitor in ethyl ether.
Definition
ChEBI: Sodium dichromate is an inorganic sodium salt. It contains a dichromate(2-).
General Description
A red or red-orange crystalline solid. May be strongly irritating to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Used as a corrosion inhibitor, and in the manufacture of other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
SODIUM DICHROMATE is a strong oxidizing agent. Incompatible with strong acids. . Contact with combustible materials may lead to fires. Toxic chromium oxide fumes may form in fire [USCG, 1999]. The well known "chromic acid mixture" of dichromate and sulfuric acid with organic residue led to violent exothermic reaction. This mixture in combination with acetone residue also led to violent reaction. The combination of the dichromate and sulfuric acid with alcohols, ethanol and 2-propanol, led to violent exothermic reaction. Because of the occurrence of many incidents involving the dichromate-sulfuric acid mix with oxidizable organic materials, SODIUM DICHROMATE is probably best to avoid such interactions. The combination of the dichromate with hydrazine is explosive (one may expect the reaction of the dichromate to be vigorous with amines in general), [Mellor, 1943, Vol. 11, 234]. The addition of the dehydrated dichromate salt to acetic anhydride led to an exothermic reaction which eventually exploded. An induction period proceeded the explosion event [Bretherick, 5th Ed., 1995]. Boron, silicon, and dichromates form pyrotechnic mixtures. A mixture of acetic acid, 2-methyl-2-pentenal and the dichromate led to a runaway reaction and eruption of the reactor contents, [J. Haz. Mat., 1987, 233-239].
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust or mist causes respiratory irritation sometimes resembling asthma; nasal septal perforation may occur. Ingestion causes vomiting, diarrhea, and (rarely) stomach and kidney complications. Contact with eyes or skin produces local irritation; repeated skin exposure causes dermatitis.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Decomposes to produce oxygen when heated. May ignite other combustibles upon contact.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Poison by ingestion, sktn contact, intravenous, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: cough, nausea or vomiting, and sweating. Human mutation data reported. A caustic and irritant. A powerful oxidizer. Potentially explosive reaction with acetic anhydride, ethanol + sulfuric acid + heat, hydrazine. Violent reaction or ignition with boron + shcon (pyrotechnic), organic residues + sulfuric acid, 2-propanol + sulfuric acid, sulfuric acid + trinitrotoluene. Incompatible with hydroxylamine. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Na2O. See also CHROMIUM COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Used to make dyes, inks, pigments, and other chromates; in leather tanning, a corrosion inhibitor in circulating water systems; metal treatment; a drilling mud additive; chemical intermediate for chromium catalysts; colorimetry, oxidizing agent; bleaching agent; an algicide, fungicide, insecticide; in wood preservation.
Shipping
UN3087 Oxidizing solid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer, 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3085 Oxidizing solid, corrosive, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer, 8-Corrosive material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Aqueous solution in a base. A strong oxidizer. Violent reaction with reducing agents; combustibles, strong acids; organic materials.
Properties of SODIUM DICHROMATE
| Melting point: | 356.7°C |
| Density | 2.52 g/cm3(Temp: 13 °C) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| form | red hygroscopic crystals |
| color | red hygroscopic crystals, crystalline |
| Water Solubility | 2355g/L at 20℃ |
| Dielectric constant | 2.9(Ambient) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10588-01-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium dichromate (10588-01-9) |
Safety information for SODIUM DICHROMATE
Computed Descriptors for SODIUM DICHROMATE
SODIUM DICHROMATE manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1