Silver nitrate
Synonym(s):Argenti nitras;Lunar Caustic;Nitric acid silver(I) salt;Silver nitrate
- CAS NO.:7761-88-8
- Empirical Formula: AgNO3
- Molecular Weight: 169.87
- MDL number: MFCD00003414
- EINECS: 231-853-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
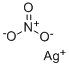
What is Silver nitrate?
Chemical properties
Silver nitrate, AgN03, is colorless,transparent,tabular,rhombic crystals that become gray or grayish-black on exposure to light in the presence of organic matter.It is odorless with a bitter,caustic,metallic taste. It is caustic,and a strong oxidizing agent that is soluble in cold water, more soluble in hot water, glycerol,and hot alcohol,slightly soluble in ether,and decomposes at boiling point Used in photographic film, silver plating,silvering mirrors,and as an antiseptic.
Chemical properties
Silver nitrate is a colorless to dark gray, odorless, crystalline solid.
Physical properties
Colorless, transparent, large rhombohedral crystals, or white small crystals; bitter, caustic metallic taste; odorless; pure compound is not sensitive to light but trace organics promote photo reduction, turning the salt to grayish black on exposure to light; density 4.35 g/cm3; melts at 212°C; decomposes at 440°C; very soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and acetone.
The Uses of Silver nitrate
The basis of nearly all photographic silver halides with the exception of the daguerreotype process, silver nitrate is a heavy white crystal made by dissolving elemental silver in nitric acid followed by evaporation. It is soluble in water, ether, and glycerin. Silver nitrate is not sensitive to light, but when combined with an organic material, a halogen, or a halide it will reduce back to a metallic state when exposed to light.
The Uses of Silver nitrate
Anti-infective, topical.
The Uses of Silver nitrate
Photographic emulsions, antiseptic, silver plating, and inks.
Background
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgNO3. In its solid form, silver nitrate is coordinated in a trigonal planar arrangement. It is often used as a precursor to other silver-containing compounds. It is used in making photographic films, and in laboratory setting as a staining agent in protein visualization in PAGE gels and in scanning electron microscopy.
What are the applications of Application
Silver nitrate is a staining compound for identification of proteins and nucleic acids
Preparation
Silver nitrate is prepared by dissolving silver metal in dilute nitric acid. The solution is evaporated and residue is heated to dull red heat with concentrated nitric acid to decompose impurities such as copper nitrate. Residue then is dissolved in water, filtered, and recrystallized to obtain pure silver nitrate.
Indications
Silver nitrate, 0.1% to 0.5%, is an excellent germicide and astringent. Its
germicidal action is due to precipitation of bacterial protein by liberated silver
ions. It may cause pain if applied in concentrations >0.5%.
Silver nitrate is another cauterizing agent and coagulates cellular protein and
removes granulation tissue. This should be applied everyday for approximately
5 days."
"Silver nitrate (AgNO3), in solid form or in solutions stronger than 5%, is used for
its caustic action; 5% to 10% solutions may be applied to fissures or excessive
granulation tissue. Silver nitrate sticks consist of a head of toughened silver nitrate (>94.5%) prepared by fusing the silver salt with sodium chloride. They
are dipped in water and applied as needed.
Definition
ChEBI: Silver(1+) nitrate is a silver salt and an inorganic nitrate salt. It has a role as an astringent.
General Description
A colorless or white crystalline solid becoming black on exposure to light or organic material.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Silver nitrate is noncombustible but, as an oxidizing agent, can accelerate the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in a fire or the combustible material is finely divided, an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires. Light sensitive. Mixtures with alkyl esters may explode owing to the formation of alkyl nitrates. Mixtures with phosphorus, tin(II) chloride, or other reducing agents may react explosively [Bretherick 1979 p. 108-109]. Reacts with acetylene in the presence of ammonia to form silver acetylide, a powerful detonator when dry [Bretherick 1979 p. 198]. Reaction with ethyl alcohol (or other alcohols) may produce silver fulminate, which can explode when disturbed [Bretherick 1979 p. 200]. An intimate mixture of Silver nitrate and magnesium may ignite spontaneously on contact with a drop of water [Bretherick 1979 p. 200]. An explosion occurred when purified phosphine was passed rapidly into a concentrated solution of Silver nitrate [Mellor 3:471 1946-47]. When a mixture of 28% ammonium hydroxide and Silver nitrate solution was treated with a small amount of sodium hydroxide. Black precipitate, silver nitride exploded on stirring [MCA Case History 1554 1968].
Hazard
Strong irritant to skin and tissue.
Health Hazard
Concentrated solutions will produce irritation, ulceration, and discoloration of the skin; also causes severe irritation of the eyes. Ingestion will produce violent abdominal pain and other gastroenteric symptoms.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Increases flammability of combustibles.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Silver nitrate (AgNO3), after salicylic acid, is widely used for the treatment of warts. AgNO3 is a highly water-soluble salt, which readily precipitates as AgCl, black in colour, when in contact with the skin. Warts are caused by a human papillomavirus, and mostly hands, feet and the anogenital areas are affected. The treatment is based on the destruction of the local tissue, and the silver salt is applied via a caustic pen to the affected area. Silver nitrate is highly corrosive and is known to destroy these types of tissue growth. Care has to be taken when this treatment option is used, as the resulting AgCl stains any skin or fabric which it has been in contact with.
Safety Profile
A human poison. Experimental poison by ingestion, intravenous, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. A severe eye irritant. A powerful caustic and irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Swallowing can cause severe gastroenteritis that may be fatal. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. A powerful oxidizer. Incompatible with acetylene, acetylides, alkalies, aluminum, antimony salts, arsenic, arsenites, bromides, carbon, carbonates, chlorides, ClF3, chlorosulfuric acid, copper, creosote, ethanol, ferrous salts, hypophosphites, iodides, Mg powder with H20, morphme salts, NH3 with KOH to yield black Ag3N, oils, PH3, phosphates, phosphonium iodide, phosphorus, plastics, sulfur, tannic acid, tartrates, thiocyanates, vegetable decoctions and extracts, zinc with NH3 with KOH. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also SILVER COMPOUNDS and NITRATES
Potential Exposure
Silver nitrate is used in photography, silver plating; as an antiseptic; in chemical reactions; and mirror manufacturing; as starting material in production of other silver compounds.
Metabolism
Not Available
Shipping
UN1493 Silver nitrate, Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer.
Purification Methods
Purify it by recrystallisation from hot water (solubility of AgNO3 in water is 992g/100mL at 100o and 122g/100mL at 0o). It has also been purified by crystallisation from hot conductivity water by slow addition of freshly distilled EtOH. CAUTION: avoid using EtOH for washing the precipitate; and avoid concentrating the filtrate to obtain further crops of AgNO3 owing to the risk of EXPLOSION (as has been reported to us) caused by the presence of silver fulminate. When using EtOH in the purification, the apparatus should be enveloped in a strong protective shield. [Tully, News Ed (Am Chem Soc) 19 3092 1941; Garin & Henderson J Chem Educ 47 741 1970, Bretherick, Handbook of Reactive Chemical Hazards 4th edn, Butterworths, London, 1985, pp 13-14.] Before being used as a standard in volumetric analysis, analytical reagent grade AgNO3 should be finely powdered, dried at 120o for 2hours, then cooled in a desiccator. Recovery of silver residues as AgNO3 [use protective shield during the whole of this procedure] can be achieved by washing with hot water and adding 16M HNO3 to dissolve the solid. Filter this through glass wool and concentrate the filtrate on a steam bath until precipitation commences. Cool the solution in an ice-bath and filter the precipitated AgNO3. Dry it at 120o for 2hours, then cool it in a desiccator in a vacuum. Store it over P2O5 in a vacuum in the dark. AVOID contact with hands due to formation of black stains.
Incompatibilities
A strong oxidizer. Reacts violently with combustible and reducing materials. Reacts with acetylene forming a shock-sensitive explosive. Reacts with alkalis, antimony salts; ammonia, arsenites, bromides, carbonates, chlorides, iodides, hydrogen peroxide; thiocyanates, ferrous salts; oils, hypophosphites, morphine salts; creosote, phosphates, tannic acid; tartarates, halides, vegetable extracts, and others. Attacks some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings.
Properties of Silver nitrate
| Melting point: | 212 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 444°C |
| Density | 4.35 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 5.8 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 17.535 mm of Hg (@ 20°C) |
| Flash point: | 40 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 5.4-6.4 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| PH Range | 7 - 9 |
| Water Solubility | 219 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8518 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 10 mg/m3; TWA 0.01 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7761-88-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | silver(I) nitrate(7761-88-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Silver nitrate (7761-88-8) |
Safety information for Silver nitrate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H290:Corrosive to Metals H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Silver nitrate
| InChIKey | SQGYOTSLMSWVJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Silver nitrate manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

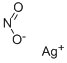
You may like
-
 Silver nitrate CAS 7761-88-8View Details
Silver nitrate CAS 7761-88-8View Details
7761-88-8 -
 Silver nitrate, For AAS analysis CAS 7761-88-8View Details
Silver nitrate, For AAS analysis CAS 7761-88-8View Details
7761-88-8 -
 Silver nitrate, For AAS analysis CAS 7761-88-8View Details
Silver nitrate, For AAS analysis CAS 7761-88-8View Details
7761-88-8 -
 Silver nitrate, For AAS analysis CAS 7761-88-8View Details
Silver nitrate, For AAS analysis CAS 7761-88-8View Details
7761-88-8 -
 Silver nitrate, For AAS analysis CAS 7761-88-8View Details
Silver nitrate, For AAS analysis CAS 7761-88-8View Details
7761-88-8 -
 Silver nitrate CAS 7761-88-8View Details
Silver nitrate CAS 7761-88-8View Details
7761-88-8 -
 Silver nitrate CAS 7761-88-8View Details
Silver nitrate CAS 7761-88-8View Details
7761-88-8 -
 Silver nitrate CAS 7761-88-8View Details
Silver nitrate CAS 7761-88-8View Details
7761-88-8