Rufinamide
Synonym(s):1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-Triazole-4-carboxamide;Rufinamide
- CAS NO.:106308-44-5
- Empirical Formula: C10H8F2N4O
- Molecular Weight: 238.19
- MDL number: MFCD00865314
- EINECS: 200-659-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-12 17:04:03
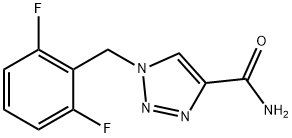
What is Rufinamide?
Absorption
The oral suspension and tablet are bioequivalent on a mg per mg basis. Rufinamide is well absorbed but the rate is slow and the extent of absorption decreases as dose is increases. Based on urinary excretion, the extent of absorption was at least 85% following oral administration of a single dose of 600 mg rufinamide tablet under fed conditions. Bioavailability= 70%-85% (decreases with increasing doses); Tmax, fed and fasted states= 4-6 hours; Cmax, 10 mg/kg/day= 4.01 μL/mL; Cmax, 30mg/kg/day= 8.68 μL/mL; AUC (0h-12h), 10mg/kg/day= 37.8±47 μg·h/mL; AUC (0h-12h), 30mg/kg/day= 89.3±59 μg·h/mL.
Toxicity
The most commonly observed adverse reactions (≥10% and greater than placebo) were headache, dizziness, fatigue, somnolence, and nausea.
Description
Approximately 2.5 million people worldwide are afflicted with epilepsy, a devastating neurological disorder diagnosed by the tendency toward recurrent, unprovoked seizures, often of unknown etiology. Rufinamide has been launched primarily as adjunctive therapy of LGS. Its proposed mechanism of action involves the limitation of firing of sodium-dependent action potentials. The ultimate result is membrane stabilization. Since it does not exhibit measurable binding to monoamine, acetylcholine, histamine, glycine, AMPA/kainate, NMDA, or GABA receptors or systems, these receptor-mediated pathways are not anticipated to be involved in the exertion of rufinamide’s effects. Rufinamide displayed efficacy in several electrical and chemical animal seizure models.
Description
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) is a severe pediatric epilepsy syndrome characterized by multiple seizure types. Rufinamide is an anticonvulsant. It inhibits the activation of voltage-gated sodium channel 1.1 (Nav1.1) when used at a concentration of 100 μM. Rufinamide inhibits Nav1.1, but not Nav1.2, Nav1.3, and Nav1.6, opening and increases the action potential threshold in primary rat hippocampal neurons. It is an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase VA (CAVA; Ki = 343.8 nM) that is selective for CAVA over CAI and CAII (Kis = >10,000 nM for both). Rufinamide (100 μM) prolongs the preictal phase and reduces seizure-like event frequency in an in vitro model of epileptiform activity in rat hippocampal slices. It inhibits seizures induced by pentylenetetrazole in a mouse model of epilepsy (ED50 = 54 mg/kg, i.p.) and reduces kainic acid-induced neuronal cell death in the mouse hippocampal CA3 region when used at doses of 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg. Formulations containing rufinamide have been used in the treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome (LGS).
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Novartis (US)
The Uses of Rufinamide
Labelled Rufinamide (R701552). Antiepileptic triazole derivative which decreases firing by neurons at sodium channels. Anticonvulsant.
The Uses of Rufinamide
Rufinamide, a triazole derivative, is an anticonvulsant medication. It is used in combination with other medication and therapy to treat Lennox–Gastaut syndrome and various other seizure disorders. Rufinamide is presumed to involve stabilization of the so
The Uses of Rufinamide
Rufinamide has been used to test its analgesic effect on neuropathic pain in spared nerve injury (SNI) model.
Indications
Adjunct therapy for treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Background
Rufinamide is a triazole derivative and an anticonvulsant medication to treat seizure disorders like Lennox-Gastuat syndrome, a form of childhood epilepsy. Clinical trials suggest its efficacy in the treatment of partial seizures.
What are the applications of Application
Rufinamide is a sodium channel protein inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: Rufinamide is a heteroarene and an aromatic amide.
brand name
Inovelon
General Description
An antiepileptic drug and anticonvulsant, Rufinamide is approved for the treatment of partial seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in adults and children 4 years and older. Rufinamide is marketed as Banzel® in the US and Inovelon® in the EU.
Biological Activity
Board spectrum anticonvulsant. Prolongs the inactivation of sodium channels and limits the frequency of action potential firing in cultured and acutely isolated neurons. Displays anticonvulsive activity in a range of animal seizure models.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Broad-spectrum anticonvulsant.
Pharmacokinetics
At high concentrations will inhibit action of mGluR5 subtype receptors thus preventing the production of glutamate.
Clinical Use
Adjunctive treatment of seizures in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
Side Effects
Rufinamide was well tolerated with the most common adverse events including fatigue, somnolence, tremors, mild-to-moderate dizziness, nausea, headache, and diplopia. Since rufinamide is not metabolized by the CYP450 system, it is anticipated to have a low potential for interaction with drugs metabolized by the CYP isozymes. Rufinamide, however, does exhibit clinically relevant interactions with other antiepileptic drugs; concomitant treatment with valproate results in a reduction in rufinamide clearance while concomitant treatment with phenytoin, primidone, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, or vigabatrin causes an increase in rufinamide clearance. In these situations, rufinamide dosage adjustment may be required.
Synthesis
While rufinamide may be prepared by several related routes, the preferred starting material is 2,6-difluorobenzyl azide. Reaction with either 2-propynoic acid or 2-chloroacrylonitrile affords 1-(2,6-difluorobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylic acid or 1-(2,6-difluorobenzyl)- 1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbonitrile, respectively. For the carboxylic acid Shridhar Hegde and Michelle Schmidt intermediate, treatment with thionyl chloride followed by concentrated aqueous ammonium hydroxide or conversion to its methyl ester (methanol/sulfuric acid) with subsequent ammonolyis provides rufinamide.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antidepressants: antagonism of anticonvulsant effect
(convulsive threshold lowered); avoid with St John’s
wort.
Antimalarials: mefloquine antagonises
anticonvulsant effect.
Antipsychotics: antagonism of anticonvulsant effect
(convulsive threshold lowered).
Oestrogens and progestogens: metabolism
accelerated by rufinamide - reduced contraceptive
effect.
Orlistat: possibly increased risk of convulsions with
orlistat.
Ulipristal: possibly reduces contraceptive effect.
Metabolism
Rufinamide is extensively metabolized but has no active metabolites. Metabolism by carboxyesterases into inactive metabolite CGP 47292, a carboxylic acid derivative, via hydrolysis is the primary biotransformation pathway. A few minor additional metabolites were detected in urine, which appeared to be acyl-glucuronides of CGP 47292. The cytochrome P450 enzyme system or glutathiones are not involved with the metabolism of rufinamide. Rufinamide is a weak inhibitor of CYP 2E1. Rufinamide is a weak inducer of CYP 3A4 enzymes.
Metabolism
Almost exclusively eliminated by metabolism via hydrolysis of the carboxylamide group to the pharmacologically inactive acid derivative CGP 47292. Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism is very minor. The formation of small amounts of glutathione conjugates cannot be completely excluded. 84.7% was excreted by the renal route.
Storage
room temperature (desiccate)
References
1) Hakimian et al. (2007), Rufinamide: a new anti-epileptic medication; Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 8 1931 2) Gilchrist et al. (2014), Nav1.1 Modulation by a Novel Triazole Compound Attenuates Epileptic Seizures in Rodents; ACS Chem. Biol. 9 1204 3) Chen et al. (2018), Rufinamide, an antiepileptic drug, improves cognition and increases neurogenesis in the aged gerbil hippocampal dentate gyrus via increasing expressions of IGF-1, IGF-1R and p-CREB; Chem. Biol. Interact. 286 71
Properties of Rufinamide
| Melting point: | 232-234?C |
| Boiling point: | 473.8±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.52±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 2℃ |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble9mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 14.37±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 14,8293 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
Safety information for Rufinamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Rufinamide
Rufinamide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Rufinamide 98%View Details
Rufinamide 98%View Details
106308-44-5 -
 Rufinamide 99%View Details
Rufinamide 99%View Details -
 106308-44-5 RUFINAMIDE 95-99%View Details
106308-44-5 RUFINAMIDE 95-99%View Details
106308-44-5 -
 Rufinamide CAS 106308-44-5View Details
Rufinamide CAS 106308-44-5View Details
106308-44-5 -
 Rufinamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 106308-44-5View Details
Rufinamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 106308-44-5View Details
106308-44-5 -
 Rufinamide CAS 106308-44-5View Details
Rufinamide CAS 106308-44-5View Details
106308-44-5 -
 Rufinamide solution CAS 106308-44-5View Details
Rufinamide solution CAS 106308-44-5View Details
106308-44-5 -
 Rufinamide CAS 106308-44-5View Details
Rufinamide CAS 106308-44-5View Details
106308-44-5
