Polyacrylamide
Synonym(s):PAM;Polyacrylamide;linear polyacrylamide;P(NIPAM)n-NH-maleimide;polyNIPAM
- CAS NO.:9003-05-8
- Empirical Formula: (C3H5NO)x
- Molecular Weight: 71.08
- MDL number: MFCD00084392
- EINECS: 231-545-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:04
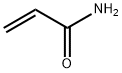
What is Polyacrylamide?
Chemical properties
white to faintly yellow granules
The Uses of Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide is a polymer formed from acrylamide subunits. Polyacrylamide has been extensively used in applications such as polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
The Uses of Polyacrylamide
Binding agent, dispersing aid, lubricant, drag reduction and crystal formation control.
The Uses of Polyacrylamide
polyacrylamide is a binder, film former, and fixative with greater use in hair and nail than in skin care preparations. It is used in some hand and body lotions and cleansing creams.
Definition
ChEBI: A macromolecule composed of repeating 1-carbamoylethylene units.
Definition
polyacrylamide: A polymerformed from 2-propenamide(CH2:CHCONH2). Polyacrylamide gelsare made using a cross-linking agentto form three-dimensional matrices.They are used in gel electrophoresis.
Preparation
Polyacrylamide resembles poly(acrylic acid) and poly(methacrylic acid)
in being water-soluble and, as with those polymers, it is mainly
this property which results in some limited commercial utilization.
Polyacrylamide is prepared by free radical polymerization, using techniques essentially similar to those described for poly(acrylic acid) and poly(methacrylic acid):

It may be noted that whereas this reaction gives a vinyl polymer, a different type of polymer is obtained when polymerization is initiated by a strong base. In this case, a polyamide (nylon 3) is formed. Active initiators for this type of polymerization include alkoxides (RO-) and reaction probably takes place according to the following scheme, which involves the rearrangement of a carbanion to a more stable amide anion:

Polyacrylamide is a hard, brittle material. It is readily soluble in cold water but solubility in organic compounds is generally very limited. The polymer undergoes reactions characteristic of the amide group; for example, alkaline hydrolysis introduces carboxylic groups and reaction with formaldehyde gives methylol groups.
Polyacrylamide has found use as a ftocculant in the processing of minerals and in water treatment. Copolymers of acrylamide and acrylic acid are used to increase the dry strength of paper.
General Description
Intelligent Swelling/Collapsing copolymer that can be used as a temperature- and pH-sensitive material.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Polyacrylamide is a water-soluble polymer made up of acrylamide subunits. It increases the viscosity of water and facilitates the flocculation of particles present in water.
Properties and Applications
|
INDEX |
Results |
|
Appearance |
White powder / Granular |
|
Molecular Weight |
5000000-30000000 |
|
Degree of Hydrolysis |
6-45% |
|
Solid Content |
89% min |
|
Dissolving Time |
60 minutes max |
|
Effective pH Range |
5~14 |
|
Residual Monomer |
0.1% max |
Properties of Polyacrylamide
| Melting point: | >300 °C |
| Density | 1.189 g/mL at 25 °C |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Water |
| form | Granules |
| color | White to faintly yellow |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, aluminium, copper, iron, iron salts |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Polyacrylamide (9003-05-8) |
Safety information for Polyacrylamide
Computed Descriptors for Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide manufacturer
Mithila Industrial Company
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 Polyacrylamide 99%View Details
Polyacrylamide 99%View Details -
 Acrylamide Polymer (containing small amounts of formalin as fungicide) (10% in Water) CAS 9003-05-8View Details
Acrylamide Polymer (containing small amounts of formalin as fungicide) (10% in Water) CAS 9003-05-8View Details
9003-05-8 -
 Polyacrylamide CAS 9003-05-8View Details
Polyacrylamide CAS 9003-05-8View Details
9003-05-8 -
 GenElute™-LPA CASView Details
GenElute™-LPA CASView Details -
 Polyacrylamide CAS No. 9003-05-8.View Details
Polyacrylamide CAS No. 9003-05-8.View Details
9003-05-8 -
 White Polyacrylamide, Grade: Industrial, PowderView Details
White Polyacrylamide, Grade: Industrial, PowderView Details
9003-05-8 -
 White Polyacrylamide Powder, For Wastewater Treatment, Grade: Technical GradeView Details
White Polyacrylamide Powder, For Wastewater Treatment, Grade: Technical GradeView Details
9003-05-8 -
 Polyacrylamide Chemical Powder, For Waste Water, Grade: TechnicalView Details
Polyacrylamide Chemical Powder, For Waste Water, Grade: TechnicalView Details
9003-05-8
