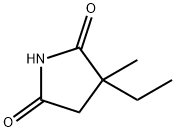
ETHOSUXIMIDE
Synonym(s):2-Ethyl-2-methylsuccinimide;Ethosuximide
- CAS NO.:77-67-8
- Empirical Formula: C7H11NO2
- Molecular Weight: 141.17
- MDL number: MFCD00072123
- EINECS: 201-048-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
What is ETHOSUXIMIDE?
Absorption
Bioavailability following oral administration is 93%.
Toxicity
Acute overdoses may produce nausea, vomiting, and CNS depression including coma with respiratory depression.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Zarontin,Parke Davis,US,1960
The Uses of ETHOSUXIMIDE
cholinergic
The Uses of ETHOSUXIMIDE
Ethosuximide is an anticonvulsant drug that is used in minor forms of epilepsy.
The Uses of ETHOSUXIMIDE
Anticonvulsant.
Background
An anticonvulsant especially useful in the treatment of absence seizures unaccompanied by other types of seizures.
Indications
For the treatment of petit mal epilepsy.
Definition
ChEBI: A dicarboximide that is pyrrolidine-2,5-dione in which the hydrogens at position 3 are substituted by one methyl and one ethyl group. An antiepileptic, it is used in the treatment of absence seizures and may be used for myoclonic seizures, but is ineffect ve against tonic-clonic seizures.
Manufacturing Process
α-Ethyl-α-methylsuccinimide is known in the prior art as a chemical entity,
having been prepared according to the method described by Sircar, J. Chem.
Soc., 128:600 (1927), and characterized in J. Chem. Soc., 128:1254 (1927).
In its manufacture, methyl ethyl ketone is condensed with ethylcyanoacetate
to give ethyl-2-cyano-3-methyl-2-pentenoate. That, in turn, adds HCN to give
ethyl-2,3-dicyano-3-methyl pentanoate. Saponification and decarboxylation
gives 2-methyl-2-ethyl succinonitrile. Heating with aqueous NH3 gives the
diamide which loses NH3 and cyclizes to ethosuximide.
brand name
Epileo Petitmal (Eisai), Pemal (Benzon), Petnidan (Desitin Arzneimittel), Suxilep (Parke – Davis, Jenapharm), Suxinutin/Zarontin (Parke – Davis).
Therapeutic Function
Anticonvulsant
Biological Functions
It is now generally accepted that the specific antiepileptic
action of ethosuximide (and the older agent trimethadione,
no longer employed) against absence
epilepsy is its ability to reduce the low-threshold calcium
current (LTCC) or T (transient) current. These
currents underlie the 3-Hz spike wave discharges that
are characteristic of absence epilepsy. A blockade of T-calcium current is likely also to be a mechanism used
by valproic acid.
The only clinical use for ethosuximide (Zarontin) is
in the treatment of absence epilepsy. If absence attacks
are the only seizure disorder present, ethosuximide
alone is effective. If other types of epilepsy are present,
ethosuximide can be readily combined with other
agents.
For the most part, ethosuximide is a safe drug. Most
of the side effects are dose related and consist of nausea,
gastrointestinal irritation, drowsiness, and anorexia.
A variety of blood dyscrasias have been reported, but
serious blood disorders are quite rare.
General Description
Ethosuximide is considered the prototypical anticonvulsantneeded for treating patients with absence seizures.Ethosuximide and the N-dealkylated active metabolite ofmethsuximide work by blocking the lowthresholdT-type calcium channels, thereby reducing thehyperexcitability of thalamic neurons that is specifically associatedwith absence seizure.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ethosuximide is an anticonvulsant drug and an antagonist for T-type calcium channel. It is known to prevent spike wave discharges, characterized in absence seizures.
Pharmacokinetics
Used in the treatment of epilepsy. Ethosuximide suppresses the paroxysmal three cycle per second spike and wave activity associated with lapses of consciousness which is common in absence (petit mal) seizures. The frequency of epileptiform attacks is reduced, apparently by depression of the motor cortex and elevation of the threshold of the central nervous system to convulsive stimuli.
Clinical Use
Although ethosuximide is the drug of choice for treatment of simple absence seizures, it is not effective against partial complex
or tonic-clonic seizures and may increase the frequency of grand mal attacks. Thus, it must be administered in combination with
other AEDs when treating persons with mixed seizure types. Ethosuximide is a substrate for both CYP3A4 and CYP2E1. The
major metabolite for ethosuximide is 3-(1-hydroxyethyl) succinimide, which is inactive and excreted unconjugated into the urine Several additional metabolites have been characterized recently. Approximately 20% of an oral dose is excreted
unchanged.
Although ethosuximide is thought to be the least toxic of the succinimides, it can cause gastrointestinal disturbances and
dose-related CNS effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, ataxia, sleep disturbances and depression. Idiosyncratic
hypersensitivity reactions include severe rashes, leukopenia, agranulocytosis (some fatal), systemic lupus erythematosus, and
parkinsonian-like symptoms. In addition to being less toxic than trimethadione, ethosuximide offers a wider range of protection
against different kinds of absence seizures.
Synthesis
Ethosuximide, 3-ethyl-3-methypyrrolidine-2,5-dione (9.3.4) is synthesized from methylethylketone and cyanoacetic ester, which are condensed in Knoevanagel reaction conditions. Then hydrogen cyanide is added to the resulting product (9.3.1). After acidic hydrolysis and decarboxylation of synthesized dinitrile (9.3.2), 2-methyl-2-ethylsuccinic acid (9.3.3) is formed. Reacting this product with ammonia gives the diammonium salt, and heterocyclization into the ethosuximide (9.3.4) takes place during subsequent heating [8,9].

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Antibacterials: concentration increased by isoniazid. Antidepressants: lower convulsive threshold; avoid with St John’s wort. Antiepileptics: concentration possibly reduced by carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenytoin and phenobarbital; concentration of fosphenytoin and phenytoin possibly increased; concentration increased by valproate. Antimalarials: anticonvulsant effect antagonised by mefloquine. Antipsychotics: lower convulsive threshold. Orlistat: possible increased risk of convulsions.
Metabolism
Ethosuximide is extensively hydroxylated in the liver to its principal metabolite which is reported to be inactive. Ethosuximide is excreted in the urine mainly in the form of its metabolites, either free or conjugated, but about 12-20% is also excreted unchanged.
Metabolism
Hepatic, via CYP3A4 and CYP2E1.
Properties of ETHOSUXIMIDE
| Melting point: | 51 °C |
| Boiling point: | 150 °C / 12mmHg |
| Density | 1.1522 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5026 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 100 mg/mL |
| form | Solid |
| form | neat |
| pka | pKa 9.5 (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 190g/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,3748 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 77-67-8 |
Safety information for ETHOSUXIMIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for ETHOSUXIMIDE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![6-azaspiro[3.4]octane-5,7-dione](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1497-16-1.gif)
![2-AZASPIRO[4.5]DECANE-1,3-DIONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure7/GIF/CB0422288.gif)
You may like
-
 Ethosuximide CAS 77-67-8View Details
Ethosuximide CAS 77-67-8View Details
77-67-8 -
 Ethosuximide >95% CAS 77-67-8View Details
Ethosuximide >95% CAS 77-67-8View Details
77-67-8 -
 Ethosuximide CAS 77-67-8View Details
Ethosuximide CAS 77-67-8View Details
77-67-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1