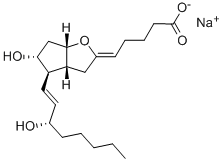
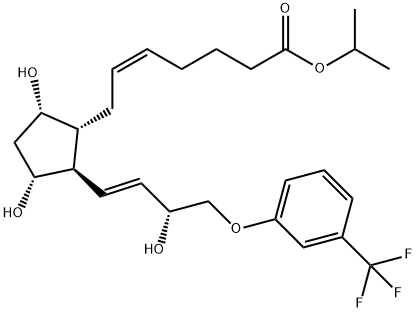
Treprostinil
- CAS NO.:81846-19-7
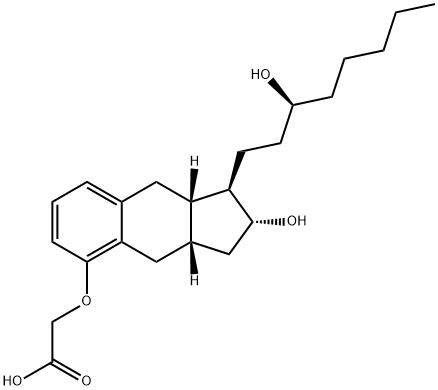
- Empirical Formula: C23H34O5
- Molecular Weight: 390.51
- MDL number: MFCD00888847
- EINECS: 808-233-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-20 09:20:20
What is Treprostinil ?
Absorption
After subcutaneous infusion, treprostinil is completely absorbed, with a bioavailability of about 100%, and it reaches steady-state concentrations in approximately 10 hours. The pharmacokinetics of treprostinil follow a two-compartment model and are linear between 2.5 and 125 ng/kg/min. Subcutaneous and intravenous doses of treprostinil are bioequivalent at 10 ng/kg/min. Compared to healthy subjects, patients with mild and moderate hepatic insufficiency had a corresponding Cmax 2- and 4-times higher and an AUC0-∞ 3- and 5-times higher when given a subcutaneous treprostinil dose of 10 ng/kg/min for 150 min.
When given orally at doses between 0.5 and 15 mg twice a day, treprostinil follows a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile. The oral bioavailability of treprostinil is 17%, and drug concentration reaches its highest level between 4 and 6 hours after oral administration. The oral absorption of treprostinil is affected by food. The AUC and Cmax of oral treprostinil increase 49% and 13%, respectively, when this drug is administered with a high-fat, high-calorie meal.
The AUC and Cmax of inhaled treprostinil were proportional to the doses administered (18 to 90 μg). The bioavailability of inhaled treprostinil was 64% in patients receiving 2 doses of 18 μg, and 72% in patients receiving two doses of 36 μg. Two separate studies that evaluated the pharmacokinetics of inhaled treprostinil at a maintenance dose of 54 μg found that the mean Cmax was 0.91 and 1.32 ng/mL, respectively, with a corresponding Tmax of 0.25 and 0.12 hr and a mean AUC of 0.81 and 0.97 hr?ng/mL.
Toxicity
Treprostinil overdose symptoms are an extension of its dose-limiting pharmacologic effects. These include flushing, headache, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Most overdose events were self-limiting and resolved by reducing or withholding treprostinil. In studies where treprostinil was infused using an external pump, several patients received an overdose due to an accidental bolus administration, errors in the programmed delivery rate and incorrect prescriptions. Only two cases of of substantial hemodynamic concern were detected among patients that received an excess of treprostinil. A pediatric patient that accidentally received 7.5 mg of treprostinil via a central venous catheter presented flushing, headache, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, and seizure-like activity with loss of consciousness for several minutes.
A rat study that evaluated the carcinogenic effects of inhaled treprostinil, found no evidence of carcinogenicity in levels up to 35 times the clinical exposure obtained with a maintenance dose of 54 μg. The infusion of treprostinil sodium did not affect fertility or mating performance in rats given subcutaneous treprostinil. Treprostinil did not show mutagenic or clastogenic effects in in vitro or in vivo studies. There was no significant increase of tumors in rats given up to 10 mg/kg/day of oral treprostinil diolamine.
The Uses of Treprostinil
Synthetic analog of Prostacyclin (P839060). Antihypertensive. Treprostinil, marketed under the trade name Remodulin is a medication used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
What are the applications of Application
Treprostinil is a cytokine inhibitor that prevents NF-κB translocation to the nucleus
Background
Treprostinil is a stable tricyclic analogue of prostacyclin that promotes the vasodilation of pulmonary and systemic arterial vascular beds and the inhibition of platelet aggregation. It reduces symptoms in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease. The first agent approved for the treatment of PAH was epoprostenol, a synthetic prostacyclin that significantly increases patients' quality of life. However, the use of epoprostenol is limited due to its short half-life (3-5 min) and instability at room temperature. The use of more stable alternatives such as treprostinil provides patients with PAH with more treatment options.
Treprostinil was approved by the FDA in 2002 for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. It is available in the following routes of administration: subcutaneous, intravenous, inhaled and oral. The first generic form of treprostinil became available in 2019.
Indications
The FDA has indicated treprostinil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension and pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease to improve exercise ability. It is also used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients requiring transition from epoprostenol. The Health Canada label specifies that treprostinil is indicated for the long-term treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension in NYHA Class III and IV patients who did not respond adequately to conventional therapy.
L24244
Definition
ChEBI: Treprostinil is a carboxylic acid and a carbotricyclic compound. It has a role as a platelet aggregation inhibitor, a vasodilator agent, an antihypertensive agent, a cardiovascular drug, a vitamin K antagonist and a human blood serum metabolite.
Pharmacokinetics
As an analogue of prostacyclin, treprostinil promotes the vasodilation of pulmonary and systemic arterial vascular beds and the inhibition of platelet aggregation . In animals, the vasodilatory effects of treprostinil lead to a reduction of right and left ventricular afterload and an increase in cardiac output and stroke volume. Treprostinil also causes a dose-related negative inotropic and lusitropic effect, and no major effects on cardiac conduction have been detected. Short-lasting effects on QTc were detected in healthy volunteers (n=240) given inhaled single doses of 54 and 84 μg of treprostinil. These effects dissipated rapidly as treprostinil concentrations lowered. When given subcutaneously or intravenously, treprostinil has the potential to reach higher concentrations. The effect of oral treprostinil on QTc has not been evaluated.
Due to its ability to inhibit platelet aggregation, treprostinil can increase the risk of bleeding, and patients with low systemic arterial pressure taking treprostinil may experience symptomatic hypotension. The abrupt withdrawal of treprostinil or drastic changes in dose may worsen the symptoms of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The inhalation of treprostinil can also cause bronchospasms in patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or bronchial hyperreactivity. When given intravenously, treprostinil can lead to infusion complications and increase the risk of bloodstream infections.
Pharmacokinetics
Treprostinil is rapidly absorbed from the subcutaneous site of infusion, with an almost 100% bioavailability and a mean half-life of 85 minutes (34 minutes for the IV infusion). The IV solution must be diluted with normal saline or sterile water before starting the infusion. Unlike epoprostenol, treprostinil is stable at room temperature for up to 5 years, with vasodilation action lasting from 4 to 6 hours, compared with the short, 2- to 3-minute action for epoprostenol. Because of its long life in the body, it can be administered under the skin with a microinfusion subcutaneous infusion pump rather than into the bloodstream and, thus, without hospitalization, as contrasted with the central IV infusion of epoprostenol.
Clinical Use
Treprostinil is a synthetic, stable form of prostacyclin for the treatment for advanced pulmonary hypertension with NYHA class III or IV symptoms as well as for late-stage peripheral vascular disease (PVD). Its sodium salt injectable form is administered either as a continuous subcutaneous infusion directly into the skin or, if the subcutaneous infusion is not tolerated, as a continuous IV infusion without an implanted catheter.
Side Effects
Side effects include jaw pain, headaches, nausea, diarrhea, flushing, and localized pain at the delivery site under the skin. This pain has been reported as slight to severe irritation. Patients using the drug seem to ex-perience improvement in their condition, including decreased fatigue, decreased shortness of breath, and decreased pulmonary artery pressures, as well as overall improvement in quality of life.
Metabolism
Treprostinil is mostly metabolized by the liver, mainly by CYP2C8, and by CYP2C9 to a lesser extent. Treprostinil does not have a single major metabolite. The five metabolites detected in urine (HU1 through HU5) accounted for 13.8, 14.3, 15.5, 10.6 and 10.2% of the dose, respectively. One of the metabolites (HU5) is the glucuronide conjugate of treprostinil. HU1, HU2, HU3 and HU4 are formed through the oxidation of the 3-hydroxyloctyl side chain. None of the metabolites of treprostinil appear to be active. In vitro studies suggest that treprostinil does not inhibit or induce any major CYP enzymes.
storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of Treprostinil
| Melting point: | 121-123° |
| Boiling point: | 587.1±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.158±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly, Heated), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 3.19±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White to Beige |
Safety information for Treprostinil
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H361:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Treprostinil
Treprostinil manufacturer
Honour Lab Limited
Turtle Pharma Private Limited
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 81846-19-7 Treprostinil 98%View Details
81846-19-7 Treprostinil 98%View Details
81846-19-7 -
 Treprostinil 81846-19-7 98%View Details
Treprostinil 81846-19-7 98%View Details
81846-19-7 -
 Treprostinil CAS 81846-19-7View Details
Treprostinil CAS 81846-19-7View Details
81846-19-7 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0