Ranolazine
Synonym(s):(±)-N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-4-[2-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propyl]piperazin-1-ylacetamide;(±)-4-[2-Hydroxy-3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)propyl]-1-piperazineaceto-2′,6′-xylidide
- CAS NO.:95635-55-5
- Empirical Formula: C24H33N3O4
- Molecular Weight: 427.54
- MDL number: MFCD00864690
- EINECS: 620-450-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
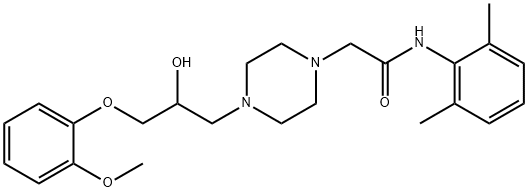
What is Ranolazine?
Absorption
The time to reach peak serum concentration is quite variable but has been observed to be in the range of 2-6 hours, with steady-state within 3 days. The FDA indicates a Tmax of 3-5 hours. The average steady-state Cmax is about 2600 ng/mL. Absorption of ranolazine is not significantly affected by food consumption. The bioavailability of ranolazine taken in the tablet form compared to that from a solution of ranolazine is about 76%.
Toxicity
The reported LD50 of oral ranolazine in the rat is 980 mg/kg. High oral doses of ranolazine have led to dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. These effects have been shown to be dose related. High intravenous doses can cause diplopia, confusion, paresthesia, in addition to syncope. In the case of an overdose, provide supportive therapy accompanied by continuous ECG monitoring for QT interval prolongation.
Description
Ranolazine is an orally available, extended release drug for the treatment of chronic angina in patients who have failed to respond to prior angina therapy. Chronic stable angina (CSA) is a common symptom of coronary artery disease wherein plaques in the coronary vasculature restrict blood flow to the heart, which in turn leads to insufficient oxygenation of the heart, typically during physical exertion or emotional stress. A vast majority of the existing anti-anginal and anti-ischemic therapies aim to correct the imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply through mechanisms that produce reductions in heart rate or blood pressure.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Roche Bioscience (US)
The Uses of Ranolazine
Ranolazine is an anti-ischemic agent which modulates myocardial metabolism. Antianginal.
The Uses of Ranolazine
antianginal, antiischemic
Indications
Ranolazine is indicated for the treatment of chronic angina. It can be used alone or in conjunction with nitrates, beta-blockers, angiotensin receptor blockers, anti-platelet drugs, calcium channel blockers, lipid-lowering drugs, and ACE inhibitors.
Ranolazine has also been used off-label for the treatment of certain arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia, however, this use is not strongly supported by scientific evidence. Ranolazine has also been studied for the treatment of acute coronary syndrome, microvascular coronary dysfunction, arrhythmia, and glycemic control, which are not yet approved indications.
Background
Chronic angina is a common cardiovascular condition affecting millions worldwide and causes significant disability while interfering with daily activities. Ranolazine is a well-tolerated piperazine derivative used for the management of this condition, offering relief from uncomfortable and debilitating symptoms. With a mechanism of action different from drugs used to treat the same condition, ranolazine is a promising anti-anginal therapy. It was originally approved by the FDA in 2006.
What are the applications of Application
Ranolazine is an anti-ischemic agent which inhibits late sodium currents
Definition
ChEBI: N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propyl]piperazin-1-yl}acetamide is an aromatic amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 2-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propyl]piperazin-1-yl}acetic acid with the amino group of 2,6-dimethylaniline. It is a monocarboxylic acid amide, an aromatic amide, a N-alkylpiperazine, a secondary alcohol and a monomethoxybenzene.
brand name
Ranexa (Sensus).
General Description
Ranolazine, N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-[4-[2-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propyl]piperazin-1-yl]acetamide (Ranexa), is an antianginal medication thatwas approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)in January 2006 for the treatment of chronic angina.Ranolazine is believed to elicit its effects by altering thetranscellular late sodium current. This, in turn, alters thesodium-dependent calcium channels during myocardial ischemia.Thus, ranolazine indirectly prevents the calciumoverload that is associated with cardiac ischemia.Ranolazine is metabolized by the cytochrome CYP3A enzymesin the liver.
Pharmacokinetics
Ranolazine exerts both antianginal and ischemic effects independent from lowering heart rate or blood pressure. It blocks IKr, the rapid portion of the delayed rectifier potassium current, and prolongs the QTc interval in a dose-dependent fashion. The Ikr is important for cardiac repolarization. Ranolazine exerts its therapeutic effects without negative chronotropic, dromotropic, or inotropic actions neither at rest, nor during exercise.
Clinical Use
Add on therapy for angina
Synthesis
Two syntheses, one from the inventors at Roche and other from a group in Hungary, of Ranolazine have been described in the patent literature. The original synthesis is highlighted in the Scheme. Reaction of 2,6-dimethylaniline 46 with chloroacetyl chloride (47) in the presence of triethylamine for 4h at 0oC gave amide 48 in 82% yield. This chloro amide 48 was reacted with piperazine in refluxing ethanol for 2 h to give piperazinyl amide 50. Reaction of amide 50 with epoxide intermediate 53, prepared by reacting 2-methoxy phenol 51 with epichlorohydrin, in refluxing isopropanol for 3 h followed by treatment with HCl/methanol gave ranolazine dihydrochloride (VII) in 73% yield.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anti-arrhythmics: avoid with disopyramide.
Antibacterials: concentration possibly increased
by clarithromycin and telithromycin - avoid
concomitant use; concentration reduced by
rifampicin - avoid.
Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole
and possibly itraconazole, posaconazole and
voriconazole - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
atazanavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, indinavir,
lopinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and tipranavir - avoid.
Beta-blockers: avoid with sotalol.
Ciclosporin: concentration of both drugs possibly
increased.
Grapefruit juice: concentration of ranolazine possibly
increased - avoid.
Statins: concentration of simvastatin increased -
maximum dose of simvastatin is 20 mg.
Tacrolimus: concentration of tacrolimus increased.
Metabolism
Ranolazine is rapidly heavily metabolized in the liver an gastrointestinal tract through the activity of the CYP3A4 enzyme with minor contributions from CYP2D6. More than 40 ranolazine metabolites have been found in plasma and more than 100 metabolites have been identified in the urine.
Ranolazine and some of its metabolites are known to weakly inhibit CYP3A4. However, the activity of the metabolites of ranolazine has not been fully elucidated.
Metabolism
Extensively metabolised in the gastrointestinal tract and
liver. Four main metabolites have been identified.
Approximately 75% of a dose is excreted in the urine with
the remainder in the faeces.
Properties of Ranolazine
| Melting point: | 119-1200C |
| Boiling point: | 624.1±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.174±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 14.06±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 95635-55-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Ranolazine
Computed Descriptors for Ranolazine
Ranolazine manufacturer
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Ranolazine 98%View Details
Ranolazine 98%View Details
95635-55-5 -
 Ranolazine 98%View Details
Ranolazine 98%View Details -
 95635-55-5 Ranolazine 98%View Details
95635-55-5 Ranolazine 98%View Details
95635-55-5 -
 Ranolazine 95-99%View Details
Ranolazine 95-99%View Details
95635-55-5 -
 Ranolazine 98%View Details
Ranolazine 98%View Details -
 Ranolazine 98%View Details
Ranolazine 98%View Details -
 Ranolazine 98% CAS 95635-55-5View Details
Ranolazine 98% CAS 95635-55-5View Details
95635-55-5 -
 Ranolazine USP RC APIView Details
Ranolazine USP RC APIView Details
2210-74-4
