Thioacetamide
Synonym(s):Ethanethioamide;TAA;Thioacetamide
- CAS NO.:62-55-5
- Empirical Formula: C2H5NS
- Molecular Weight: 75.13
- MDL number: MFCD00008070
- EINECS: 200-541-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-07 19:09:50
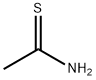
What is Thioacetamide?
Description
Thioacetamide (TAA) is not known to occur in nature. It is prepared by heating ammonium acetate and aluminum sulfide.
Chemical properties
White solid
Chemical properties
Thioacetamide is combustible, crystalline compound. Slight mercaptan odor.
The Uses of Thioacetamide
Thioacetamide is a carcinogen, a hepatotoxicant. Thioacetamide induces acute chronic liver injury through the activation of protein synthesis of RNA, DNA, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptitase. Thioacetamide has been used in the synthesis of [email?protected] nano-array core-shell structure.
The Uses of Thioacetamide
Sulfide generation
The Uses of Thioacetamide
Substitute for H2S in laboratory qualitative analyses.
The Uses of Thioacetamide
It is used as an intermediate in organicsynthesis.
What are the applications of Application
Thioacetamide is a hepatotoxin
Definition
ChEBI: A thiocarboxamide consiting of acetamide having the oxygen replaced by sulfur.
General Description
White crystals with a mercaptan odor.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Thioacetamide reacts with aqueous acid to generate hydrogen sulfide. Forms addition compounds and sulfides with salts of heavy metals. Hydrolyzed by acids or bases .
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, a possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
The toxicity of this compound is moderatein rats; an oral lethal dose is 200 mg/kg.Oral administration of thioacetamide causedliver cancer in rats and mice. It is, however, a weak liver carcinogen. Malvaldi and associates (1988) investigated the mechanism of its carcinogenic activity on rat liver.Whereas the initiating ability of this compound is quite low, its promoting effect isstrong. Thus thioacetamide is a very effectivepromoter of the liver carcinogenesis. A similar promoting activity of liver carcinogenesishas been observed with other thioamide substances, such as thiobenzamide (Malvaldi et al. 1986). Low et al. (2004) have proposed a modelto explain thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity and cirrhosis in rat livers. The pathways of thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosiswere found to be initiated by thioacetamideS-oxide derived from the biotransformationof thioacetamide by the microsomal flavinadenine nucleotide containing monooxygenase and cytochrome P450 systems andinvolve oxidative stress and depletion ofsuccinyl-CoA, thus affecting heme and ironmetabolism. Karabay et al. (2005) observedsuch hepatic damage in rats with elevationof total nitrite level in livers and decrease inarginase activity. The authors have reportedthat nitrosative stress was essentially the critical factor in thioacetamide-induced hepaticfailure in rats.Pretreatment of rats with jigrine exhibited hepatoprotective action againstthioacetamide-induced toxicity (Ahmed et al.1999). Thioacetamide decreased the concentration of glutathione in the liver of rats.Jigrine pretreatment, however, restored theglutathione levels to the near normal values.The authors claimed that the effects of jigrinewere comparable to that of silymarin. Thehepatotoxicity in rats was found to potentiatefollowing pretreatment with phenobarbital.Al-Bader et al. (2000) investigated thetoxicity of thioacetamide in the spleen inexperimental animals. The authors foundan intimate association between the levelsof trace metals and spleen pathology, asobserved in studies of other organs.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data on Thioacetamide are not available; Thioacetamide is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplas tigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. Human mutation data reported. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Exposure has caused liver damage. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx. See also SULFIDES and MERCAPTANS.
Potential Exposure
Thioacetamide is used as a replacement for hydrogen sulfide in qualitative analyses. Thioacetamide has been used as an organic solvent in the leather, textile, and paper industries; as an accelerator in the vulcanization of buna rubber; and as a stabilizer of motor fuel.
Carcinogenicity
Thioacetamide is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogenbased on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
TAA’s production and use as a substitute for hydrogen sulfide in the laboratory may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. If released to air, TAA’s estimated vapor pressure indicates that it will exist solely as a vapor in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase TAA will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 18 h. TAA was not biodegraded by activated sludge after 5 days, and therefore may be resistant to biodegradation in the environment. Hydrolysis is not expected since amides hydrolyze very slowly under environmental conditions. An estimated bioconcentration factor for TAA suggests that the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. TAA is expected to be highly mobile in soil, and to volatilize into the atmosphere from moist soil surfaces. In an aquatic environment, most of the substance will leave via volatilization and is not expected to adsorb to solids.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the amide from absolute diethyl ether or *benzene. Dry it at 70o in a vacuum and store it over P2O5 at 0o under nitrogen. (It develops an obnoxious odour on storage, and absorption at 269nm decreases, hence it should be freshly recrystallised before use). [Beilstein 2 IV 565.]
Toxicity evaluation
TAA acts as an indirect hepatotoxin and causes parenchymal cell necrosis. It can be metabolized in vivo to acetamide, which itself is carcinogenic. Acetamide is then hydrolyzed to acetate. TAA-induced liver necrosis has been explained by a scheme that includes the metabolic conversion of TAA to its S-oxide, followed by the further metabolism of TAA-S-oxide to a reactive intermediate that can either bind to liver macromolecules or be further degraded to acetamide and polar products. Examples of TAA’s biochemical effects in the liver include glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase being induced within days after rats are treated with TAA, and the level of urea product is decreased as are the activities of hepatic carbamyl phosphate synthetase, ornithine transcarbamylase, and arginase. Thus, TAA can produce marked disturbances in the urea cycle in the liver. Further, TAA administered to rats leads to functional disturbances in mitochondria isolated from livers after 24 h, and the maximum respiratory activity of the mitochondria is also depressed, mitochondrial Ca2+ content is significantly increased, and the Ca2+ transport behavior of the hepatic mitochondria is altered. The results are indicative of structural alterations of the inner mitochondrial membranes. The potential role of TAA in the initiation phase of carcinogenesis may be associated with an increase in nucleoside triphosphate activity in cell nuclear envelopes with a corresponding increase in RNA transport activity. Alterations in the transport phenomenon of nuclear RNA sequences are considered an early response to carcinogens.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Treatment in an incinerator, boiler or cement kiln.
Properties of Thioacetamide
| Melting point: | 108-112 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 111.7±23.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.37 |
| refractive index | 1.5300 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | passes test2% |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 13.25±0.29(Predicted) |
| color | Off-white to slightly beige |
| PH Range | 5.2 |
| PH | 5.2 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 16.3 g/100 mL (25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9319 |
| BRN | 506006 |
| Stability: | Stability Incompatible with water, mineral acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 62-55-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 7, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethanethioamide(62-55-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thioacetamide (62-55-5) |
Safety information for Thioacetamide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H350:Carcinogenicity H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Thioacetamide
| InChIKey | YUKQRDCYNOVPGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Thioacetamide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Thioacetamide 99%View Details
Thioacetamide 99%View Details -
 Thioacetamide CAS 62-55-5View Details
Thioacetamide CAS 62-55-5View Details
62-55-5 -
 Thioacetamide CAS 62-55-5View Details
Thioacetamide CAS 62-55-5View Details
62-55-5 -
 Thioacetamide CAS 62-55-5View Details
Thioacetamide CAS 62-55-5View Details
62-55-5 -
 Thioacetamide (CAS Number: 62-55-5)View Details
Thioacetamide (CAS Number: 62-55-5)View Details
62-55-5 -
 Thioacetamide Powder ChemicalView Details
Thioacetamide Powder ChemicalView Details
62-55-5 -
 ThioacetamideView Details
ThioacetamideView Details
62-55-5 -
 Powder Thioacetamide, Packaging Type: Bag, 5 kgView Details
Powder Thioacetamide, Packaging Type: Bag, 5 kgView Details
62-55-5
