N,N-Dimethylacetamide
Synonym(s):DMAC;N,N-Dimethylacetamide;N,N-Dimethylacetamide solution;N,N-Dimethylacetamide;N,N-Dimethylacetamide ZerO2
- CAS NO.:127-19-5
- Empirical Formula: C4H9NO
- Molecular Weight: 87.12
- MDL number: MFCD00008686
- EINECS: 204-826-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-28 17:38:58
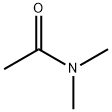
What is N,N-Dimethylacetamide?
Description
N, N-Dimethylacetamide (DMAc) is a dipolar, aprotic, high-boiling, oily solvent and reagent. N, N-Dimethylacetamide (DMAc) traces its roots at least as far back as 1914, when Marc Tiffeneau* and K. Fuhrer at H pital Boucicaut1 (Paris) identified it as a product of heating N, N-dimethylbenzylamine and acetic anhydride to 200 °C in a sealed tube. Then, in 1931, in a treatise on the synthesis of aliphatic amides, James A. Mitchell and E. Emmet Reid at Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore) described preparing DMAc in 84% yield by heating acetic acid and dimethylamine at 150 °C for 3 h. This, along with using acetic anhydride or methyl acetate instead of the acid, is the process for manufacturing DMAc today.
Description
Dimethylacetamide (DMA) is a polar aprotic solvent with a high boiling point (165 C). A closely related solvent is dimethyformamide (DMF).
Description
Dimethylacetamide (DMAC) is a synthetic organic compound that is produced from a reaction of dimethylamine and acetic acid or acetic anhydride. It is a colorless to yellow liquid with a faint odor resembling ammonia. DMAC has similar density to water and is miscible with water and organic substances. This organic compound is commonly associated with many industrial uses, either as a starting material or an intermediate. DMAC is a good solvent that is used in polymer dissolution, especially in the fiber industry. Historically, DMAC was also tested as a possible antineoplastic agent in a phase 1 study involving 17 patients. However, liver and central nervous system (CNS) toxicity associated with DMAC was observed and these patients had altered mental states, resulting in no further drug development.
Chemical properties
Dimethylacetamide occurs as a clear, colorless, slightly hygroscopic liquid with a weak ammonia-like or fish-like odor. odor threshold concentration is 46.8 ppmv (Leonardos et al., 1969). It is soluble in a wide variety of solvents.
The Uses of N,N-Dimethylacetamide
N, N-dimethylacetamide is an excellent solvent and often acts as a catalyst in halogenation, cyclization, and alkylation reactions. It is an important industrial solvent for polyacrylonitrile, vinyl resins, cellulose derivatives, styrene polymers and linear polyesters. It is also used in all analytical laboratories as a major component of the mobile phase in High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and in Liquid Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS). N, N-dimethylacetamide lithium chelate complexes intercalate cationic sites in layered silicates. DMAc is a solvent for producing fibers and synthesizing organic compounds, notably pharmaceuticals. Its broad range of miscibility makes it useful in mixed solvents. It is also stable to strong bases but hydrolyzes in the presence of acids. It must be handled with care.
What are the applications of Application
N,N-Dimethylacetamide is N,N-Dimethylacetamide is an organic compound that has been utilized as a non-polar solvent.
Definition
ChEBI: N,N-dimethylacetamide is a member of the class of acetamides that is acetamide in which the hydrogens attached to the N atom have been replaced by two methyl groups respectively. Metabolite observed in cancer metabolism. It has a role as a human metabolite. It is a member of acetamides and a monocarboxylic acid amide. It is functionally related to an acetamide.
What are the applications of Application
N,N-Dimethylacetamide is primarily used as an industrial solvent and intermediate in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, agrochemicals, polymers, and resins. It is also used as a spinning solvent in the production of fibers of various polymers, including acrylic, polyurethane, polyurea copolymer, and meta-aramid. Moreover, this aprotic dipolar solvent is also used in X-ray and photographic products and in the production of polyimide films. The polyimide films are produced for a variety of industries, including consumer electronics, solar photovoltaic and wind energy, aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. N,N-Dimethylacetamide has other minor uses, including removal of ink, stripping of paint, and also for laboratory use.
Preparation
N,N-Dimethylacetamide is prepared by reaction of dimethylamine with acetic acid, acetic anhydride, or acetate esters. Heating dimethylamine acetate with, or without a catalyst affords N,N-Dimethylacetamide. Reaction of dimethylamine with acetate esters requires a catalyst; sodium methoxide is typically used.
General Description
Dimethylacetamide appears as a clear colorless liquid with a faint odor similar to ammonia. About the same density as water. Flash point 145°F. Vapors heavier than air. May by toxic by skin absorption. May irritate eyes and skin.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
N,N-Dimethylacetamide is an amide. Incompatible with oxidizing agents and halogenated compounds. Exothermic reactions occur with carbon tetrachloride and hexachlorocyclohexane. N,N-Dimethylacetamide can react violently in the presence of iron. Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Emits carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides, and dimethylamine when heated to decomposition.
Health Hazard
A study of 41 workers who had been exposed to dimethylacetamide from 2 to 10 years revealed the occurrence of disorders reflecting liver damage (Corsi, 1971). Retention of bromosulfophthalein was increased in 9 of 10 workers who had been exposed to dimethylacetamide for 7 to 10 years, and in 10 of 20 workers who had been exposed to dimethylacetamide for 2 to 7 years. Other parameters of hepatic function which were altered in the exposed individuals include proteinemia, cholesterolemia, activities of hepatic transaminases and alkaline phosphatase in serum, and bilirubinemia. Hepatomegaly was diagnosed in 14 workers.
In a clinical trial, dimethylacetamide was administered to patients with advanced malignancies and caused abnormal mental states (Weiss et al 1962a, b). This effect was observed at a dose of 400 mg/kg given daily for 3 or more days.
The symptoms were not seen at 300 mg/kg or lower. The second or third dose caused depression, lethargy, occasional confusion or disorientation. The fourth or fifth dose produced striking hallucinations, perceptual distortions and delusions in all nine patients. All patients reverted to normal several days after discontinuation of treatment with dimethylacetamide.
Fire Hazard
N,N-Dimethylacetamide is combustible.
Industrial uses
Dimethylacetamide is a powerful industrial solvent, the uses of which are very similar to those of dimethylformamide (Siegle, 1980). Its strong solvent action renders it particularly useful in the manufacture of films and fibers and as a solvent for polyacrylonitrile, polyvinyl chloride, polyamides, cellulose derivatives and polystyrenes and in coatings and adhesive formulations. Dimethylacetamide dissolves many inorganic salts.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by skin contact, inhalation, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by ingestion. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. A skin and eye irritant. Less toxic than dimethylformamide. Mutation data reported. Combustible when exposed to heat and flame. A moderate explosion hazard. Violent reaction with halogenated compounds (e.g., carbon tetrachloride, hexachlorocyclohexane) when heated above 9OOC. Iron powder catalyzes the reaction so that it initiates at 71OC. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx
Safety
Dimethylacetamide is used in pharmaceutical preparations as a solvent in parenteral formulations and is generally regarded as a nontoxic material when used as an excipient. Animal toxicity studies indicate that dimethylacetamide is readily absorbed into the bloodstream following inhalation or topical application. Repeated exposure to dimethylacetamide may be harmful and can result in liver damage. High intravenous doses (>400mg/kg/day for 3 days) may be hallucinogenic.
LD50 (rabbit, SC): 9.6g/kg(11) LD50 (rat, IP): 2.75g/kg LD50 (rat, IV): 2.64g/kg LD50 (rat, oral): 4.93g/kg LD50 (mouse, inhalation): 7.2g/kg LD50 (mouse, IP): 2.8g/kg
Potential Exposure
Drug,Mutagen; Reproductive Effector; Primary Irritant.Dimethylacetamide is used primarily as a solvent for synthetic and natural resins, especially acrylic fibers and spandex. About 15% of dimethylacetamide production is used tomake alkyl (C12-14) dimethylamine oxide (a surfactant) andrubber chemicals. Dimethylacetamide is also used as anextraction solvent for butadiene manufacture.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPRif heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to amedical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed,get medical attention. Give large quantities of water andinduce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious personvomit.
Chemical property
N, N-Dimethylacetamide (DMAc) is a synthetic organic compound produced from a reaction of dimethylamine and acetic acid or acetic anhydride. It is a colourless to yellow liquid with a faint odour resembling ammonia. DMAC has a similar density to water and is miscible with water and organic substances. DMAc is a dipolar, aprotic, high-boiling, oily solvent and reagent.
Carcinogenicity
DMAC was not carcinogenic in rats administered 100, 300, or 1000 mg/kg/day in drinking water for 2 years. Rats and mice were exposed by inhalation to 0, 25, 100, or 350 ppm DMAC for 6 h/day, 5 days/week for 18 months (mice) or 2 years (rats). DMAC was not oncogenic under these conditions in either the rat or the mouse.
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Releases toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987).
Metabolism
33 mg or 92 mg of 14C-labelled DMAC were given by gavage to two rats. The major urinary components were:60-70% MMAC, 7-10% N -hydroxymethylacetamide, 7- 10%, Acetamide and some residual DMAC. A small proportion of DMAC and its intermediates was hydrolysed and eliminated as Carbon Dioxide.
Twenty male rats were given two subcutaneous injections of 300 mg DMAC, MMAC and Acetamide were found in the urine.
20 rats had 20-80% DMAC solutions (0.12 ml) applied to their backs. The amount of MMAC increased as the solution concentration increased. Recovery ranged from 13% for the 20% solution to 42% for undiluted DMAC (Du Pont, 1988).
These studies show that the major metabolic pathway of DMAC "in vivo" in rats is sequential N-demethylation and elimination from the body.
https://hpvchemicals.oecd.org/ui/handler.axd?id=16564422-daff-4489-8c27-735d3ab0b260
Storage
Dimethylacetamide should be stored in an airtight container, protected from light, in a cool, dry place. Dimethylacetamide has an almost unlimited shelf-life when kept in closed containers and under nitrogen. It is combustible.
Shipping
This material is not covered in DOT’sPerformance-Oriented Packaging Standards. It may,however, be classified as a combustible liquid, n.o.s. Thisclass requires no shipping label. It falls in Hazard Class 3[each reference to a Class 3 material is modified to read“COMBUSTIBLE LIQUID” when that material is reclassified in accordance with y173.150 (e) or (f) of this subchapter or has a flash point above 60.5℃/141°F but below93℃/200°F] and Packing Group III. The symbol “D” identifies proper shipping names which are appropriate fordescribing materials for domestic transportation but may beinappropriate for international transportation under the provisions of international regulations (e.g., IMO, ICAO). Analternate proper shipping name may be selected when eitherdomestic or international transportation is involved.
Purification Methods
Shake the amide with BaO for several days, reflux it with BaO for 1hour, then fractionally distil it under reduced pressure. Store it over molecular sieves. [Beilstein 4 IV 180.]
Toxicity evaluation
Little data on the metabolism of DMAC are available in the literature. Hepatotoxicity of DMAC is believed to be metabolism dependent. From its metabolic activation (by cytochrome P450s and probably CYP2E1), reactive species and free radical metabolites are produced and readily attack the heme prosthetic group of the liver, leading to suicidal hepatic enzyme inactivation.
Incompatibilities
Dimethylacetamide is incompatible with carbon tetrachloride, oxidizing agents, halogenated compounds, and iron. It attacks plastic and rubber. Contact with strong oxidizers may cause fire.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM injections, IV injections and infusions). Included in parenteral medicines licensed in the UK.
Properties of N,N-Dimethylacetamide
| Melting point: | -20 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 164.5-166 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.937 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.89 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 40 mm Hg ( 19.4 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 158 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | >1000g/l soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| pka | -0.41±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Colorless to yellowish |
| Odor | Faint ammonia odor |
| Relative polarity | 6.3 |
| PH | 4 (200g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| PH Range | 4 at 200 g/l at 20 °C |
| explosive limit | 1.7-11.5%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.76ppm |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| λmax | λ: 270 nm Amax: 1.00 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.30 λ: 290 nm Amax: 0.15 λ: 310 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 320 nm Amax: 0.03 λ: 360-400 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,3227 |
| BRN | 1737614 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 10 ppm (35 mg/m3), IDLH 300 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 10
ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 37.8(25℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 127-19-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetamide, N,N-dimethyl-(127-19-5) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 123) 2020 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dimethylacetamide (127-19-5) |
Safety information for N,N-Dimethylacetamide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for N,N-Dimethylacetamide
| InChIKey | FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
N,N-Dimethylacetamide manufacturer
Global Impex.
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 DMAC (Dimethyl acetamide) 98%View Details
DMAC (Dimethyl acetamide) 98%View Details -
 Dimethyl Acetamide (DMAC) 99%View Details
Dimethyl Acetamide (DMAC) 99%View Details -
 Di Methyl Acetamide 99%View Details
Di Methyl Acetamide 99%View Details -
 N, N-Dimethylacetamide CAS 127-19-5View Details
N, N-Dimethylacetamide CAS 127-19-5View Details
127-19-5 -
 N, N-Dimethylacetamide CAS 127-19-5View Details
N, N-Dimethylacetamide CAS 127-19-5View Details
127-19-5 -
 Dimethylacetamide CASView Details
Dimethylacetamide CASView Details -
 N,N-Dimethylacetamide (DMA) for HPLC CAS 127-19-5View Details
N,N-Dimethylacetamide (DMA) for HPLC CAS 127-19-5View Details
127-19-5 -
 Di Methyl Acetamide Dmac, 99.90%View Details
Di Methyl Acetamide Dmac, 99.90%View Details
127-19-5
