Acetamide
Synonym(s):Acetamide;Acetic acid amide;Amide C2
- CAS NO.:60-35-5
- Empirical Formula: C2H5NO
- Molecular Weight: 59.07
- MDL number: MFCD00008023
- EINECS: 200-473-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
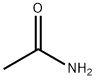
What is Acetamide?
Description
Acetamide (MEA or ethanamide), the amide of acetic acid, is a white crystalline solid in pure form with a mousy odor. Low toxicity. It is produced by dehydrating ammonium acetate. Acetamide is found in red beetroot.
Acetamide is used primarily as a solvent, plasticizer, and a wetting and penetrating agent. it was used as an intermediate in the synthesis of methylamine, thioacetamide, hypnotics, insecticides, medicinals and various plastics, a soldering flux ingredient, a wetting agent and penetration accelerator for dyes, and as a plasticizer in leather, cloth and coatings.
ethanolamine is an amide made from acetamide and monoethanolamine. It is a clear liquid. In cosmetics and personal care products, It is used in the formulation of bubble baths, hair conditioners, shampoos, wave sets, moisturizers, and other bath and hair care products.It increases the water content of the top layers of the skin by drawing moisture from the surrounding air. It also enhances the appearance and feel of hair, by increasing hair body, suppleness, or sheen, or by improving the texture of hair that has been damaged physically or by chemical treatment.
Chemical properties
Acetamide occurs as hexagonal colourless deliquescent crystals with a musty odour. It is incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidising agents, strong bases, and triboluminescent materials. Acetamide is used primarily as a solvent, a plasticiser, and a wetting and penetrating agent. Workplace exposures to acetamide are associated with the plastic and chemical industries.
Chemical properties
Acetamide is a colorless to yellow, deliquescent, crystalline solid. Odorless if pure, “mousy” odor if impure. Odor threshold5140 160 milligram per cubic meter.
The Uses of Acetamide
As a dipolar solvent, acetamide finds many uses as a solvent for both inorganic and organic compounds. The solvency has led to widespread uses in industry including applications in cryoscopy, soldering, and the textile industry. The neutral and amphoteric characteristics allow its use as an antacid in the lacquer, explosives, and cosmetics industries. Its hygroscopic properties make it useful as a plasticizer in coatings, fixtures, cloth, and leather, and as a humectant for paper. It is also a raw material in organic synthesis of methylamine and thioacetamide and as an intermediate in preparation of medicines, insecticides, and plastics.
The Uses of Acetamide
- Acetamide is often used as plasticizer and as industrial solvent.
- molten acetamide is an excellent solvent for many organic and inorganic compounds.
- Solubilizer.
- renders sparingly soluble substances more soluble in water by mere addition or by fusion.
- stabilizer.
- manufacture of methylamine, denaturing alcohol.
- In organic syntheses.
- Acetamide is used as a co-monomer in the production of polymeric materials such as polyvinyl acetamide, a polymeric product used as an absorbent.
- It can be used for the transamidation of carbxamides in 1,4-dioxane in the absence of a catalyst.
The Uses of Acetamide
Cryoscopy; organic synthesis; general solvent; lacquers; explosives, soldering flux; wetting agent; plasticizer
Definition
ChEBI: Acetamide is a member of the class of acetamides that results from the formal condensation of acetic acid with ammonia. It is a monocarboxylic acid amide, a N-acylammonia and a member of acetamides. It is a tautomer of an acetimidic acid.
General Description
Colorless crystals with a mousy odor (NTP, 1999). Low toxicity.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Very soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Acetamide may react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. May form flammable gases with strong reducing agents. Reacts as a weak bases (weaker than water). Mixing with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates acetonitrile Burns to give toxic mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Health Hazard
After oral exposures to acetamide, animals developed liver tumors. However, no informa- tion is available on the carcinogenic effects of acetamide in humans. The US EPA has not classifi ed acetamide for carcinogenicity. The IARC has classifi ed acetamide as a Group 2B, meaning a possible human carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Mild irritant; acute oral toxicity in animals very low; oral LD50 value (rats):7000 mg/kg; carcinogenic to animals; oraladministration caused blood and liver tumorsin mice and rats; carcinogenicity: animal limited evidence, no evidence in humans.
Fire Hazard
The flash point of Acetamide has not been determined, but Acetamide is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Suspected carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and neoplastigenic data. Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal and possibly other routes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. See also AMIDES. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx,.
Potential Exposure
Used as a stabilizer, plasticizer, wetting agent; solvent in plastics, lacquers, explosive; soldering flux ingredient; and chemical manufacturing
Carcinogenicity
The IARC has determined that there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity for acetamide in experimental animals and that it is possibly carcinogenic to humans.
Environmental Fate
The mechanism of toxicity of acetamide is not known; the response profile is quite different from the better studied dimethyl derivative. Acetamide appears to be in a class of chemicals which, although producing liver cancer in rodents, is less sensitive to inactive in genetic tests looking at formation of micronuclei. The carcinogenic response in rodents appears related to the formation of hydroxylamine from the primary metabolite acetohydroxamic acid.
Storage
Acetamide should be kept stored in a tightly closed container, in a cool, dry, ventilated area. It should be protected against physical damage, away from any source of heat, ignition, or oxidizing materials.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
Acetamide is crystallised by dissolving in hot MeOH (0.8mL/g), diluting with Et2O and allowing to stand [Wagner J Chem Edu 7 1135 1930]. Alternate crystallisation solvents are acetone, *benzene, chloroform, dioxane, methyl acetate or *benzene/ethyl acetate mixtures (3:1 and 1:1). It has also been recrystallised from hot water after treating with HCl-washed activated charcoal (which had been repeatedly washed with water until free from chloride ions), then crystallised again from hot 50% aqueous EtOH and finally twice from hot 95% EtOH [Christoffers & Kegeles J Am Chem Soc 85 2562 1963]. Finally it is dried in a vacuum desiccator over P2O5. Acetamide is also purified by distillation (b 221-223o) or by sublimation in vacuo. It has also been purified by two recrystallisations from cyclohexane containing 5% (v/v) of *benzene. Needle-like crystals separate and are filtered, washed with a small volume of distilled H2O and dried with a flow of dry N2. [Slebocka-Tilk et al. J Am Chem Soc 109 4620 1987, Beilstein 2 H 175, 2 I 80, 2 II 177, 2 III 384, 2 IV 399.]
Toxicity evaluation
Acetamide will exist as a vapor in the ambient atmosphere. Atmospheric degradation occurs by reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals. The half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 7.6 days. If released to soil, acetamide is expected to have very high mobility and is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment. Experiments suggest that this chemical may break down in the environment through biodegradation and not through hydrolysis. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based on this compound’s estimated Henry’s law constant.
Incompatibilities
Reacts with strong acids, such as hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric, strong oxidizers; strong bases; strong reducing agents such as hydrides; ammoniaisocyanates, phenols, cresols. Contact with water causes slow hydrolyzation to ammonia and acetate salts.
Waste Disposal
Add to alcohol or benzene as a flammable solvent and incinerate; oxides of nitrogen produced may be scrubbed out with alkaline solution. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Precautions
During handling and/use of acetamide, workers should wear special protective equipment. After leaving work areas, workers should wash hands, face, forearms, and neck, dispose of outer clothing, and change to clean garments at the end of the day.
Properties of Acetamide
| Melting point: | 78-80 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 221 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.159 |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 65 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4274 |
| Flash point: | 220-222°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.5 g/mL, Hazen ≤50 |
| form | Crystals |
| pka | 0.63(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Odor | Mousy odor |
| Water Solubility | 2000 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,43 |
| JECFA Number | 1592 |
| BRN | 1071207 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 ppm |
| Dielectric constant | 41.0(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. Deliquescent. Triboluminescent. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 60-35-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 7, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetamide(60-35-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetamide (60-35-5) |
Safety information for Acetamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Acetamide
| InChIKey | DLFVBJFMPXGRIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Acetamide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 60 - 35 - 5 Acetamide 98%View Details
60 - 35 - 5 Acetamide 98%View Details
60 - 35 - 5 -
 Acetamide (SQ) CAS 60-35-5View Details
Acetamide (SQ) CAS 60-35-5View Details
60-35-5 -
 Acetamide CASView Details
Acetamide CASView Details -
 Acetamide pure CAS 60-35-5View Details
Acetamide pure CAS 60-35-5View Details
60-35-5 -
 Acetamide 98% CAS 60-35-5View Details
Acetamide 98% CAS 60-35-5View Details
60-35-5 -
 Acetamide CAS No. 60-35-5, Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25/50kgView Details
Acetamide CAS No. 60-35-5, Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25/50kgView Details
60-35-5 -
 Acetamide, Purity: PowderView Details
Acetamide, Purity: PowderView Details
60-35-5 -
 Acetamide (For Synthesis)View Details
Acetamide (For Synthesis)View Details
60-35-5
