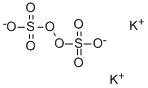
Potassium chromate
Synonym(s):Chromate standard for aqueous matrices ready foruse, Nota 1 A;chromic acid potassium salt;Potassium chromate
- CAS NO.:7789-00-6
- Empirical Formula: CrK2O4
- Molecular Weight: 194.1903
- MDL number: MFCD00011368
- EINECS: 232-140-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
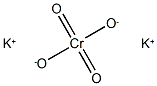
What is Potassium chromate ?
Chemical properties
lemon-yellow crystals
Chemical properties
Potassium chromate(VI) is a yellow crystalline solid.
The Uses of Potassium chromate
Potassium chromate (K2CrO4) is soluble in water and is used to make bright yellow inks and paint pigments. It is also used as a reagent in chemical laboratories and as a mordant to “fix” dyes in colored textiles.
The Uses of Potassium chromate
It is used as an oxidizing agent.
The Uses of Potassium chromate
Has a limited application in enamels, finishing leather, rustproofing of metals, being replaced by the sodium salt; as reagent in analytical chemistry.
What are the applications of Application
Potassium chromate is a chemical reagent used as a yellow indicator and oxidizing agent
Definition
ChEBI: A potassium salt consisting of potassium and chromate ions in a 2:1 ratio.
Definition
A salt containing the ionCrO42-.
Definition
potassium chromate: A bright yellowcrystalline solid, K2CrO4, solublein water and insoluble in alcohol;rhombic; r.d. 2.73; m.p. 968.3°C; decomposes without boiling. It is producedindustrially by roasting powderedchromite ore with potassiumhydroxide and limestone and leachingthe resulting cinder with hotpotassium sulphate solution. Potassiumchromate is used in leatherfinishing, as a textile mordant, and inenamels and pigments. In the laboratoryit is used as an analyticalreagent and as an indicator. Likeother chromium(III) compounds it istoxic when ingested or inhaled.
General Description
Potassium chromate is a yellow crystalline solid. Potassium chromate is soluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Potassium chromate is used in chemical analysis, in making pigments for paints and inks, as a fungicide, and to make other chromium compounds.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Oxidizing agents, such as Potassium chromate , can react with reducing agents to generate heat and products that may be gaseous (causing pressurization of closed containers). The products may themselves be capable of further reactions (such as combustion in the air). The chemical reduction of materials in this group can be rapid or even explosive, but often requires initiation (heat, spark, catalyst, addition of a solvent). Explosive mixtures of inorganic oxidizing agents with reducing agents often persist unchanged for long periods if initiation is prevented. Such systems are typically mixtures of solids, but may involve any combination of physical states. Some inorganic oxidizing agents are salts of metals that are soluble in water; dissolution dilutes but does not nullify the oxidizing power of such materials. Organic compounds, in general, have some reducing power and can in principle react with compounds in this class. Actual reactivity varies greatly with the identity of the organic compound. Inorganic oxidizing agents can react violently with active metals, cyanides, esters, and thiocyanates.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes local irritation of mucous membranes; continuing nose irritation can result in perforation of nasal septum. Ingestion may cause violent gastroenteritis, circulatory collapse, vertigo, coma, and toxic nephritis; ingestion of excessive quantities can be fatal. Contact with eyes causes severe irritation and conjunctivitis. Repeated or prolonged exposure to dust, mist, or solutions may cause dermatitis; contact with breaks in the skin may cause ``chrome sores'' appearing as slow-healing, hard-rimmed ulcers which leave the area vulnerable to infection.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: May increase intensity of fire if in contact with combustible materials. Cool containers and spilled material with plenty of water.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Poison by ingestion, intravenous, subcutaneous, and intramuscular routes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. A powerful oxidizer. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of K2O. Used as a mordant for wool, in the oxidizing and treatment of dyes on materials. See also CHROMIUM COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Potassium chromate is used in printing: photomechanical processing; chrome-pigment production; and wool preservative methods; to make dyes, pigments, inks and enamels; as an oxidizing agent; analytical reagent; in electroplating; explosives.
Shipping
UN1479 Oxidizing solid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer, Technical Name Required. UN3288 Toxic solids, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from conductivity water (0.6g/mL at 20o), and dry it between 135o and 170o.
Incompatibilities
A powerful oxidizer. Violent reactions with combustibles, organics, powdered metals; or easily oxidizable substances. Contact with hydroxylamine, hydrazine causes explosion.
Properties of Potassium chromate
| Melting point: | 971 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor density | 6.7 (vs air) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | Solid |
| color | Yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 2.732 |
| PH | 9.0-9.8 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 640 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,7622 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.0002 mg/m3; STEL 0.0005 mg/m3 (Skin) OSHA: Ceiling 0.1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 15 mg/m3; TWA 0.0002 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Strong oxidizing agent - contact with combustible materials may lead to fire or violent reaction. Incompatible with strong reducing agents, combustible materials. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7789-00-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium chromate(VI) (7789-00-6) |
Safety information for Potassium chromate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Potassium chromate
| InChIKey | XMXNVYPJWBTAHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Potassium chromate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Zama Chemical
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Potassium chromate, For analysis ACS CAS 7789-00-6View Details
Potassium chromate, For analysis ACS CAS 7789-00-6View Details
7789-00-6 -
 Potassium chromate, For analysis ACS CAS 7789-00-6View Details
Potassium chromate, For analysis ACS CAS 7789-00-6View Details
7789-00-6 -
 Potassium Chromate pure CAS 7789-00-6View Details
Potassium Chromate pure CAS 7789-00-6View Details
7789-00-6 -
 potassium chromate CASView Details
potassium chromate CASView Details -
 Chromate standard solution CASView Details
Chromate standard solution CASView Details -
 Potassium Chromate, 99%, 50Kg DrumView Details
Potassium Chromate, 99%, 50Kg DrumView Details
7789-00-6 -
 POTASSIUM CHROMATE 99.5% AR 1 KGView Details
POTASSIUM CHROMATE 99.5% AR 1 KGView Details
7789-00-6 -
 Potassium Chromate, 98%, 25Kg bagView Details
Potassium Chromate, 98%, 25Kg bagView Details
7789-00-6
