Potassium bicarbonate
Synonym(s):Potassium bicarbonate;Potassium hydrogen carbonate
- CAS NO.:298-14-6
- Empirical Formula: CHKO3
- Molecular Weight: 100.12
- MDL number: MFCD00011402
- EINECS: 206-059-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:38
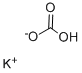
What is Potassium bicarbonate?
Absorption
Potassium bicarbonate intake is done mainly in the small intestine in which approximately 90% of the potassium will be absorbed by passive diffusion.
Toxicity
Potassium bicarbonate does not contain any toxic chemicals and it is not listed as a carcinogenic or a potential carcinogen. Potassium bicarbonate is also considered safe in pregnancy as the current data do not suggest a teratogenic potential or any developmental toxicity.
Chemical properties
Potassium bicarbonate occurs as colorless, transparent crystals or as a white granular or crystalline powder. It is odorless, with a saline or weakly alkaline taste.
The Uses of Potassium bicarbonate
Potassium Bicarbonate is an alkali and leavening agent obtained as colorless prisms or white powder. it is very soluble, with 1 g dis- solving in 2.8 ml of water. upon heating, it liberates carbon dioxide which provides leavening in baked goods. it is also used in confec- tionary products.
The Uses of Potassium bicarbonate
Used as a buffer.
The Uses of Potassium bicarbonate
In baking powders, effervescent salts.
Indications
Potassium bicarbonate is used as an antacid, electrolyte replenisher and potassium supplement. It can also be used as an excipient in drug formulations. An antacid is a medication used to neutralize gastric acid in a short timeframe after ingestion and the effect is soon overcome by meal-stimulated acid secretion.
Background
Potassium bicarbonate is a white, crystalline, slightly alkaline and salty substance. It is produced by the passage of carbon dioxide through an aqueous potassium carbonate solution. It is used in medicine as an antacid. It is registered in the FDA under the section of suitable, safe and effective ingredients for OTC antacids. This FDA denomination classifies potassium bicarbonate as a GRAS ingredient.
What are the applications of Application
Potassium bicarbonate is a catalyst in synthetic fiber polymerization and olefin dehydrogenation
Definition
ChEBI: A potassium salt that is the monopotassium salt of carbonic acid. It has fungicidal properties and is used in organic farming for the control of powdery mildew and apple scab.
Production Methods
Potassium bicarbonate can be made by passing carbon dioxide into
a concentrated solution of potassium carbonate, or by exposing
moist potassium carbonate to carbon dioxide, preferably under
moderate pressure.
Potassium bicarbonate also occurs naturally in the mineral
calcinite.
General Description
Potassium bicarbonate is water soluble alkaline potassium salt with monoclinic crystalline structure. It is a raw material for the synthesis of many potassium compounds. It is a better coolant than sodium bicarbonate in the aerosol fire extinguishing apparatus. It shows potential as an antifungal agent.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Agricultural Uses
Potassium bicarbonate (KHCO3), also called potassium
hydrogen carbonate, is a white crystalline solid, soluble
in water (insoluble in ethanol). It decomposes at about
120°C. Potassium bicarbonate contains about 28%
potassium (K2O) and used as a potassium supplying
fertilizer.
Potassium bicarbonate, which occurs naturally as
calcinite, is made by passing carbon dioxide into
saturated potassium carbonate solution. It is used as
baking powder and as a fire extinguisher.
Pharmaceutical Applications
As an excipient, potassium bicarbonate is generally used in
formulations as a source of carbon dioxide in effervescent
preparations, at concentrations of 25–50% w/w. It is of particular
use in formulations where sodium bicarbonate is unsuitable, for
example, when the presence of sodium ions in a formulation needs
to be limited or is undesirable. Potassium bicarbonate is often
formulated with citric acid or tartaric acid in effervescent tablets or
granules; on contact with water, carbon dioxide is released through
chemical reaction, and the product disintegrates. On occasion, the
presence of potassium bicarbonate alone may be sufficient in tablet formulations, as reaction with gastric acid can be sufficient to cause
effervescence and product disintegration.
Potassium bicarbonate has also been investigated as a gasforming
agent in alginate raft systems.The effects of potassium
bicarbonate on the stability and dissolution of paracetamol and
ibuprofen have been described.
Potassium bicarbonate is also used in food applications as an
alkali and a leavening agent, and is a component of baking powder.
Therapeutically, potassium bicarbonate is used as an alternative
to sodium bicarbonate in the treatment of certain types of metabolic
acidosis. It is also used as an antacid to neutralize acid secretions in
the gastrointestinal tract and as a potassium supplement.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Alkali metal carbonates and bicarbonates have wide-ranging pharmaceutical applications. Potassium bicarbonate or citrate is used in over-the-counter drugs as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) against urinary-tract infections (increasing the pH of the urine) in the United Kingdom.
Oralbicarbonate solutions such as potassium bicarbonate are typically given orally for chronic acidosis states low pH of the blood plasma. This can be again due to impaired kidney function. The use of potassium bicarbonate for the treatment of acidosis has to be carefully evaluated, as even small changes of the potassium plasma levels can have severe consequences.
Pharmacokinetics
Potassium is the principal intracellular cation in most body tissues. The concentration of potassium ions is essential to conduct nerve impulses in specialized tissues like brain, heart and skeletal muscle, as well as to maintain normal renal function, acid-base balance, and cellular metabolic functions. The use of compounds containing bicarbonate is showed to produce the release of CO2. This effect has been one of the problems of the use of potassium bicarbonate as it can cause eructation.
Safety
Potassium bicarbonate is used in cosmetics, foods, and oral pharmaceutical formulations, where it is generally regarded as a relatively nontoxic and nonirritant material when used as an excipient. However, excessive consumption of potassium bicarbonate or other potassium salts may produce toxic manifestations of hyperkalemia.
Metabolism
Not Available
Storage
Potassium bicarbonate should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry location. Potassium bicarbonate is stable in air at normal temperatures, but when heated to 100–200°C in the dry state, or in solution, it is gradually converted to potassium carbonate.
Purification Methods
It is crystallised from water at 65-70o (1.25mL/g) by filtering and then cooling to 15o (~0.4ml/g). During all operations, CO2 is passed through the stirred mixture. The crystals are sucked dry at the pump, washed with distilled water, dried in air and then over H2SO4 in an atmosphere of CO2. It is much less soluble than the carbonate in H2O (see below).
Incompatibilities
Potassium bicarbonate reacts with acids and acidic salts with the evolution of carbon dioxide.
Regulatory Status
E501 refers to potassium carbonates). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK and USA (chewable tablets; effervescent granules; effervescent tablets; lozenges; oral granules; oral suspensions; powder for oral solutions). Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Potassium bicarbonate
| Melting point: | 292 °C |
| Density | 2,17 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | fine crystals |
| pka | 10.33(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 2.17 |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 8.27(1 mM solution);8.25(10 mM solution);8.13(100 mM solution); |
| PH Range | 8 - 9 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. Insoluble in alcohol. |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.010 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,7609 |
| BRN | 4535309 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 298-14-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium bicarbonate (298-14-6) |
Safety information for Potassium bicarbonate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Potassium bicarbonate
| InChIKey | TYJJADVDDVDEDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Potassium bicarbonate manufacturer
Aashi Chem
Buradon Inc.
Canton Laboratories Private Limited
Techno Pharmchem
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Potassium Bi Carbonate 98%View Details
Potassium Bi Carbonate 98%View Details -
 Potassium Bicarbonate 98%View Details
Potassium Bicarbonate 98%View Details -
 Potassium hydrogen carbonate 98%View Details
Potassium hydrogen carbonate 98%View Details -
 Potassium hydrogen carbonate, Dried basis CAS 298-14-6View Details
Potassium hydrogen carbonate, Dried basis CAS 298-14-6View Details
298-14-6 -
 Potassium hydrogen carbonate, Dried basis CAS 298-14-6View Details
Potassium hydrogen carbonate, Dried basis CAS 298-14-6View Details
298-14-6 -
 Potassium Bicarbonate CASView Details
Potassium Bicarbonate CASView Details -
 Potassium Bicarbonate PowderView Details
Potassium Bicarbonate PowderView Details
298-14-6 -
 White Potassium Bicarbonate, Canton Laboratory, 50 KgView Details
White Potassium Bicarbonate, Canton Laboratory, 50 KgView Details
298-14-6
