Pirimicarb
Synonym(s):2-Dimethylamino-5,6-dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl dimethylcarbamate
- CAS NO.:23103-98-2
- Empirical Formula: C11H18N4O2
- Molecular Weight: 238.29
- MDL number: MFCD00055520
- EINECS: 245-430-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
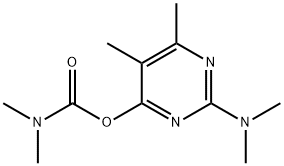
What is Pirimicarb?
Description
Pirimicarb is a colorless solid that is
moderately soluble in water, acetone, ethanol, xylene, and
chloroform.
Pirimicarb is produced by reaction of 2-dimethylamino-
5,6-dimethyl-4-pyrimidone with dimethylcarbamic acid
chloride in the presence of a base or phosgene and dimethylamine.
Pirimicarb is a systemic, selective aphicide used
largely on grain crops, but also on ornamentals, cotton,
fruit, and in greenhouses.
Chemical properties
Colorless crystalline solid. Odorless. Commercial product may be available as a liquid
The Uses of Pirimicarb
Pirimicarb is a systemic insecticide with contact, stomach and respiratory action. It is a selective aphicide used in cereals, fruit, ornamentals, strawberries, potatoes, sugar beet, fodder beet, cotton, oilseed rape, tobacco and glasshouse crops.
The Uses of Pirimicarb
Insecticide.
Definition
ChEBI: An aminopyrimidine that is N,N,4,5-tetramethylpyrimidin-2-amine substituted by a (dimethylcarbamoyl)oxy group at position 4.
Health Hazard
Highly toxic insecticide by oral and possibly other routes of entry; cholinesteraseinhibitor; median oral lethal doses in experimental animals ranged at 100–150 mg/kg;toxic symptoms include excessive salivation,lacrimation, slow heartbeat, blurred vision,headache, muscle twitching, tremor and convulsion; gastrointestinal effects include vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea;severe poisoning can progress to death.
LD50 oral (rat): ~50 mg/kg
LD50 oral (dog): 100 mg/kg.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide: Originally registered in the U.S. for non-food use on alfalfa grown for seed in selected. Elsewhere it is used on a wide range of cereals, potatoes, fruits, vegetables and other crop.
Trade name
ABOL®; AFICIDA®; APHOX®; FERNOS®; PIRIMIKARB; PIRIMOR®; PP 062®; PYRIMOR®; RAPID®
Potential Exposure
Primicarb is a carbamate (N-methyl) insecticide. Originally registered in the United States for non-food use on alfalfa grown for seed in selected. Elsewhere it is used on a wide range of cereals, potatoes, fruits, vegetables and other crop
Metabolic pathway
The influence on the qualitative photochemical behavior of pirimicarb which leads to the photoproducts N-formylpirimicarb and demethylpirimicarb is modified by the waxes that are extracted from nectarines, oranges, and mandarin oranges. The formation of the photoproducts is hindered by the waxes.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Pirimicarb is hydrolysed in alkaline solutions (PM). Sterilised buffer solutions
of unlabelled pirimicarb at pH values of 4,7 and 9 were incubated in
the dark at 50 °C for 5 days. Samples were taken and analysed by HPLC.
No hydrolysis of pirirnicarb was detected. At longer incubation times,
some of the N-formyl derivative (2) (see Scheme 1) was produced (PSD,
1995). [14C-pyrimidinyl]Pirimicarb was dissolved in buffer solutions of pH
5,7 or 9 and exposed to natural sunlight (August in southern England) for
up to 27 days. Losses of radioactivity by volatilisation were insignificant.
After 3 weeks virtually all the pirimicarb was degraded. In neutral and
acid solutions the main product was the N-formyl derivative (2). At pH 9
this was unstable. The N-monodemethylpirimicarb (3), aminopirimicarb
(4) and the pyrimidinol(5) were also identified and some polar products
were formed.
A further study under similar conditions (August 1974) afforded
compounds 14 and the pyrimidinol derivatives (5, 6, 7). N,N-Dimethylguanidine
(8), N-methylguanidine (9) and guanidine (10) were
identified by electrophoretic methods. The guanidines were formed by
opening of the pyrimidine ring (PSD, 1995). These pathways are illustrated
in Scheme 1.
In other studies in which aqueous solutions or solid samples of pirimicarb
were exposed to sunlight or lamps in the laboratory, the products 2,
3, 4 and 5 were also found, the first usually being the major product.
Pirisi ef al. (1996) also detected a formylaminodimethylcarbamate (11)
whilst Romero et al. (1994) reported that the formaminopyrimidinol (12)
was formed via the N-formyl compound (2). [14C-pyrimidinyl]Pirimicarb
was applied to a silty-clay loam on a thin-layer plate coated with soil. The
plate was exposed under polythene to sunlight in southern England.
Pirimicarb was completely degraded over 20 days. The major degradation
product was the pyrimidinol (5) formed by hydrolysis of the carbamate
ester group. No volatile products were detected (Hill, 1976; PSD, 1995).
Incompatibilities
May react with strong oxidizers such as chlorates, peroxides, and nitrates. May form explosive materials with phosphorus pentachloride.
Waste Disposal
Do not discharge into drains or sewers. Dispose of waste material as hazardous waste using a licensed disposal contractor to an approved landfill. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Incineration with effluent gas scrubbing is recommended. Containers must be disposed of properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Pirimicarb
| Melting point: | 90.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 380.88°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1387 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 2.1 x 10-3 Pa (30 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6081 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | >100 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | Acetone (Slightly), Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 4.34 (weak base) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 3060 mg l-1 |
| Merck | 13,7579 |
| BRN | 663442 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 23103-98-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Pirimicarb(23103-98-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pirimicarb (23103-98-2) |
Safety information for Pirimicarb
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H351:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Pirimicarb
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Pirimicarb CAS 23103-98-2View Details
Pirimicarb CAS 23103-98-2View Details
23103-98-2 -
 Pirimicarb CAS 23103-98-2View Details
Pirimicarb CAS 23103-98-2View Details
23103-98-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1