Dithiooxamide
Synonym(s):Dithiooxalic diamide;Dithiooxamide, Rubean-hydrogen, Ethanedithioamide;Rubeanic acid
- CAS NO.:79-40-3
- Empirical Formula: C2H4N2S2
- Molecular Weight: 120.2
- MDL number: MFCD00004941
- EINECS: 201-203-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
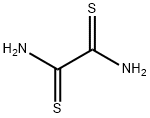
What is Dithiooxamide?
Description
Dithiooxamide, originally known as rubeanic acid, is a deep red crystalline solid with a decomposition temperature of ≈200 oC. It is a chelating agent for the detecting determining copper, cobalt, and nickel. It is also used to stabilize ascorbic acid in acidic solutions.
In early 2015, H. Firouzabadi, N. Iranpoor, and co-workers at Shiraz University (Iran) discovered that dithiooxamide can be used as a thiolating agent. Because it is stable, odorless, and commercially available, it is an excellent alternative to thiol reagents, which are foul-smelling and often require harsh reaction conditions. It reacts with alkyl or benzyl halides in base at 35 oC to form sulfides. With aryl halides, the reaction is run at 120 oC with a catalyst
Chemical properties
orange to brown crystalline powder
The Uses of Dithiooxamide
Dithiooxamide acts as a chelating agent and used in the determination of copper(II), nickel(II) and cobalt(II). It is used as a building block in the synthesis of cyclen. It is involved in the preparation of thiazolothiazole-linked porous organic polymers and N,N'-disubstituted dithiooxamides. It is also employed as a modifier to prepare the modified glassy carbon electrode which is used to investigate the electrochemical properties of quercetin, an important flavonoid derivative. Further, it is involved in the preparation of chelating resin with formaldehyde, which finds application in separation and concentration of silver ions.
The Uses of Dithiooxamide
As a reagent for copper, cobalt, and nickel. As a stabilizer of ascorbic acid solutions: Smoczkiewicz, Grochmalicka, Nature 192, 16 (1961).
The Uses of Dithiooxamide
Rubeanic acid may be used for the quantitative precipitation of copper, nickel
and cobalt. The copper complex is dark green, the cobalt brownish-red and the
nickel violet. All these complexes are chelates of outstanding stability, and this,
together with their vivid Colours, affords the reaction great analytical sensitivity.
The copper complex is the most stable of the three; it can be precipitated even
from mild mineral acidic solution, while precipitation of the corresponding cobalt
and nickel complexes requires buffered media. On the other hand, palladium,
platinum and silver react with rubeanic acid to give precipitates in strongly acidic
solution. It should be mentioned, however, that in the case of platinum and
some other metals (zinc, cadmium, silver, lead, mercury) the product is the corresponding
sulfide rather than the rubeanate complex.
Rubeanic acid reacts with ruthenium to give a blue water-soluble complex ion,
which is utilized for the spectrophotometric determination of ruthenium.
Rubeanic acid has similarly been used for the spectrophotometric determination
of osmium.
It has also proved suitable for the solvent extraction separation and determination
of thallium. It has been found that thallium exists in the organic phase
in the form of a complex of composition Tl/dto/Hdto, where dto represents the
rubeanate anion with one negative charge.
General Description
Dithiooxamide is reported to form complexes with Ni(II).
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx
Purification Methods
Crystallise dithiooxamide from EtOH and sublime it at high vacuum. [Beilstein 2 IV 1871.]
Properties of Dithiooxamide
| Melting point: | ≥300 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 287.76°C (estimate) |
| Density | 1.353 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5300 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble40mg/10 mL, clear, red |
| form | solid |
| pka | pK1:10.89 (25°C) |
| color | Orange to Amber to Dark red |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in alcohols. Slightly soluble in water. Insoluble in ether |
| Merck | 14,8279 |
| BRN | 605577 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 79-40-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethanedithioamide(79-40-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethanedithioamide (79-40-3) |
Safety information for Dithiooxamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Dithiooxamide
| InChIKey | OAEGRYMCJYIXQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Dithiooxamide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Dithiooxamide 79-40-3 99%View Details
Dithiooxamide 79-40-3 99%View Details
79-40-3 -
 79-40-3 Dithiooxamide 99%View Details
79-40-3 Dithiooxamide 99%View Details
79-40-3 -
 Dithiooxamide (Rubeanic Acid) extrapure AR CAS 79-40-3View Details
Dithiooxamide (Rubeanic Acid) extrapure AR CAS 79-40-3View Details
79-40-3 -
 Dithioxamide, GR 99%+ CAS 79-40-3View Details
Dithioxamide, GR 99%+ CAS 79-40-3View Details
79-40-3 -
 Rubeanic Acid CAS 79-40-3View Details
Rubeanic Acid CAS 79-40-3View Details
79-40-3 -
 DITHIOOXAMIDE AR CAS 79-40-3View Details
DITHIOOXAMIDE AR CAS 79-40-3View Details
79-40-3 -
 Dithiooxamide (Rubeanic Acid) AR CAS 79-40-3View Details
Dithiooxamide (Rubeanic Acid) AR CAS 79-40-3View Details
79-40-3 -
 Dithiooxamide CAS 79-40-3View Details
Dithiooxamide CAS 79-40-3View Details
79-40-3
