Linolenic acid
Synonym(s):α-Lnn;cis,cis,cis-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid;cis,cis,cis-9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid;gamma-Linolenic acid
- CAS NO.:463-40-1
- Empirical Formula: C18H30O2
- Molecular Weight: 278.43
- MDL number: MFCD00065720
- EINECS: 207-334-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
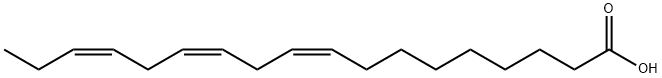
What is Linolenic acid?
Description
Linolenic acid (LA), also known as Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), is an omega-3 essential fatty acid with a wide range of biological activities such as cardiovascular protection, anticancer, neuroprotection, anti-osteoporosis, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant.LA is mainly sourced from plants, such as nuts and seeds, and is used for the endogenous synthesis of LC omega-6 fatty acids. It is used medicinally as a nutritional supplement and to treat dietary deficiencies or imbalances.
Chemical properties
clear light yellow to yellow liquid
Occurrence
linolenic acid occurs as the glyceride in many seed fats. It is an essential fatty acid in the diet.
The Uses of Linolenic acid
linolenic acid is also known as alpha-linolenic acid; omega-3. An essential fatty acid found in most drying oils. It is slightly irritating to the mucous membranes. It may be used in a cosmetic preparation for any of the following broad uses: anti-static, cleansing, emollient, skin-conditioning, and surfactant properties.
The Uses of Linolenic acid
An essential fatty acid. Occurs as the glyceride in most drying oils. Nutrient.
The Uses of Linolenic acid
Linolenic acid has been used:
- to assess the total antioxidative activity of serum and bacteria
- in palleroni chamber assay
- to prepare free fatty acid mixture
Background
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is a polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acid. It is a component of many common vegetable oils and is important to human nutrition.
Indications
For nutritional supplementation and for treating dietary shortage or imbalance.
What are the applications of Application
α-Linolenic Acid is a polyunsaturated essential fatty acid
Definition
ChEBI: Alpha-linolenic acid is a linolenic acid with cis-double bonds at positions 9, 12 and 15. Shown to have an antithrombotic effect. It has a role as a micronutrient, a nutraceutical and a mouse metabolite. It is an omega-3 fatty acid and a linolenic acid. It is a conjugate acid of an alpha-linolenate and a (9Z,12Z,15Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoate.
Definition
linolenic acid: A liquid polyunsaturatedfatty acid with three doublebonds in its structure:CH3CH2CH:CHCH2CH:CHCH2CH:CH-(CH2)7COOH. It occurs in certainplant oils, e.g. linseed and soya-beanoil, and in algae. It is one of the essentialfatty acids.
Benefits
Linolenic acid (LA) is an essential fatty acid with anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-atherosclerotic and anti-cancer activities, and has a variety of health benefits, including: lowering high blood pressure and cholesterol, lowering the risk of heart disease, maintaining the membrane fluidity of the epidermal transdermal water barrier, improving the barrier function of the skin, decreasing inflammation, regulating sebum secretion, moisturising the scalp, promoting hair growth and prevents hair breakage. It also has a whitening effect on over-pigmented skin.
General Description
Linolenic acid is a clear colorless liquid. (NTP, 1992)
Air & Water Reactions
Oxidizes in air to form peroxides, which spontaneously ignite. Insoluble in water. Sensitive to heat and moisture.
Reactivity Profile
Linolenic acid is incompatible with bases, oxidizing agents and reducing agents. Also incompatible with peroxides, oxygen and water.
Fire Hazard
Linolenic acid is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
An ω-3 fatty acid that serves as a precursor to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) but not docosahexaenoic acid. Conversion is greater in women than men, and conversely, β-oxidation metabolism is greater in men than women.
Pharmacokinetics
Alpha Linolenic Acid (ALA) is an 18-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid with three double bonds. It is also called an omega-3 fatty acid, and is essential for all mammals. Alpha-linolenic acid (or omega 3 fatty acid) intake can decrease the risk of cardiovascular diseases by 1) preventing arrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac death, 2) decreasing the risk of thrombosis (blood clot formation) that can lead to heart attack or stroke, 3) decreasing serum triglyceride levels, 4) slowing the growth of atherosclerotic plaque, 5) improving vascular endothelial function, 6) lowering blood pressure slightly, and 7) decreasing inflammation. ALA deficiencies can lead to visual problems and sensory neuropathy. Scaly and hemorrhagic skin or scalp inflammations may also develop.
Carcinogenicity
Narisawa et al. found that diets high in perilla oil (with high a-linolenic acid but also high levels of linoleic acid) lowered the risk of colon cancer in a rat model initiated with the carcinogen N-methyl-Nnitrosourea. Okuno found a suppressive effect on diethylnitrosamine- induced heptaocarcinogenesis in male Fischer 344 rats treated with either safflower (high in linoleic acid) or perilla oil (high in both linoleic and α-linolenic acids). Kitano et al. found that 10% α-linolenic acid did not promote urninary bladder cancer initiated in rats with N-butyl-N-(4-hydrocybutyl)nitrosamine. Mice fed a-linolenic acid at 5–10% of the diet had increased mammary gland ductular cell proliferation.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Linolenic acid
| Melting point: | -11 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 230-232 °C1 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 0.914 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 3380 | 9,12-OCTADECADIENOIC ACID (48%) AND 9,12,15-OCTADECATRIENOIC ACID (52%) |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform, Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 4.78±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Clear colorless to light yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 0.91 |
| Odor | faint fatty |
| Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE |
| Merck | 14,5506 |
| BRN | 1727693 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 463-40-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid, (Z,Z,Z)-(463-40-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Linolenic acid (463-40-1) |
Safety information for Linolenic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. P403+P235:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. |
Computed Descriptors for Linolenic acid
| InChIKey | DTOSIQBPPRVQHS-PDBXOOCHSA-N |
Linolenic acid manufacturer
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Linolenic Acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
Linolenic Acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
463-40-1 -
 Linolenic acid 95.00% CAS 463-40-1View Details
Linolenic acid 95.00% CAS 463-40-1View Details
463-40-1 -
 Linolenic acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
Linolenic acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
463-40-1 -
 Linolenic acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
Linolenic acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
463-40-1 -
 alpha-Linolenic acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
alpha-Linolenic acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
463-40-1 -
 Linolenic acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
Linolenic acid CAS 463-40-1View Details
463-40-1 -
 Purity: 98% Powder Alpha-Linolenic AcidView Details
Purity: 98% Powder Alpha-Linolenic AcidView Details
463-40-1 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
