α-Lipoic Acid
Synonym(s):Thioctic acid;DL-Thioctic Acid;(±)-1,2-Dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid;6,8-Dithiooctanoic acid;DL -α-Lipoic acid
- CAS NO.:1077-28-7
- Empirical Formula: C8H14O2S2
- Molecular Weight: 206.33
- MDL number: MFCD00005474
- EINECS: 214-071-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:51
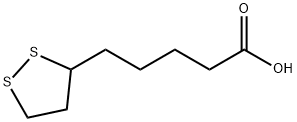
What is α-Lipoic Acid?
Description
DL-
Chemical properties
Light-Yellow Solid
Originator
Neurium,Hexal
The Uses of α-Lipoic Acid
(±)-α-Lipoic acid has been used in in vitro lipoylation studies and in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)-pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDHK) functional assay. It has also been used to investigate its antioxidative effect on developing cerebellum of rats exposed to arsenic during postnatal period.
The Uses of α-Lipoic Acid
A fat-metabolism stimulator
The Uses of α-Lipoic Acid
thioctic acid is also known as alpha lipoic acid. It is an anti-oxidant.
The Uses of α-Lipoic Acid
Lipoic acid [CAS: 1077-28-7] (6,8-dimercaptooctanoic acid), a lipophilic endogenous disulfide that can be reduced to the dithiol dihydrolipoic acid, protects against free-radical-mediated injury both in vivo and in vitro.
What are the applications of Application
α-Lipoic Acid is a metabolic antioxidant that regulates NF-κB signal transduction
Definition
ChEBI: Lipoic acid is a heterocyclic thia fatty acid comprising pentanoic acid with a 1,2-dithiolan-3-yl group at the 5-position. It has a role as a fundamental metabolite and a geroprotector. It is a member of dithiolanes, a heterocyclic fatty acid and a thia fatty acid. It is functionally related to an octanoic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a lipoate.
Manufacturing Process
To a suspension of 106 g of anhydrous aluminum chloride in 450 ml of
carbontetrachloride is added dropwise, with vigorous stirring, 70 g of ethyl 8-
chloroformylvalerate (H. Bergs, C. Wittfeld and H. Frank, Ber., 67B, 1622
(1947)). The temperature is maintained at 25°C. The cooling bath is removed
and ethylene is passed in for a period of 2 hours. The reaction mixture is
poured onto cracked ice, the organic layer separated, and the aqueous layer
extracted with 200 ml of chloroform. The combined organic extracts are dried
over anhydrous sodium sulfate and the solvent removed in vacuo. The dark
colored oil remaining, crude ethyl 8-chloro-6-oxooctanoate is distilled in vacuo
through a 6 in. Vigreaux column. After small forerun, the main fraction, 48-54
g (72-80%), B.P. 112-114°C (2 mm.); n25
D1-4485, is collected.
Redistilled thiolacetic acid (14.7 g) is cooled in an ice-bath and neutralized to
the phenolphthalein end-point with a 10% solution of potassium hydroxide in
ethanol (approximately 135 ml required). To this solution is added 29 g of
ethyl-6,8-dibromooctanoate and the mixture is stirred and heated under reflux
in an atmosphere of nitrogen for 5 hours. The reaction mixture, which
contains ethyl 6,8-diacetyl-mercaptooctanoate, is cooled and 35 g of
potassium hydroxide (85%) is added. The reaction mixture is stirred at room
temperature in an atmosphere of nitrogen for 17 hours, then acidified (pH less
than 1) with 6 N hydrochloric acid. Ethanol is removed in vacuo, sufficient
water is added to dissolve the inorganic solids and the mixture is extracted
with two 150 ml portions of chloroform. To the combined organic extracts,
which contain 6,8-dimercaptooctanoic acid , is added 575 ml of chloroform
and 210 ml of water. This mixture is stirred vigorously in an atmosphere of
nitrogen While sufficient iodoform reagent (R. L. Shriner and R. C. Fuson,
"Identification of Organic Compounds," 2nd. Ed., John Wiley and Sons, New
York, N.Y., 1940, p. 53) is added dropwise during a 6 hour period to give a
permanent brown color. Approximately 185 ml of iodoform reagent is
required. The organic layer is separated, washed with 500 ml of 1% sodium
thiosulfate solution, and then extracted with two 250 ml portions of 5%
sodium bicarbonate solution. The aqueous extracts are acidified (pH less than
1) with 6 N hydrochloric acid and extarcted with two 125 ml portions of
chloroform. The combined chloroform extracts are dried over anhydrous
sodium sulfate and the solvent is then removed in vacuo. The yellow viscous
oil remaining solidifies when cooled and scratched. This solid material is
extracted with three 300 ml portions of boiling Skelly B solvent (essentially nhexane).
The combined extracts are seeded with crystalline DL-α-lipoic acid
and allowed to stand at room temperature overnight and then in a refrigerator
for several hours. Large yellow crystals separate, M.P. 60.5-61.5°C. The yield
of product is 10.8-12.3 g (60-68%). 1,2-Dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid was
recrystallized from Skelly B solvent, M.P. 61-62°C.
brand name
Liposan;Thioactacid.
Therapeutic Function
Growth factor, Lipotropic, Detoxicant
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 79, p. 6483, 1957 DOI: 10.1021/ja01581a033
General Description
Oxidized form. Has antioxidant properties. Growth factor for many bacteria and protozoa.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmaceutical Applications
Lipoic acid(ALA), also known as α-lipoic acid (alpha-lipoic acid) or thioctic acid, has the formula C8H14S2O2 and
systematic name 5-(1,2-dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid. It contains a disulfide group, which can be transformed
in the body to a dithiol group.
ALA has been on the market since the 1950s as a dietary supplement. It is a natural antioxidant usually
made by the body. The advantage of ALA over other antioxidants such as vitamin C and E is that it is soluble
both in water and in fat. Researchers in the former Soviet Union found that ALA can chelate mercury
once it is transformed into the dithiol-containing compound. ALA can penetrate both the blood–brain barrier
and the cell membrane and therefore would be a very interesting chelating agent. Nevertheless, there is much
debate about its mode of action, side effects and effectiveness. Other antidotes, such as BAL and DMSA, are
more efficient in the removal of heavy metals. ALA has not received FDA approval as a chelating agent, but
it is still sold as a food supplement.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Antioxidant and coenzyme needed for the activity of enzyme complexes such as those of pyruvate dehydrogenase and glycine decarboxylase. Exogenous thioctic acid is reduced intracellularly by two or more enzymes. The reduced form then influences a number of cell processes by direct radical scavenging, recycling of other antioxidants, increasing glutathione synthesis, and modulating transcription factor activity particularly that of NF-κB. Decreases the phagocytosis of myelin by macrophages.
Biological Functions
Two forms of α-Lipoic Acid (ALA) are oxidized lipoic Acid (LA) and reduced dihydrolipoic Acid (DHLA). Both are capable of scavenging a variety of ROS. DHLA is a potent antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals. Furthermore, ALA simultaneously regenerates other antioxidant factors, such as vitamins C and E, increasing glutathione synthesis. ALA is generally involved in keto Acid oxidative decarboxylation processes and is a growth factor for some organisms. In the pathogenesis of inflammation, factor NF-kB modulates inflammatory cytokines, including interleukins (ILs) such as IL-1β and IL-6. ALA inhibits I Kappa B kinase, suppressing the activation of inflammatory cytokines.
Side Effects
Side effects are rare and may include insomnia, fatigue, diarrhea, and skin rash. α-Lipoic Acid can lower blood sugar levels, so people with diabetes or low blood sugar should take alpha-lipoic Acid only under the supervision of their healthcare provider.
Storage
Store at +4°C
Purification Methods
It forms yellow needles from cyclohexane or hexane and has been distilled at high vacuum; and sublimes at ~90o and very high vacuum. It is insoluble in H2O but dissolves in alkaline solution. [Lewis & Raphael J Chem Soc 4263 1962, Soper et al. J Am Chem Soc 76 4109, Reed & Niu J Am Chem Soc 77 416 1955, Tsuji et al. J Org Chem 43 3606 1978, Calvin Fed Proc USA 13 703 1954.] The S-benzylisothiuronium salt has m 153-154o (evacuated capillary, from MeOH), 132-134o, 135-137o (from EtOH). The dand lforms have m 45-47.5o and [] D 23 ±113o (c 1.88, *C6H6) and have UV in MeOH with max at 330nm ( 140). [Beilstein 19/7 V 237.] The reduced form, (±)-6,8-dimercaptooctanoic acid, [7516-48-5] M 208.3, is a light yellow liquid which is sold in sealed ampoules.
Properties of α-Lipoic Acid
| Melting point: | 60-62 °C |
| Boiling point: | 160-165 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.2888 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5200 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 160-165°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 50 mg/mL |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 4.75±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Yellow |
| Water Solubility | 0.9 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9326 |
| BRN | 81853 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1077-28-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Dl-thioctic acid(1077-28-7) |
Safety information for α-Lipoic Acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for α-Lipoic Acid
| InChIKey | AGBQKNBQESQNJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
α-Lipoic Acid manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 DL-6,8-Thioctic Acid extrapure (a-Lipoic Acid) CAS 1077-28-7View Details
DL-6,8-Thioctic Acid extrapure (a-Lipoic Acid) CAS 1077-28-7View Details
1077-28-7 -
 2-Thioctic acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
2-Thioctic acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
1077-28-7 -
 DL-α-Lipoic Acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
DL-α-Lipoic Acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
1077-28-7 -
 DL-6,8-Thioctic Acid (a-Lipoic Acid) CAS 1077-28-7View Details
DL-6,8-Thioctic Acid (a-Lipoic Acid) CAS 1077-28-7View Details
1077-28-7 -
 α-Lipoic Acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
α-Lipoic Acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
1077-28-7 -
 (±)-α-Lipoic acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
(±)-α-Lipoic acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
1077-28-7 -
 Alpha Lipoic Acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
Alpha Lipoic Acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
1077-28-7 -
 Alpha Lipoic Acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
Alpha Lipoic Acid CAS 1077-28-7View Details
1077-28-7
