Oxalic acid dihydrate
Synonym(s):Ethanedioic acid;Ethanedioic acid dihydrate;Ethanedioic Acid, Dihydrate, Ethanedioic Acid;Oxalic acid dihydrate;Oxalic Acid, Dihydrate
- CAS NO.:6153-56-6
- Empirical Formula: C2H6O6
- Molecular Weight: 126.07
- MDL number: MFCD00149102
- EINECS: 612-167-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-09 18:56:23
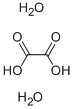
What is Oxalic acid dihydrate?
Chemical properties
Oxalic acid dihydrate is a crystalline granules or crystalline powder, soluble in water (143 mg/ml at 20° C), ethanol (400 mg/ml), ether (10 mg/ml), and glycerol. Insoluble in chloroform.
The Uses of Oxalic acid dihydrate
Oxalic acid dihydrate is a purifying agent in pharmaceutical industry, special in antibiotic medication, such as Oxytetracycline , Chloramphenicol , etc; * Precipitating agent in Rare-earth mineral processing; * Bleaching agent in the textile activities, wood pulp bleaching; * Rust-remover for Metal treatment; * Grinding agent, such as Marble polishing; * Waste water treatment, removing calcium from water.
The Uses of Oxalic acid dihydrate
Oxalic acid occurs in the cell sap of Oxalisand Rumex species of plants as the potassium and calcium salt. It is the metabolicproduct of many molds (Merck 1989). Thereare a large number of applications of thiscompound, including indigo dyeing; calicoprinting; removal of paint, rust, and inkstains; metal polishing; bleaching leather; inpesticide compositions and manufacture ofoxalates. It is also used as an analyticalreagent and as a reducing agent in organicsynthesis.
Addition of oxalic acid to chromic acid forthe anodizing of Al alloy has been reported tomodify the morphology and improve the corrosion performance of anodic films (Moutarlier et al. 2004). Also, it is a very effectiveadditive for the ozone treatment of cellulose.It prevents the degradation of cellulose fromozone bleaching.
Definition
Oxalic acid dihydrate (OAD) which has very high initial phase transition enthalpy is a promising phase change material (PCM). This compound is low manufacturing cost and wide usage. In OAD, alternating acid and water molecules that act both as hydrogen-bond donors and acceptors. OAD needs a lot of energy to break the hydrogen-bond in the melting process. Therefore, OAD has a very high heat of fusion of 370 J·g-1,which is a very promising PCM in TES for applications such as industrial waste heat recovery or solar energy storage systems[1].
General Description
Oxalic acid dihydrate (OAD) crystals are reported to be monoclinic with P21/n space group. The electron density of OAD has been obtained using X-ray diffraction studies under high resolution.
Reactivity Profile
At high temperatures oxalic acid decomposes, producing toxic carbon monoxide, andformic acid. Mixing with warm sulfuric acidmay produce the same products: CO2, CO,and formic acid. It reacts with many silvercompounds, forming explosive silver oxalate(NFPA 1986). An explosion occurred whenwater was added to an oxalic acid/sodiumchlorite mixture in a stainless steel beaker.There was also evolution of highly toxicchlorine dioxide gas (MCA 1962). Oxalicacid reacts violently with strong oxidizingsubstances.
Health Hazard
Oxalic acid is a strong poison. The toxicsymptoms from ingestion include vomiting, diarrhea, and severe gastrointestinaldisorder, renal damage, shock, convulsions,and coma. Death may result from cardiovascular collapse. The toxicity arises asoxalic acid reacts with calcium in the tissuesto form calcium oxalate, thereby upsettingthe calcium/potassium ratio (ACGIH 1986).Deposition of oxalates in the kidney tubulesmay result in kidney damage (Hodgson et al.1988).
Oxalic acid may be absorbed into the bodythrough skin contact. It is corrosive to theskin and eyes, producing burns. Dilute solutions of 10% strength may be a mild irritantto human skin. However, the inhalation toxicity is low because of its low vapor pressure.Airborne dusts can produce eyeburn and irritation of the respiratory tract.
LD50 value, oral (rats): 375 mg/kg.
Purification Methods
Crystallise oxalic acid from distilled water. Dry it in a vacuum over H2SO4. The anhydrous acid can be obtained by drying at 100o overnight. [Beilstein 2 IV 1819.]
Structure and conformation
The dihydrate H2C2O 4·2H2O has space group C52h–P21/n, with lattice parameters a = 611.9 pm, b = 360.7 pm, c = 1205.7 pm, β = 106°19′, Z = 2. The main inter-atomic distances are: C-C 153 pm, C-O1 129 pm, C-O2 119 pm. In theory, oxalic acid dihydrate is one of the very few crystalline substances that exhibit negative area compressibility. Namely, when subjected to isotropic tension stress (negative pressure), the a and c lattice parameters increase as the stress decreases from -1.17? to -0.12 GPa and from -1.17 to -0.51 GPa, respectively.
References
[1] Han, Lipeng , S. Xie , and J. Sun . "Preparation and thermal characterization of oxalic acid dihydrate/bentonite composite as shape-stabilized phase change materials for thermal energy storage." IUMRS International Conference in Asia 2017.
Properties of Oxalic acid dihydrate
| Melting point: | 104-106 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 108-109°C |
| Density | 1,65 g/cm3 |
| vapor density | 4.4 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.01 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| Flash point: | 157°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble1M at 20°C, clear, colorless |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| color | Yellow to yellow-green |
| Specific Gravity | 1.65 |
| PH | ~1.0 (25℃, 1M in H2O) |
| PH Range | 6 - 8 at 25 °C |
| Water Solubility | 138 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,6911 |
| Sublimation | 157 ºC |
| BRN | 3679436 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA for anhydrous acid 1 mg/m3
(ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); TLV-STEL
2 mg/m3 (ACGIH). |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with bases, acid chlorides, steel, silver, silver compounds, moisture. Avoid contact with metals. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 6153-56-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Oxalic acid dihydrate(6153-56-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Oxalic acid dihydrate (6153-56-6) |
Safety information for Oxalic acid dihydrate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Oxalic acid dihydrate
| InChIKey | GEVPUGOOGXGPIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Oxalic acid dihydrate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
ALS India Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
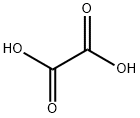
 Oxalic Acid 99.6 % 99%View Details
Oxalic Acid 99.6 % 99%View Details -
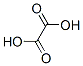
 Oxalic acid dihydrate 98%View Details
Oxalic acid dihydrate 98%View Details -
 Oxalic acid dihydrate CAS 6153-56-6View Details
Oxalic acid dihydrate CAS 6153-56-6View Details
6153-56-6 -
 Oxalic acid dihydrate CAS 6153-56-6View Details
Oxalic acid dihydrate CAS 6153-56-6View Details
6153-56-6 -
 Oxalic acid dihydrate CAS 6153-56-6View Details
Oxalic acid dihydrate CAS 6153-56-6View Details
6153-56-6 -
 Oxalic acid dihydrate CAS 6153-56-6View Details
Oxalic acid dihydrate CAS 6153-56-6View Details
6153-56-6 -
 Oxalic acid dihydrate, 98% 99%View Details
Oxalic acid dihydrate, 98% 99%View Details -
 Oxalic Acid Dihydrate extrapure AR CAS 6153-56-6View Details
Oxalic Acid Dihydrate extrapure AR CAS 6153-56-6View Details
6153-56-6
