Sodium oxalate
Synonym(s):di-Sodium oxalate;Ethanedioic acid sodium salt;Oxalic acid disodium salt;Oxalic acid sodium salt
- CAS NO.:62-76-0
- Empirical Formula: C2Na2O4
- Molecular Weight: 134
- MDL number: MFCD00012465
- EINECS: 200-550-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:52

What is Sodium oxalate?
Description
Sodium oxalate, or disodium oxalate, is the sodium salt of oxalic acid with the molecular formula Na2C2O4. It is usually a white, crystalline, odorless powder, that decomposes at 250–270 °C.
Disodium oxalate can act as a reducing agent, and it may be used as a primary standard for standardizing potassium permanganate (KMnO4) solutions.
The mineral form of sodium oxalate is natroxalate. It is only very rarely found and restricted to extremely sodic conditions of ultraalkaline pegmatites.
Chemical properties
White, crystalline powder. Soluble in water; insolu- ble in alcohol.
Physical properties
White crystalline powder; density 2.34 g/cm3; decomposes around 250° C; sparingly soluble in water, 3.7 g/100 mL at room temperature; moderately soluble in boiling water, about 6.25 g/100 mL; the aqueous solution is practically neutral; insoluble in alcohol.
The Uses of Sodium oxalate
Sodium Oxalate is obtained in such high purity and is so stable that it is used as a titrimetric standard.
The Uses of Sodium oxalate
Finishing textiles, tanning and finishing leather; for standardizing potassium permanganate solution.
The Uses of Sodium oxalate
Sodium Oxalate illustrate the elimination of broadening due to 2nd-?order quadrupolar effects leading to a 30-?fold increase in resolution compared to magic-?angle spinningin NMR of polycrystalline.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium oxalate is a compound that can be used as a primary standard for standardizing KMnO4 solutions
Definition
ChEBI: An organic sodium salt consisting of sodium and oxalate ions in a 2:1 ratio.
Preparation
Sodium oxalate can be prepared through the neutralization of oxalic acid with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in a 1:2 acid-to-base molar ratio. Half-neutralization can be accomplished with NaOH in a 1:1 ratio which produces NaHC2O4, monobasic sodium oxalate or sodium hydrogenoxalate.
Reactions
Sodium oxalate is used to standardize potassium permanganate solutions. It is desirable that the temperature of the titration mixture is greater than 60 °C to ensure that all the permanganate added reacts quickly. The kinetics of the reaction is complex, and the manganate (II) ions formed catalyze the further reaction between permanganate and oxalic acid (formed in situ by the addition of excess sulfuric acid). The final equation is as follows:
5Na2C2O4 + 2KMnO4 + 8H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 10CO2 + 8H2O.
General Description
Odorless white solid. Sinks and mixes slowly with water.
Reactivity Profile
Disodium oxalate gives basic aqueous solutions. Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions. Can serve as a reducing agent in reactions that generate carbon dioxide.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
Inhalation or ingestion causes pain in throat, esophagus, and stomach; mucous membranes turn white; other symptoms include vomiting, severe purging, weak pulse, cardiovascular collapse, neuromuscular symptoms, and kidney damage. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation.
Toxicology
Like several other oxalates, sodium oxalate is toxic to humans. It can cause burning pain in the mouth, throat and stomach, bloody vomiting, headache, muscle cramps, cramps and convulsions, drop in blood pressure, heart failure, shock, coma, and possible death. Mean lethal dose by ingestion of oxalates is 10-15 grams (per MSDS).
Sodium oxalate, like citrates, can also be used to remove calcium ions (Ca2+) from blood plasma. It also prevents blood from clotting. Note that by removing calcium ions from the blood, sodium oxalate can impair brain function, and deposit calcium oxalate in the kidneys.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from hot water (16mL/g) by cooling to 0o. Before use as a volumetric standard, analytical grade quality sodium oxalate should be dried for 2hours at 120o and allowed to cool in a desiccator. [Beilstein 2 IV 1819.]
Properties of Sodium oxalate
| Melting point: | 250-270 °C |
| Density | 2.34 |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| PH | 7-8.5 (25℃, 2.5% in H2O) |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 37 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8650 |
| BRN | 3631622 |
| Stability: | Stability Stable; hygroscopic. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 62-76-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Sodium oxalate(62-76-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium oxalate (62-76-0) |
Safety information for Sodium oxalate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium oxalate
Sodium oxalate manufacturer
New Alliance Fine Chem Private Limited
Powder Pack Chem
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

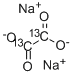
You may like
-
 Sodium Oxalate 99%View Details
Sodium Oxalate 99%View Details -
 Sodium oxalate 99%View Details
Sodium oxalate 99%View Details -
 Sodium oxalate 98%View Details
Sodium oxalate 98%View Details -
 Sodium oxalate CAS 62-76-0View Details
Sodium oxalate CAS 62-76-0View Details
62-76-0 -
 Sodium oxalate CAS 62-76-0View Details
Sodium oxalate CAS 62-76-0View Details
62-76-0 -
 Sodium OxalateView Details
Sodium OxalateView Details
62-76-0 -
 Sodium Oxalate Purified, Packaging Size: 25-50 Kg ,Packaging Type: DrumView Details
Sodium Oxalate Purified, Packaging Size: 25-50 Kg ,Packaging Type: DrumView Details
62-76-0 -
 Sodium Oxalate, Packaging Type: Hdpe Bag, Packaging Size: 25KGView Details
Sodium Oxalate, Packaging Type: Hdpe Bag, Packaging Size: 25KGView Details
62-76-0
