Nimodipine
Synonym(s):1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3ʹ-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid 2-methoxyethyl-1-methylethyl Ester;1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid 2-methoxyethyl 1-methylethyl ester;Isopropyl 2-methoxyethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate;Nimodipine;Nimodipine - CAS 66085-59-4 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:66085-59-4
- Empirical Formula: C21H26N2O7
- Molecular Weight: 418.44
- MDL number: MFCD00153848
- EINECS: 266-127-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-25 18:47:31
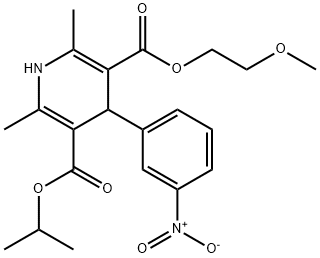
What is Nimodipine?
Absorption
In humans, nimodipine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, and peak concentrations are generally attained within one hour. Bioavailability is 100% following intravenous administration and 3-30% following oral administration due to extensive first-pass metabolism.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdosage would be expected to be related to cardiovascular effects such as excessive peripheral vasodilation with marked systemic hypotension.
Description
Nimodipine is a cerebral vasodilating calcium antagonist related to nifedipine. It is indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of neurological deficits due to cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Bayer (W. Germany)
The Uses of Nimodipine
Nimodipine has been used:
- as a L-type calcium channel (LTCC) inhibitor, to evaluate its neuroprotective activity in the vibrosections
- as a standard, in the enantioseparation of chiral drugs by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- in the pharmacological studies for the measurement of spine voltage escape
The Uses of Nimodipine
Used as a cerebral vasodilator. A dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker
The Uses of Nimodipine
A dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It is used as a vasodilator (cerebral).
The Uses of Nimodipine
provitamin, antixerophthalamic
Indications
For use as an adjunct to improve neurologic outcome following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) from ruptured intracranial berry aneurysms by reducing the incidence and severity of ischemic deficits.
Background
Nimodipine is a 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It acts primarily on vascular smooth muscle cells by stabilizing voltage-gated L-type calcium channels in their inactive conformation. By inhibiting the influx of calcium in smooth muscle cells, nimodipine prevents calcium-dependent smooth muscle contraction and subsequent vasoconstriction. Compared to other calcium channel blocking agents, nimodipine exhibits greater effects on cerebral circulation than on peripheral circulation. Nimodipine is used to as an adjunct to improve the neurologic outcome following subarachnoid hemorrhage from ruptured intracranial aneurysm.
What are the applications of Application
Nimodipine is an L-type calcium channel protein inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A dihydropyridine that is 1,4-dihydropyridine which is substituted by methyl groups at positions 2 and 6, a (2-methoxyethoxy)carbonyl group at position 3, a m-nitrophenyl group at position 4, and an isopropoxycarbonyl group at position 5. An L type calcium channel blocker, it acts particularly on cerebral circulation, and is used both orally and intravenously for the prevention and treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage from ruptured intracranial aneurysm.
Manufacturing Process
After 8 hours boiling of solution of 3.8 g of 3'-nitro-benzylideneacetoacetic acid isopropylester, 8 grams of acetoacetic acid β-metoxyethyl ester and 6 ml conc ammonia in 80 ml ethanol under reflux, 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3'-nitrophenyl)- 1,4-dihydropyridine 3-β-methoxyethyl ester 5-isopropyl ester of melting point 125°C (petroleum ether/ acetic ester) was obtained. Yield 49% of theory.
brand name
Nimotop (Bayer).
Therapeutic Function
Vasodilator
General Description
Nimodipine, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)- 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid 2-methoxyethyl1-methylethyl ester (Nimotop), is another dihydropyridinecalcium channel blocker but differs in that it dilatesthe cerebral blood vessels more effectively than do the otherdihydropyridine derivatives. This drug is indicated for treatmentof subarachnoid hemorrhage-associated neurologicaldeficits.
Biological Activity
L-type Ca 2+ channel blocker.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nimodipine enhances the survival of dopaminergic substantia nigra neurons.
Pharmacokinetics
Nimodipine belongs to the class of pharmacological agents known as calcium channel blockers. Nimodipine is indicated for the improvement of neurological outcome by reducing the incidence and severity of ischemic deficits in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage from ruptured congenital aneurysms who are in good neurological condition post-ictus (e.g., Hunt and Hess Grades I-III). The contractile processes of smooth muscle cells are dependent upon calcium ions, which enter these cells during depolarization as slow ionic transmembrane currents. Nimodipine inhibits calcium ion transfer into these cells and thus inhibits contractions of vascular smooth muscle. In animal experiments, nimodipine had a greater effect on cerebral arteries than on arteries elsewhere in the body perhaps because it is highly lipophilic, allowing it to cross the blood brain barrier.
Clinical Use
Calcium-channel blocker:
Prevention and treatment of ischaemic neurological
deficits following subarachnoid haemorrhage
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aminophylline: possibly increases aminophylline
concentration.
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifampicin;
metabolism possibly inhibited by clarithromycin,
erythromycin and telithromycin.
Antidepressants: enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs .
Antiepileptics: effect reduced by carbamazepine,
barbiturates, phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: metabolism possibly inhibited by
itraconazole and ketoconazole; negative inotropic
effect possibly increased with itraconazole.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect,
increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect of post synaptic alpha-blockers.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir; use telaprevir with caution.
Grapefruit juice: concentration increased - avoid.
Theophylline: possibly increased theophylline
concentration.
Metabolism
Hepatic metabolism via CYP 3A4.
Metabolism
Nimodipine is extensively metabolised in the liver via the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4. It is eliminated as metabolites, mainly by dehydrogenation of the dihydropyridine ring and oxidative O-demethylation. Oxidative ester cleavage, hydroxylation of the 2- and 6-methyl groups, and glucuronidation as a conjugation reaction are other important metabolic steps. The three primary metabolites occurring in plasma show no or only therapeutically negligible residual activity. The metabolites are excreted about 50% renally and 30% in faeces via the bile.
storage
Store at RT
References
1) Cohen and McCarthy (1987),?Nimodipine block of calcium channels in rat anterior pituitary cells; J. Physiol.,?387?195 2) Batuecas?et al.?(1998),?Effects of chronic nimodipine on working memory of old rats in relation to defects in synaptosomal calcium homeostasis; Eur. J. Pharmacol.,?350?141 3) LeVere?et al.?(1989),?Recovery of function after brain damage: facilitation by the calcium entry blocker nimodipine; Behav. Neurosci.,?103?561 4) Herzfeld?et al.?(2014),?Investigation of the neuroprotective impact of nimodipine on Neuro2a cells by means of a surgery-like stress model; Int. J. Mol. Sci.,?15?18453 5) Schampel?et al.?(2017),?Nimodipine fosters remyelination in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis and induces microglia-specific apoptosis; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,?114?E3295 6) Allen?et al.?(1983),?Cerebral arterial spasm – a controlled trial of nimodipine in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage; N. England J. Med.,?308?619
Properties of Nimodipine
| Melting point: | 125°C |
| Boiling point: | 536.21°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3268 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: 62.5 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 2.77±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 14,6551 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 66085-59-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Nimodipine(66085-59-4) |
Safety information for Nimodipine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Nimodipine
| InChIKey | UIAGMCDKSXEBJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Nimodipine manufacturer
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 66085-59-4 Nimodipine 99%View Details
66085-59-4 Nimodipine 99%View Details
66085-59-4 -
 Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
66085-59-4 -
 Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
66085-59-4 -
 Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
66085-59-4 -
 Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
66085-59-4 -
 Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
66085-59-4 -
 Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
66085-59-4 -
 Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
Nimodipine CAS 66085-59-4View Details
66085-59-4
