Nifedipine
Synonym(s):1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester;L-Type Calcium Channel Blocker III;Nifedipine;Nifedipine - CAS 21829-25-4 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:21829-25-4
- Empirical Formula: C17H18N2O6
- Molecular Weight: 346.33
- MDL number: MFCD00057326
- EINECS: 244-598-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
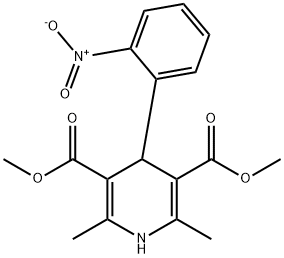
What is Nifedipine?
Absorption
Sublingual dosing leads to a Cmax of 10ng/mL, with a Tmax of 50min, and an AUC of 25ng*h/mL. Oral dosing leads to a Cmax of 82ng/mL, with a Tmax of 28min, and an AUC of 152ng*h/mL.
Nifedipine is a Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class II drug, meaning it has low solubility and high intestinal permeability. It is almost completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract but has a bioavilability of 45-68%, partly due to first pass metabolism.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is 1022mg/kg and in mice is 202mg/kg.
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with hypotension, sinus node dysfunction, atrioventricular node dysfunction, and reflex tachycardia. Overdose may be managed by monitoring cardiovascular and respiratory function; elevating extremities; and administering vasopressors, fluids, and calcium infusions.
Description
Nifedipine (21829-25-4) is a clinically useful L-type calcium blocker.
Chemical properties
Yellow Crystalline Solid
Originator
Adalat,Bayer,W. Germany,1975
The Uses of Nifedipine
Nifedipine is used for preventing and relieving angina pectoris attacks, for hypertension, and as an ingredient in combination therapy for chronic cardiac insufficiency.
The Uses of Nifedipine
Used as an antihypertensive and antianginal. A dihydorpyridine calcium channel blocker
The Uses of Nifedipine
For the management of vasospastic angina, chronic stable angina, hypertension, and Raynaud's phenomenon. May be used as a first line agent for left ventricular hypertrophy and isolated systolic hypertension (long-acting agents).
Indications
Nifedipine capsules are indicated to treat vasospastic angina and chronic stable angina. Extended release tablets are indicated to treat vasospastic angina, chronic stable angina, and hypertension.
Background
Nifedipine, or BAY a 1040, is a first generation dihydropyridine L-type calcium channel blocker, similar to nicardipine. Nifedipine was developed by Bayer and first described in the literature, along with other dihydropyridines, in 1972. Since nifedipine's development, second and third generation dihydropyridines have been developed with slower onsets and longer durations of action. The most popular of the third generation dihydropyridines is amlodipine.
Nifedipine was granted FDA approval on 31 December 1981.
What are the applications of Application
Nifedipine is a selective calcium channel protein inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: Nifedipine is a dihydropyridine, a methyl ester and a C-nitro compound. It has a role as a calcium channel blocker, a vasodilator agent, a tocolytic agent and a human metabolite.
Manufacturing Process
45 grams 2-nitrobenzaldehyde, 80 cc acetoacetic acid methyl ester, 75 cc methanol and 32 cc ammonia are heated under reflux for several hours, filtered off, cooled and, after suction-filtration, 75 grams of yellow crystals of MP 172° to 174°C are obtained, according to US Patent 3,485,847.
brand name
Adalat (Bayer); Afeditab (Watson);Procardia (Pfizer).
Therapeutic Function
Coronary vasodilator
World Health Organization (WHO)
Nifedipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It is listed in the WHO Model List of Essential Drugs. The 10mg tablet is retained on the list for short-term treatment of hypertension. Sustained-release preparations are advised for long-term treatment.
General Description
Odorless yellow crystals or powder. Tasteless.
General Description
Nifedipine, 1,4-dihydro-2, 6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate dimethyl ester(Adalat, Procardia), is a dihydropyridine derivative thatbears no structural resemblance to the other calcium antagonists.It is not a nitrate, but its nitro group is essential for itsantianginal effect. As a class, the dihydropyridines possessa central pyridine ring that is partially saturated. To this, positions2 and 6 are substituted with an alkyl group that mayplay a role in the agent’s duration of action. In addition, positions3 and 5 are carboxylic groups that must be protectedwith an ester functional group. Depending on the type ofester used at these sites, the agent can be distributed to variousparts of the body. Finally, position 4 requires an aromaticsubstitution possessing an electron-withdrawinggroup (i.e., Cl or NO2) in the ortho and/or meta position.
Air & Water Reactions
Aqueous solutions are very sensitive to light. . Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Nifedipine is sensitive to light.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Nifedipine are not available; however, Nifedipine is probably combustible.
Biological Activity
L-type calcium channel blocker.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nifedipine is a L-type Ca2+ channel blocker; and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Nifedipine has neuroprotection activity and protects substantia nigra. Nifedipine has antioxidant potential. Nifedipine downregulates inflammatory cytokines like macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Nifedipine has antihypertensive properties. Nifedipine inhibits extracellular region of adenosine A2a receptor (ADORA2A) gene.
Mechanism of action
Nifedipin causes relaxation of smooth musculature, dilation of coronary and peripheral arteries, and reduction of peripheral resistance and arterial blood pressure, and enhances oxygen supply to the heart.
Pharmacokinetics
Nifedipine is an inhibitor of L-type voltage gated calcium channels that reduces blood pressure and increases oxygen supply to the heart. Immediate release nifedipine's duration of action requires dosing 3 times daily. Nifedipine dosing is generally 10-120mg daily. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of excessive hypotension, angina, and myocardial infarction.
Clinical Use
The prototype of this class, nifedipine, has potent peripheralvasodilatory properties. It inhibits the voltage-dependentcalcium channel in the vascular smooth muscle but has littleor no direct depressant effect on the SA or AV nodes, eventhough it inhibits calcium current in normal and isolated cardiactissues. Nifedipine is more effective in patients whoseanginal episodes are caused by coronary vasospasm and isused in the treatment of vasospastic angina as well as classicangina pectoris. Because of its strong vasodilatory properties,it is used in selected patients to treat hypertension.
Synthesis
Nifedipine, dimethyl ether 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2??-nitrophenyl)-3,5- piridindicarboxylic acid (19.3.16), is synthesized by a Hantsch synthesis from two molecules of a |?-dicarbonyl compound?amethyl acetoacetate, using as the aldehyde component?a 2-nitrobenzaldehyde and ammonia. The sequence of the intermediate stages of synthesis has not been completely established.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aminophylline: possibly increases aminophylline
concentration.
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: concentration of dronedarone
increased.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifampicin;
metabolism possibly inhibited by clarithromycin,
erythromycin and telithromycin.
Antidepressants: metabolism possibly inhibited by
fluoxetine; concentration reduced by St John’s wort;
enhanced hypotensive effect with MAOIs.
Antiepileptics: effect reduced by carbamazepine,
barbiturates, phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: metabolism possibly inhibited by
itraconazole and ketoconazole; concentration
increased by micafungin; negative inotropic effect
possibly increased with itraconazole.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect,
increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect of
post-synaptic alpha-blockers; occasionally severe
hypotension and heart failure with beta-blockers.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir; use telaprevir with caution.
Cardiac glycosides: digoxin concentration possibly
increased.
Ciclosporin: may increase ciclosporin level, but not a
problem in practice; nifedipine concentration may be
increased.
Cytotoxics: metabolism of vincristine possibly
reduced.
Grapefruit juice: concentration increased - avoid.
Magnesium salts: profound hypotension with IV
magnesium.
Tacrolimus: increased tacro
Metabolism
Nifedipine is predominantly metabolized by CYP3A4. Nifedipine is predominantly metabolized to 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-5-methoxycarbonyl-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, and then further metabolized to 2-hydroxymethyl-pyridine carboxylic acid. Nifedipine is also minorly metabolized to dehydronifedipine.
Metabolism
Nifedipine is metabolised in the gut wall and oxidised in the liver via the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4, to inactive metabolites. Excreted mainly as metabolites via the kidney
Storage
+4°C (desiccate)
References
1) Vater et al., (1972), (Pharmacology of 4-(2′-nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester (Nifedipine, BAY a 1040); Arzneimittelforschung, 22 1
Properties of Nifedipine
| Melting point: | 171-175 °C |
| Boiling point: | 481.08°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2109 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5486 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble |
| pka | pKa -0.9/>13(DMF,t undefined) (Uncertain) |
| form | powder |
| color | yellow |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 19.5 ºC |
| Merck | 14,6528 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions are not stable and must be used within one working day. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 21829-25-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Nifedipine(21829-25-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dimethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate (21829-25-4) |
Safety information for Nifedipine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Nifedipine
| InChIKey | CYCWGQFQPAYBHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Nifedipine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 21829-25-4 NIFEDIPINE 10% ER PELLETS 98%View Details
21829-25-4 NIFEDIPINE 10% ER PELLETS 98%View Details
21829-25-4 -
 Nifedipine 98% CAS 21829-25-4View Details
Nifedipine 98% CAS 21829-25-4View Details
21829-25-4 -
 Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
21829-25-4 -
 Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
21829-25-4 -
 Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
21829-25-4 -
 Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
21829-25-4 -
 Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
21829-25-4 -
 Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
Nifedipine CAS 21829-25-4View Details
21829-25-4
