Nilutamide
Synonym(s):5,5-Dimethyl-3-[4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2,4-imidazolidinedione;Anandron;RU-23908
- CAS NO.:63612-50-0
- Empirical Formula: C12H10F3N3O4
- Molecular Weight: 317.22
- MDL number: MFCD00864670
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
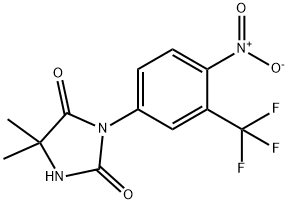
What is Nilutamide?
Absorption
Rapidly and completely absorbed, yielding high and persistent plasma concentrations.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include dizziness, general discomfort, headache, nausea, and vomiting.
Description
Nilutamide is a non-steroidal anti-androgen similar in potency to the acyclic urea flutamide (55) and useful in the management of prostatic carcinoma.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Roussel (France)
History
The second nonsteroidal anti-androgen to be marketed was nilutamide. It was discovered from a series of flutamide analogues at Roussel Uclaf (now Sanofi) in the 1970s using a rat prostate assay determining the inhibition of androgen uptake.The investigational compound code was RU 23908. Its structure is closely related to hydroxyflutamide, particularly under the assumption that the α-hydroxyamide engages in an internal hydrogen bond when bound to the AR LBD. The hydantoin moiety of nilutamide mimics the active conformation of hydroxyflutamide.
Like flutamide, nilutamide blocks the action of androgens originating from both testis and adrenal. It also has neither agonist nor any other hormonal activity. Nilutamide has an elimination half-life of approximately 2 days in patients, which is significantly longer than that of flutamide. Thus, a single oral dose of 150 mg daily was feasible.
The Uses of Nilutamide
Nonsteroidal antiandrogen. Antineoplastic (hormonal)
Background
Nilutamide is an antineoplastic hormonal agent primarily used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Nilutamide is a pure, nonsteroidal anti-androgen with affinity for androgen receptors (but not for progestogen, estrogen, or glucocorticoid receptors). Consequently, Nilutamide blocks the action of androgens of adrenal and testicular origin that stimulate the growth of normal and malignant prostatic tissue. Prostate cancer is mostly androgen-dependent and can be treated with surgical or chemical castration. To date, antiandrogen monotherapy has not consistently been shown to be equivalent to castration.
Indications
For use in combination with surgical castration for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer involving distant lymph nodes, bone, or visceral organs (Stage D2).
What are the applications of Application
Nilutamide is an androgen receptor inhibitor
Indications
Clinical trials with nilutamide were conducted predominantly in combination with orchiectomy. Results indicated retardation of disease progression and relief of metastatic bone pain in patientswith advanced prostate cancer.However, patient survival benefit was small compared with castration alone. Studies of nilutamide monotherapy or combination with LHRH agonists did not have sufficient patient numbers to allow reliable conclusions on efficacy. Nilutamide was first launched in France in 1987 for treatment of metastatic prostate cancer in adjuvant therapy with surgical castration. Approval in several major markets was granted in the following years.
The tolerability profile of nilutamide was similar to that of flutamide. Hot flushes, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, gastrointestinal pain, abnormal liver function, and gynecomastia were frequently reported adverse events with both drugs. Additional side effects were predominantly associated with nilutamide treatment: interstitial pneumonitis, impaired adaptation to darkness, and alcohol intolerance.
The nonsteroidal anti-androgens flutamide and nilutamide established combined androgen blockade as first-line treatment for metastatic prostate cancer. Still, there was room for improvement with regard to overall survival (OS) and tolerability.
Definition
ChEBI: Nilutamide is an imidazolidinone, a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes and a C-nitro compound. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent and an androgen antagonist.
Manufacturing Process
There are at least five methods to prepare desired compound.
1. 1-(3'-Trifluoromethyl-4'-nitropheyl)-4,4-dimethyl-imidazoline-2,5-dione
The following were introduced into 383.52 ml of phenyl oxide: 225.60 grams
of 2-nitro-5-chloro-trifluoromethylbenzene, described in the German Patent No. DRP 637,318, 128.10 grams of 5,5-dimethylhydantoin described in Beil.,
Vol. 24, 289 and 198.53 grams of cuprous oxide. The mixture was heated to
200°C for 24 hours, then cooled to 20°C and filtered. The residue was rinsed
with phenyl oxide, then extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate phase
was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure at 60°C and the residue
was taken up in ammoniacal dichloroethane. The crystals obtained were dried
at 60°C to obtain 66.55 grams of crude product which, after purification from
aqueous ethanol yielded 62.55 grams of purified desired product.
2. 1-(3'-Trifluoromethyl-4'nitrophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-imidazoline-2,5-dione
The following were introduced into 282 ml of triglyme: 112.8 grams of 2-
nitro-5-chloro-trifluoromethylbenzene, 64.1 grams of 5,5-dimethyl-hydantoin
and 33.5 grams of cuprous oxide. The mixture was heated to about 215°C ±
5°C for 4 hours, then cooled to 20°C and filtered. The triglyme solution was
recovered and a 22 Be ammonia solution (1 volume), toluene (1 volume) and
demineralized water (4 volume) were added to the solution of triglyme (1
volume). The solution was stirred at 20°C for 15 minutes, then cooled to
about -10°C and stirred again at -10°C. After washing and drying, 47.6 grams
of the desired product were obtained.
3. 1-(3'-Trifluoromethyl-4'-nitrophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-imidazoline-2,5-dione
30 ml of dimethylsulfoxide and 24.8 grams of 2-nitro-5-chloro
trifluoromethylbenzene were introduced at 20°C with stirring into 100 ml of
dimethylsulfoxide, 12.80 grams of 5,5-dimethyl-hydantoin and 6.28 grams of
potassium hydroxide in the form of flakes. The mixture was heated to 110°C
for a period of time variable between 3 and 18 hours. The product was
characterized and determined by thin layer chromatography.
4. 1-(3'-Trifluoromethyl-4'-nitrophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-imidazoline-2,5-dione
71.5 grams of copper in powder form were added to 96.10 grams of 5,5-
dimethyl-hydantoin and 170.86 grams of 2-nitro-5-chloro
trifluoromethylbenzene. The mixture was heated to 200°C for about 21 hours,
the pressure being maintained at 450 millibars, then, was cooled to 20°C and
taken up in 480 ml of ethanol. The product was characterized and determined
by thin layer chromatography of the ethanol solution.
5. 1-(3'-Trifluoromethyl-4'-nitrophenyl)4,4-dimethyl-imidazoline-2,5-dione
The following were introduced into 288 ml of phenyl oxide: 96.10 grams of
5,5-dimethyl-hydantoin, 170.86 grams of 2-nitro-5-chloro
trifluoromethylbenzene and 89.40 grams of cupric oxide. The mixture was
heated to 190°C for about 23 hours, then cooled to 20°C and filtered. The
residue was characterized in the phenyl oxide filtrate by thin layer
chromatography. The analytical results obtained for these 5 examples were
identical to those obtained and indicated in French Patent No. 2,329,276.
brand name
Nilandron (Sanofi Aventis);Anandron.
Therapeutic Function
Antiandrogen
General Description
Nilutamide, 5,5-dimethyl-3-[4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2,4-imidazolidinedione, is usedin combination with surgical castration for the treatment ofmetastatic prostate cancer. Nilutamide, which has an eliminationhalf-life of approximately 40 hours, can also be usedin once-daily dosing, but it has side effects that limit itsuse—visual disturbances, alcohol intolerance, and allergicpneumonitis.
Biological Activity
Non-steroidal and silent antiandrogen. Binds to androgen receptors and also inhibits androgen biosynthesis in vitro . In rats in vivo it inhibits androgen-induced prostate weight increase and inhibits negative androgen-dependent gonadotropin feedback leading to an increase in luteinising hormone and testosterone. Orally active.
Mechanism of action
The therapeutic effects of nilutamide are overshadowed, however, by the occurrence of several adverse reactions mediated by toxic mechanisms, which are poorly investigated. The reduction of nilutamide is catalyzed by NO synthases via the formation of either or both a nitro anion free radical or its reduction to its hydroxylamino derivative could explain some of the toxic effects of this drug. Nitric oxide synthases also are involved in the formation of reactive NO and oxygen species and in the interactions with some xenobiotic compounds.
Pharmacokinetics
Nilutamide is an antineoplastic hormonal agent primarily used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Nilutamide is a pure, nonsteroidal anti-androgen with affinity for androgen receptors (but not for progestogen, estrogen, or glucocorticoid receptors). Consequently, Nilutamide blocks the action of androgens of adrenal and testicular origin that stimulate the growth of normal and malignant prostatic tissue. Prostate cancer is mostly androgen-dependent and can be treated with surgical or chemical castration. To date, antiandrogen monotherapy has not consistently been shown to be equivalent to castration. The relative binding affinity of nilutamide at the androgen receptor is less than that of bicalutamide, but similar to that of hydroxuflutamide.
Clinical Use
Nilutamide is a hepatotoxic nitroaromatic antiandrogen used for the treatment of metastatic prostate carcinoma in men.
Metabolism
The results of a human metabolism study using 14C-radiolabelled tablets show that nilutamide is extensively metabolized and less than 2% of the drug is excreted unchanged in urine after 5 days.
Metabolism
Nilutamide is a nitroaromatic hydantoin analog of flutamide, that is completely absorbed after oral administration, with a mean elimination half-life of approximately 50 hours. One of the methyl groups attached to the hydantoin ring is stereoselectively hydroxylated to a chiral metabolite, which subsequently is oxidized to its carboxylic acid metabolite. Less than 2% of nilutamide is excreted unchanged in the urine. In vitro, the nitro group of nilutamide was reduced to the amine and hydroxylamine moieties by nitric oxide (NO) synthases, a flavin monooxygenase (FMO) system.
Properties of Nilutamide
| Melting point: | 1490C |
| Density | 1.463±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in acetone, soluble in anhydrous ethanol. |
| form | solid |
| pka | 7.59±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Light yellow to yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 63612-50-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Nilutamide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. |
Computed Descriptors for Nilutamide
| InChIKey | XWXYUMMDTVBTOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 63612-50-0 Nilutamide 98%View Details
63612-50-0 Nilutamide 98%View Details
63612-50-0 -
 63612-50-0 98%View Details
63612-50-0 98%View Details
63612-50-0 -
 Nilutamide 98%View Details
Nilutamide 98%View Details
63612-50-0 -
 Nilutamide 63612-50-0 98%View Details
Nilutamide 63612-50-0 98%View Details
63612-50-0 -
 Nilutamide 99%View Details
Nilutamide 99%View Details -
 Nilutamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 63612-50-0View Details
Nilutamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 63612-50-0View Details
63612-50-0 -
 Nilutamide CAS 63612-50-0View Details
Nilutamide CAS 63612-50-0View Details
63612-50-0 -
 Nilutamide CAS 63612-50-0View Details
Nilutamide CAS 63612-50-0View Details
63612-50-0
