Naratriptan
- CAS NO.:121679-13-8
- Empirical Formula: C17H25N3O2S
- Molecular Weight: 335.46
- MDL number: MFCD00866221
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
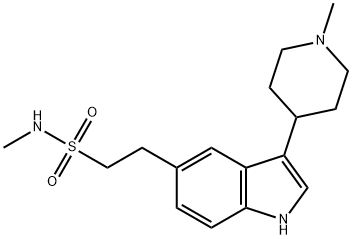
What is Naratriptan?
Absorption
Well absorbed (74% oral biovaility), absorption is rapid with peak plasma concentrations after 2-5 hours. The rate of absorption is slower during a migraine attack.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include light-headedness, loss of coordination, tension in the neck, and tiredness.
Originator
Amerge,Glaxo Wellcome,UK
The Uses of Naratriptan
Naratriptan is a triptan drug that is used for the treatment of migraine headaches.
The Uses of Naratriptan
Antimigraine.
Background
Naratriptan is a triptan drug that is selective for the 5-hydroxytryptamine1 receptor subtype. It is typically used for the treatment of migraine headaches.
Indications
For the acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without aura in adults.
Definition
ChEBI: Naratriptan is a sulfonamide, a member of tryptamines and a heteroarylpiperidine. It has a role as a serotonergic agonist and a vasoconstrictor agent.
Manufacturing Process
N-Methyl-3-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-1-methyl-4-pyridinyl)-1H-indole-5-
ethanesulphonamide oxalate
A solution of N-methyl-1H-indole-5-ethanesulphonamide (1.0 g) in methanol
(50 ml) containing potassium hydroxide (5.6 g) and N-methyl-4-piperidone
(1.0 ml) was heated at reflux for 24 h, cooled, and the resulting solid filtered
off (1.0 g). A sample of the solid (0.2 g) was dissolved in a hot methanolic
solution of oxalic acid (0.06 g), the solution cooled, and the salt precipitated
by adding ethyl acetate (20 ml) and dry ether (50 ml). The salt was filtered
off, and dried in vacuo to give the title compound as a solid (0.12 g), m.p.
87°-90°C (shrinks).
Analysis Found: C,52.2; H,5.6; N,9.5. C17H23N3O2S · C2H2O4 · 0.6H2O
requires C,52.5; H,6.0; N,9.7%.
N-Methyl-3-(1-methyl-4 -piperidinyl)-1H-indole-5-ethansulphonamide
N-Methyl-3-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-1-methyl-4-pyridinyl)-1H-indole-5-
ethanesulphonamide oxalate (as the free base) (0.36 g, 0.001 mol) in
absolute alcohol (70 ml) and anhydrous dimethylformamide (5 ml) was
hydrogenated, in the presence of 5% palladium on activated carbon (0.36 g)
at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure. After 20 h, hydrogen
absorption (25 cm3, theoretical = 24 cm3) ceased. The catalyst was filtered
off and the solvent removed in vacuo to given an opaque gum which solidified
as a soft white solid (0.3 g). Purification by flash chromatography (Sorbsil C60
silica gel, CH2Cl2/EtOH/0.88 ammonia; 50:80:1) gave a colorless oil (0.21 g)
that was triturated with ether to give the title compound (0.17 g) m.p. 156°-
158°C. TLC SiO2(CH2Cl2/EtOH/0.88 ammonia; 50:8:1) Rf 0.4.
N-Methyl-3-(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)-1H-indole-5-ethanesulphonamide may be
prepared the another way.
A solution of 4-hydrazino-N-methyl-benzenethanesulphonamide (0.5 g) and 1-
methyl-4-piperidineacetaldehyde (0.35 g) in a mixture of water (10 ml) of 2 N
hydrochloric acid (1.0 ml, 2.00 mmol) was stirred for 2 days at room
temperature. A further quantity of the aldehyde (0.35 g) was added and
stirring continued for a further 30 min. The solution was then basified with
8% sodium bicarbonate to pH 8 and extracted with chloroform (3 times 50
ml). The combined organic extracts were dried (Na2SO4) and evaporated in
vacuo to give the crude hydrazone as an oil (1.0 g). A solution of the
hydrazone (1.0 g) in chloroform (20 ml) containing polyphosphate ester (10
g) was heated at reflux for 8 min. The solution was poured onto ice (200 g),
stirred for 2 h treated with 2 M sodium carbonate (20 ml) and extracted with
chloroform (3 times 50 ml). The combined organic extracts were dried
(Na2SO4), evaporated in vacuo and the residue purified by flash
chromatography (silica 9385, 100 g) eluting with CH2Cl2/EtOH/NH3(75:8:1) to
give impure material as a yellow oil. Further flash chromatography (silica
9385, 100 g) eluting with CH2Cl2/EtOH/NH3 (100:8:1) gave the product as an
oil (0.05 g). This was crystallised from ethyl acetate to give the title compound
solid m.p. 156°-157°C. TLC SiO2(CH2Cl2/EtOH/NH3(50:8:1)) Rf 0.6.
brand name
Amerge (GlaxoSmithKline).
Therapeutic Function
Serotonin antagonist, Migraine therapy
General Description
Naratriptan, the third triptan approved in 1998, is one of themost lipophilic triptans marketed to date. It has a much improvedbioavailability (63% in men and 74% in women), agreater affinity for 5-HT1B/1D receptors (3–6 times), and alower recurrence rate than sumatriptan because of its muchlonger elimination half-life. Naratritan also has a favorableCNS side effect profile when compared with sumatriptanor zolmitriptan because of its metabolic stability,thereby lacking a N-demethylated active metabolite and asignificant renal excretion ( 70% of naratriptan is excretedunchanged and the rest of the administered dose is degradedvia several CYP isozymes).
Pharmacokinetics
Naratriptan is a selective agonist of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) type 1B and 1D receptors. It is structurally and pharmacologically related to other selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist. Naratriptan has only a weak affinity for 5-HT1A, 5-HT5A, and 5-HT7 receptors and no significant affinity or pharmacological activity at 5-HT2, 5-HT3 or 5-HT4 receptor subtypes or at alpha1-, alpha2-, or beta-adrenergic, dopamine1,; dopamine2; muscarinic, or benzodiazepine receptors. This action in humans correlates with the relief of migraine headache. In addition to causing vasoconstriction, experimental data from animal studies show that Naratriptan also activates 5-HT1 receptors on peripheral terminals of the trigeminal nerve innervating cranial blood vessels, which may also contribute to the antimigrainous effect of Naratriptan in humans.
Clinical Use
5HT1
receptor agonist:
Acute treatment of migraine
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antidepressants: increased CNS toxicity with
citalopram - avoid; possibly increased serotonergic
effects with duloxetine, SSRIs and venlafaxine;
increased serotonergic effects with St John’s wort -
avoid.
Dapoxetine: possible increased risk of serotonergic
effects - avoid for 2 weeks after stopping 5HT1
agonists.
Ergot alkaloids: increased risk of vasospasm - avoid.
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic. In vitro, naratriptan is metabolized by a wide range of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes into a number of inactive metabolites.
Metabolism
Naratriptan undergoes some hepatic metabolism via a wide range of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes to form inactive metabolites. Naratriptan is excreted by glomerular filtration and active secretion into the renal tubules. It is mainly excreted in the urine with 50% of a dose being recovered as unchanged drug and 30% as inactive metabolites.
Properties of Naratriptan
| Melting point: | 170-171° |
| Boiling point: | 541.3±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.227±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 11.52±0.40(Predicted) |
Safety information for Naratriptan
Computed Descriptors for Naratriptan
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Naratriptan 98%View Details
Naratriptan 98%View Details -
 Naratriptan 98%View Details
Naratriptan 98%View Details
121679-13-8 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
