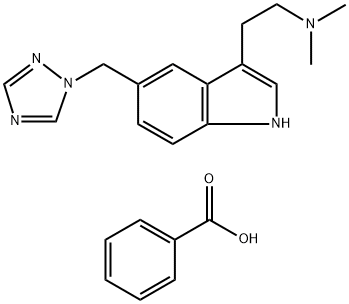
Rizatriptan
- CAS NO.:144034-80-0
- Empirical Formula: C15H19N5
- Molecular Weight: 269.34
- MDL number: MFCD03840591
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-29 15:43:00
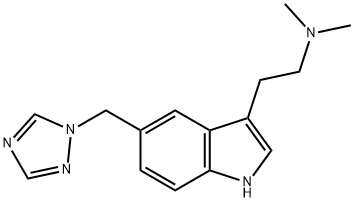
What is Rizatriptan?
Absorption
Rizatriptan is readily absorbed (approximately 90%) following oral administration; however, the mean oral absolute bioavailability of the rizatriptan tablet is about 45%, owing to extensive first-pass metabolism. The Tmax is approximately one to 1.5 hours. The presence of a migraine headache did not appear to affect the absorption or pharmacokinetics of rizatriptan. Food has no significant effect on the bioavailability of rizatriptan but delays the time to reach peak concentration by an hour. In clinical trials, rizatriptan was administered without regard to food.
The bioavailability and Cmax of rizatriptan were similar following the administration of rizatriptan tablets and rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablets. Still, the absorption rate is somewhat slower with orally disintegrating tablets, with Tmax delayed by up to 0.7 hours. The AUC of rizatriptan is approximately 30% higher in females than males. No accumulation occurred on multiple dosing.
Toxicity
The acute oral toxicity (LD50) was 2,227 mg/kg in rats and 700-1,631 mg/kg in mice.
No overdoses of rizatriptan were reported in clinical trials. Some adult patients who received 40 mg of rizatriptan either a single dose or as two doses with a two-hour interdose interval had dizziness and somnolence. Syncope, dizziness, bradycardia including third degree AV block, vomiting, and/or incontinence were experienced by two adults who received a total cumulative doses of 80 mg (given within four hours) in a clinical pharmacology study. Some adolescent patients (aged 12 to 17 years old) receiving two 10-mg doses of orally disintegrating tablets of rizatriptan experienced abdominal discomfort, fatigue, and dyspnea.
Based on the pharmacological properties of rizatriptan, hypertension and myocardial ischemia are possible after overdosage. Gastrointestinal decontamination, (i.e., gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal) should be considered in patients suspected of an overdose with rizatriptan. Clinical and electrocardiographic monitoring should be continued for at least 12 hours, even if clinical symptoms are not observed. The effects of hemo- or peritoneal dialysis on serum concentrations of rizatriptan are unknown.
The Uses of Rizatriptan
Rizatriptan is reported to be a very effective acute migraine drug. It is reported to display high agonist activity at mainly the serotonin 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptor subtypes.
The Uses of Rizatriptan
Ca channel blocker
Indications
Rizatriptan is indicated for the acute treatment of diagnosed migraine with or without aura. Rizatriptan is not indicated for the prophylactic therapy of migraine nor the treatment of cluster headache.
In Canada, rizatriptan is approved in adults. In the US, the oral tablet formulations are used in patients six years of age and older and the oral film formation is approved for patients 12 years of age and older weighing 40 kg or more.
Background
Rizatriptan is a second-generation triptan and a selective 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptor agonist. Used in the treatment of migraines, rizatriptan was first approved in the US in 1998. Rizatriptan is available in oral tablets, orally disintegrating tablets (wafers), and oral film formulations.
Definition
ChEBI: Rizatriptan is a member of tryptamines. It has a role as a serotonergic agonist, a vasoconstrictor agent and an anti-inflammatory drug. It is functionally related to a N,N-dimethyltryptamine.
brand name
Maxalt (Merck).
General Description
Rizatriptan, approved in 1998, is a fast-acting triptan becauseof its moderate lipophilicity yet has a very shortelimination half-life similar to sumatriptan (i.e., like sumatriptan,it is mainly metabolized by MAO-A). The only advantagesof this drug when compared with sumatriptan arethat it has a slightly faster onset and that it has an orallydisintegrating tablet formulation which can be taken withoutwater.
Pharmacokinetics
Rizatriptan relieves migraine-associated symptoms. Rizatriptan is reported to reach the maximum plasma concentrations more quickly and produces a more rapid onset of pain relief than other triptans, such as sumatriptan; however, it has a relatively shorter elimination half-life than other triptans. Rizatriptan causes transient increases in blood pressure to some extent. In vitro, rizatriptan was shown to contract isolated human coronary arteries; however, since the EC50 for this effect is high, rizatriptan is not expected to cause myocardial ischemia at therapeutic plasma concentrations in patients with normal coronary circulation.
Rizatriptan has a weak affinity for other 5-HT1 receptor subtypes (5-HT1A, 5-HT1E, 5-HT1F) and the 5-HT7 receptor but has no significant activity at 5-HT2, 5-HT3, alpha- and beta-adrenergic, dopaminergic, histaminergic, muscarinic or benzodiazepine receptors.
Clinical Use
5HT1
receptor agonist:
Acute treatment of migraine
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antidepressants: increased risk of CNS excitation
with citalopram - avoid; risk of CNS toxicity
with MAOIs, moclobemide and linezolid - avoid
for 2 weeks after discontinuation of MAOI and
moclobemide; possibly increased serotonergic
effects with duloxetine and venlafaxine; increased
serotonergic effects with St John’s wort - avoid.
Dapoxetine: possible increased risk of serotonergic
effects - avoid for 2 weeks after stopping 5HT1
agonists.
Ergot alkaloids: increased risk of vasospasm - avoid.
Propranolol: rizatriptan levels increased, reduce dose
of rizatriptan to 5 mg (max 10 mg in 24 hours).
Metabolism
Rizatriptan primarily undergoes oxidative deamination mediated by monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A) to form triazolomethyl-indole-3-acetic acid, which is not pharmacologically active. N-monodesmethyl-rizatriptan is a minor metabolite with a pharmacological activity comparable to the parent compound's. Plasma concentrations of N-monodesmethyl-rizatriptan are approximately 14% of those of the parent compound, which is eliminated at a similar rate. Other pharmacologically inactive minor metabolites include the N-oxide, the 6-hydroxy compound, and the sulfate conjugate of the 6-hydroxy metabolite.
Metabolism
The main route of rizatriptan metabolism is via oxidative
deamination by monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A)
to the indole acetic acid metabolite, which is not
pharmacologically active. N-monodesmethyl-rizatriptan,
a metabolite with activity similar to that of parent
compound, is formed to a minor degree, but does not
contribute significantly to the pharmacodynamic activity
of rizatriptan.
Less than 1% is excreted in the urine as active
N-monodesmethyl metabolite.
Properties of Rizatriptan
| Melting point: | 178-180°C |
| Boiling point: | 504.8±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.21±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2-8°C |
| pka | 16.98±0.30(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 42 mg/mL |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 144034-80-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetonitrile, 2,2-dibromo-2-chloro- (144034-80-0) |
Safety information for Rizatriptan
Computed Descriptors for Rizatriptan
Rizatriptan manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 144034-80-0 Rizatriptan 98%View Details
144034-80-0 Rizatriptan 98%View Details
144034-80-0 -
 Rizatriptan 98%View Details
Rizatriptan 98%View Details -
 Rizatriptan 95% CAS 144034-80-0View Details
Rizatriptan 95% CAS 144034-80-0View Details
144034-80-0 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
