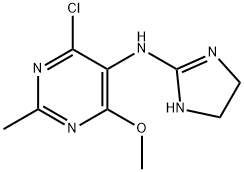
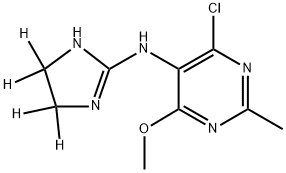
Moxonidine
Synonym(s):4-Chloro-N-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinamine
- CAS NO.:75438-57-2
- Empirical Formula: C9H12ClN5O
- Molecular Weight: 241.68
- MDL number: MFCD06795643
- EINECS: 629-833-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-20 11:41:24
What is Moxonidine?
Absorption
90% of an oral dose is absorbed with negligible interference from food intake or first pass metabolism, resulting in a high bioavailability of 88%.
Toxicity
Contraindicated due to known hypersensitivity to an ingredient (Physiotens tablets contain lactose), heart failure, severe renal impairment, < 16 years old, >75 years old, bradycardia, severe bradyarrhythmia, sick sinus syndrome, second or third degree atrioventricular block, malignant arrhythmias. Used with caution in patients with history of severe coronary artery disease (CAD), unstable angina, angioneurotic edema. Pregnancy Category B3:Avoid use during pregnancy (inadequate data in pregnant woman) and lactation (maternal blood stream transfer to breast milk shown) unless benefit clearly justifies risk. Lack of specific therapeutic experience in cases of intermittent claudication, Raynaud's disease, Parkinson's disease, epileptic disorders, gluacoma, and depression suggest moxonidine should not be used in such instances . Carcinogenicity and genotoxicity does not appear significant. Concurrent administration of other hypotensives or sedative and hypnotics can enhance the hypotensive effect and intensify sedation respectively. Avoid concurrent Tricyclic Antidepressant (TCA) use to avoid reduction of monoxidine efficacy. Generally well tolerated with dry mouth and headache the most common adverse effects Symptoms of overdose correlate with pharmacodynamic properties:hypotension, sedation, orthostatic dysregulation, bradycardia, dry mouth with no specific counter-treatment known.
Description
Moxonidine, which is structurally related to clonidine, is a new centrally acting antihypertensive that acts as a stronger agonist at imidazole receptors and a weaker agonist at α2-adrenergic receptors than clonidine. It is also reported to have less side effects and a much reduced potential to produce a rebound in blood pressure on withdrawal. Clinically, moxonidine appears to have comparable antihypertensive efficacy with the ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Beiersdorf (Germany)
The Uses of Moxonidine
Moxonidine is an antihypertensive agent.
The Uses of Moxonidine
Antihypertensive;Imidazoline receptor agonist
Background
Moxonidine is a new-generation centrally acting antihypertensive drug approved for the treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension. It is suggested to be effective in cases where other agents such as thiazides, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers are not appropriate or irresponsive. As well, moxonidine has been shown to present blood pressure-independent beneficial effects on insulin resistance syndrome.
Indications
For the treatment of mild to moderate essential or primary hypertension . Effective as most first-line antihypertensives when used as monotherapy .
What are the applications of Application
Moxonidine hydrochloride is an Imidazoline receptor and an α2-adrenergic agonist
Definition
ChEBI: Moxonidine is an organohalogen compound and a member of pyrimidines.
brand name
Cynt (Lilly); Nucynt (Lilly); Norcynt (Lilly);Physiotens.
Biological Activity
Mixed I 1 imidazoline receptor and α 2 -adrenergic agonist; displays 40-fold higher affinity for I 1 receptors versus α 2 -adrenoceptors. Centrally acting antihypertensive agent.
Pharmacokinetics
Antihypertensive agent whose site of action is the Central Nervous System (CNS), specifically involving interactions with I1- imidazoline and alpha-2-adrenergic rececptors within the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RSV).
Clinical Use
Antihypertensive agent (centrally acting agonist at I1 receptor, imidazoline and alpha2 adrenoceptors)
Metabolism
Biotransformation is unimportant with 10-20% of moxonidine undergoing oxidation reactions to the primary 4,5-dehydromoxonidine metabolite and a guanidine derivative by opening of the imidazoline ring.
The antihypertensive effects of these 4,5-dehydromoxonidine and guanidine metabolites are only 1/10 and 1/100 the effect of moxonidine .
Oxidation on either the methyl group (pyrimidine ring) or on the imidazole ring of moxonidine results in the formation of the hydroxylmethyl moxonidine metabolite or the hydroxy moxonidine metabolite . The hydroxy moxonidine metabolite can be further oxidized to the dihydroxy metabolite or it can lose water to form the dehydrogenated moxonidine metabolite, which itself can be further oxidized to form an N-oxide . Aside from these Phase I metabolites, Phase II metabolism of moxonidine is also evident with the presence of a cysteine conjugate metabolite minus chlorine . Nevertheless, the identification of the hydroxy moxonidine metabolite with a high level of dehydrogenated moxonidine metabolite in human urine samples suggests that dehydrogenation from the hydroxy metabolite to the dehydrogenated moxonidine metabolite represents the primary metabolic pathway in humans .
The cytochromes P450 responsible for the metabolism of moxonidine in humans have not yet been determined .
Ultimately, the parent moxonidine compound was observed to be the most abundant component in different biological matrices of urinary excretion samples, verifying that metabolism only plays a modest role in the clearance of moxonidine in humans .
Metabolism
10-20% metabolised, predominantly to 4,5-dehydromoxonidine and to an aminomethanamidine derivative both of which are much less active than moxonidine. Moxonidine and its metabolites are almost entirely eliminated via the kidney. More than 90% of the dose is eliminated in the first 24 hours via the kidney, while approximately 1% is eliminated in the faeces
Properties of Moxonidine
| Melting point: | 217-219° (dec) |
| Boiling point: | 364.7±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.52±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in methylene chloride, very slightly soluble in acetonitrile. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 7.11±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Almost white |
| Water Solubility | 800.3mg/L(temperature not stated) |
| Merck | 14,6293 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75438-57-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Moxonidine
Computed Descriptors for Moxonidine
| InChIKey | WPNJAUFVNXKLIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Moxonidine manufacturer
Honour Lab Limited
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Moxonidine 98%View Details
Moxonidine 98%View Details -
 Moxonidine 75438-57-2 98%View Details
Moxonidine 75438-57-2 98%View Details
75438-57-2 -
 75438-57-2 Moxonidine 98%View Details
75438-57-2 Moxonidine 98%View Details
75438-57-2 -
 75438-57-2 98%View Details
75438-57-2 98%View Details
75438-57-2 -
 Moxonidine CAS 75438-57-2View Details
Moxonidine CAS 75438-57-2View Details
75438-57-2 -
 Moxonidine 98% (HPLC) CAS 75438-57-2View Details
Moxonidine 98% (HPLC) CAS 75438-57-2View Details
75438-57-2 -
 Moxonidine CAS 75438-57-2View Details
Moxonidine CAS 75438-57-2View Details
75438-57-2 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8