Fursultiamine
- CAS NO.:804-30-8
- Empirical Formula: C17H26N4O3S2
- Molecular Weight: 398.54
- MDL number: MFCD00867383
- EINECS: 212-357-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
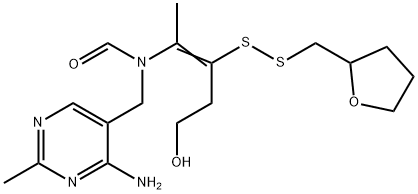
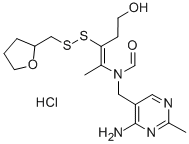
What is Fursultiamine?
Description
Fursultiamine (syn. thiamine tetrahydrofurfuryl disulfide) is a vitamin B1 derivative which is rarely used, is only sparingly soluble in water and thus is usually employed only for solid drug forms. Lyophilisates are stabilized by sodium dextran sulfate.
Chemical properties
white or slightly yellow crystalline powder. melting point 130-136 °C (decomposition). soluble in methanol, ethanol, chloroform, slightly soluble in acetone, insoluble in benzene, ether, slightly garlic odor.
Originator
Alinamin F,Takeda,Japan,1961
The Uses of Fursultiamine
Fursultiamine is an oral source of thiamine, used in comparative pharmacokinectic analysis of thiamine and it’s phosphorylated metabolites administered as multivitamin preparations, identification of drug candidate against prostate cancer from aspect of somatic cell reprogramming, therapeutic tool in number of human neurological diseases.
What are the applications of Application
Fursultiamine is a disulfide derivative of thiamine
Background
Compound used for therapy of thiamine deficiency. It has also been suggested for several non-deficiency disorders but has not yet proven useful. Fursultiamine is a vitamin B1 derivative.
What are the applications of Application
Fursultiamine, a lipophilic vitamin B1 derivative, which is more readily absorbed in large amounts in the small intestine and has a longer half-life than its active counterpart vitamin B1. It is suitable for the treatment of beriberi or Wernicke encephalopathy due to vitamin B1 deficiency. It can also be used for the adjuvant treatment of peripheral neuritis and indigestion caused by vitamin B1 deficiency.
Preparation
Furanthiamine is obtained by condensing thiamine hydrochloride with sodium tetrahydrofuranmethyl thiosulfate after ring opening.
Definition
ChEBI: Fursultiamine is a member of pyrimidines.
Manufacturing Process
To a solution of 20 parts of thiamine hydrochloride in 30 parts of water is added an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (7.2 parts of NaOH in 30 parts of water), and the mixture is cooled with water. The mixture is allowed to stand for 30 minutes, 60 parts of chloroform is added, followed by a solution of 30 parts of crude sodium tetrahydrofurfurylthiosulfate in 30 parts of water, and the whole is stirred for 30 minutes. The chloroform layer is separated and the aqueous layer is extracted twice with 20 parts of chloroform. All the chloroform solutions are combined and shaken with 50 parts of 5% hydrochloric acid. The acid solution is decolorized and neutralized with alkali carbonate, whereupon thiamine tetrahydrofurfuryl disulfide separates out in the resinous state but soon solidifies [MP 129°C (decamp.)] . The yield is 16 parts. Recrystallization from ethyl acetate gives colorless prisms melting at 132°C (decomp.).
Therapeutic Function
Enzyme cofactor vitamin
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Fursultiamine
| Melting point: | 130-136°C (decompos.) |
| Boiling point: | 652.3±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.29 |
| refractive index | 1.6270 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, DMSO, and dimethyl formamide (DMF). |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 14.42±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 804-30-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Fursultiamine
Computed Descriptors for Fursultiamine
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 804-30-8 Fursultiamine 99%View Details
804-30-8 Fursultiamine 99%View Details
804-30-8 -
 Fursultiamine 98% (HPLC) CAS 804-30-8View Details
Fursultiamine 98% (HPLC) CAS 804-30-8View Details
804-30-8 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
