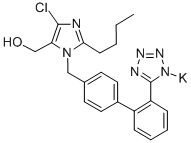
Losartan potassium
Synonym(s):2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2′-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]- 1H-Imidazole-5-methanol potassium salt;2-Butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2′-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-yl]methyl}-1H-imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt;Losartan potassium;Potassium 5-(4′-((2-butyl-4-chloro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)tetrazol-1-ide
- CAS NO.:124750-99-8
- Empirical Formula: C22H23ClKN6O
- Molecular Weight: 462.01
- MDL number: MFCD02092704
- EINECS: 200-287-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
What is Losartan potassium?
Description
Losartan potassium is the first potent and selective non-peptide angiotensin II (AT II) AT1 receptor antagonist introduced to the market as a once-daily oral antihypertensive. It is efficacious and long lasting in controlling blood pressure in spontaneous hypertensive rats, in patients with essential hypertension in addition to those patients with renal impairment. Since losartan functions by competitive antagonism at the level of receptor, which represents the most direct way of selectively inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) independent of the source of AT II, its use has been reported to be free of the coughing side effect exhibited by the ACE inhibitors. In contrast to calcium channel blockers, losartan does not appear to cause ankle edema, headache and tachycardia. It is also reported to be in clinical trials for the treatment of heart failure. Other reports indicate that losartan may have potential efficacy as an anxiolytic, an antiglaucoma agent, in addition to in providing protection against stroke and in preventing the myointimal proliferative response of the vascular wall after coronary angioplasty and surgery.
Description
Angiotensin II is a hormone that plays an important role in regulating blood pressure. Elevated levels of angiotensin II are implicated in inducing and maintaining hypertension, and also in the development of atherosclerosis. Both of these effects are mediated by the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor. Losartan is an AT1 receptor antagonist with a Ki value of 5-
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Crystalline Powder
Originator
DuPont Merck (U.S.A.)
The Uses of Losartan potassium
A nonpeptide angiotensin II AT1-receptor antagonist. Antihypertensive.
The Uses of Losartan potassium
antihypertensive, AT1 angiotensin II antagonist
The Uses of Losartan potassium
Coronary vasodilator used in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease (adenosine A2A agonist).
What are the applications of Application
Losartan Potassium is a specific antagonist of the AT1 receptor with significant downstream effects.
Manufacturing Process
2-Butyl-4-chloro-1-(2'-(tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)-1H-imidazole-5- methanolpotassium was synthesized in 5 stages.
1. Methyl 4'-methylbiphenyl-2-carboxylate (44.2 mmol), 0.5 N KOH in methanol (133 mmol), and water (50 mL) were mixed and refluxed under nitrogen. After 5 hours, the solvent was removed in vacuo and water (200 mL) and ethyl acetate (200 mL) added. The aqueous layer was acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid to a pH of 3 and the layers were separated. The aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate, the organic layers collected, dried (MgSO4) and the solvent removed in vacuo to yield 8.71 g of a 4'-methylbiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid, melting point 140.0-145.0°C.
2. 4'-Methylbiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (41 mmol) and thionyl chloride (411 mmol) were mixed and refluxed for 2 hours. The excess thionyl chloride was removed in vacuo and the residue was taken up in toluene. The toluene was removed by rotary evaporation. The crude acid chloride was then added slowly to cold (0°C) concentrated NH4OH (50 mL) so that the temperature was kept below 15°C. After 15 minutes of stirring, water (100 mL) was added and solids precipitated. These were collected, washed with water and dried under high vacuum over P2O5 to yield 7.45 g of a white solid, melting point 126.0-128.5°C. The above product amide (35 mmol) and thionyl chloride (353 mmol) were mixed and refluxed for 3 hours. The thionyl chloride was removed using the same procedure as described above. The residue was washed with a little hexane to yield 6.64 g of 4'-methyl-2-cyanobiphenyl, melting point 44.0- 47.0°C.
3. 4'-Methyl-2-cyanobiphenyl (5.59 g) was brominated using benzoyl peroxide as an initiator. The product was recrystallized from ether to yield 4.7 g of 4'- bromomethyl-2-cyanobiphenyl, melting point 114.5-120.0°C.
4. 4'-Bromomethyl-2-cyanobiphenyl (4.6 g) was alkylated onto 2-n-butyl-4-
chloro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-imidazole. For separation of the product was used a
flash chromatography in 1:1 hexane/ethyl acetate over silica gel. The
regioisomeric products yielded 2.53 g of the faster eluting isomer.
Recrystallization from acetonitrile yielded 1.57 g of analytically pure 2-n-butyl4-chloro-1-[2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)-imidazole,
melting point 153.5 -155.5°C.
5. 2-n-Butyl-4-chloro-1-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)-methyl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)-
imidazole (10 mmole), sodium azide (10 mmol), and ammonium chloride (30
mmol) were mixed in DMF (150 mL) under N2 at 100°C for 2 days, after
which the temperature was raised to 120°C for 6 days. The reaction was
cooled and 3 more equivalents each of ammonium chloride and sodium azide
were added. The reaction was again heated for 5 days at 120°C. The reaction
was cooled, the inorganic salts filtered, and the filtrate solvent removed in
vacuo. Water (200 mL) and ethyl acetate (200 mL) were added to the residue
and the layers were separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl
acetate, the organic layers were collected, dried (MgSO4) and the solvent
removed in vacuo, to yield a dark yellow oil. The product was purified by flash
chromatography in 100% ethyl acetate to 100% ethanol over silica gel to
yield 5.60 g of a light yellow 2-n-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1Htetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl]imidazole. Recrystallization from acetonitrile
yielded 4.36 g of light yellow crystals which still melted broadly. The crystals
were taken up in 100 mL of hot acetonitrile. The solid that did not dissolve
was filtered off to yield 1.04 g of product as a light yellow solid, melting point
of 2-n-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-
yl)methyl]imidazole 183.5-184.5°C.
2-n-Butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-
yl)methyl]imidazole may be converted to potassium salt.
brand name
Cozaar (Merck).
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
Biological Activity
Selective non-peptide angiotensin AT 1 receptor antagonist. Inhibits the contractile effects of angiotensin II on rabbit aorta and jugular vein (pA 2 = 8.27). Orally active antihypertensive agent.
Chemical properties
Losartan potassium is a white to off-white free-flowing crystalline powder.Oxidation of the 5-hydroxymethyl group on the imidazole ring results in the active metabolite of losartan.
Metabolism
Losartan potassium is an orally active agent that undergoes substantial first-pass metabolism by cytochrome P450 enzymes. It is converted, in part, to an activecarboxylic acid metabolite that is responsible for most of the angiotensin II receptor antagonism that follows losartan treatment. About 14% of an orally-administereddose of losartan is converted to the active metabolite. In addition to the active carboxylic acid metabolite, several inactive metabolites are formed. In vitro studiesindicate that cytochrome P450 2C9 and 3A4 are involved in the biotransformation of losartan to its metabolites.
Side Effects
Side effects of Losartan potassium include:
diarrhea
stomach pain
muscle cramps
leg or back pain
dizziness
headache
sleep problems (insomnia)
tiredness, and
cold or flu symptoms such a stuffy nose, sneezing,sore throat, fever, and cough
Storage
RT (desiccate)
References
1) Merck 14:5583 2) Chiu et al. (1990), Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. VII. Cellular and biochemical pharmacology of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 252 711 3) McIntyre et al. (1997), Losartan, an orally active angiotensin (AT1) receptor antagonist: a review of it’s efficacy and safety in essential hypertension; Pharmacol. Ther., 74 181 4) Diop-Frimpong et al. (2011), Losartan inhibits collagen I synthesis and improves the distribution and efficacy of nanotherapeutics in tumors; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 108 2909 5) Pantazi et al. (2015), Losartan activates sirtuin 1 in rat reduced-size orthotopic liver transplantation; World J. Gastroenterol., 21 8021 6) Kumar et al. (2015), Neuroprotective mechanism of losartan and its interaction with nimesulide against chronic fatigue stress; Inflammopharmacology, 23 291 7) Miguel-Carrasco et al. (2017), Mechanisms underlying the cardiac antifibrotic effects of losartan metabolites; Sci. Rep. 7 41865
Properties of Losartan potassium
| Melting point: | 263-265°C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Freely soluble in water and in methanol, slightly soluble in acetonitrile. |
| form | powder or crystals |
| color | Off-white |
| Merck | 14,5583 |
| BRN | 5845770 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 2 months. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C22H22ClN6O.K/c1-2-3-8-20-24-21(23)19(14-30)29(20)13-15-9-11-16(12-10-15)17-6-4-5-7-18(17)22-25-27-28-26-22;/h4-7,9-12,30H,2-3,8,13-14H2,1H3;/q-1;+1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 124750-99-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Losartan potassium
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P312:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Losartan potassium
| InChIKey | OXCMYAYHXIHQOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(C=CC=CC=1C1=CC=C(CN2C(CO)=C(Cl)N=C2CCCC)C=C1)C1=NN=NN1[K] |
Losartan potassium manufacturer
Jai Radhe Sales
Indexim International
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Losartan Potassium 99%View Details
Losartan Potassium 99%View Details -
 LOSARTAN POTASSIUM 99%View Details
LOSARTAN POTASSIUM 99%View Details -
 Losartan potassium 99%View Details
Losartan potassium 99%View Details -
 Losartan potassium 98%View Details
Losartan potassium 98%View Details -
 Losartan potassium 98%View Details
Losartan potassium 98%View Details -
 Losartan Potassium Api ManufacturersView Details
Losartan Potassium Api ManufacturersView Details
124750-99-8 -
 Losartan Potassium Api, Grade Standard: IPView Details
Losartan Potassium Api, Grade Standard: IPView Details
124750-99-8 -
 Losartan Potassium IP/BP/USP, 114798-26-4, Packaging Size: 10View Details
Losartan Potassium IP/BP/USP, 114798-26-4, Packaging Size: 10View Details
114798-26-4
