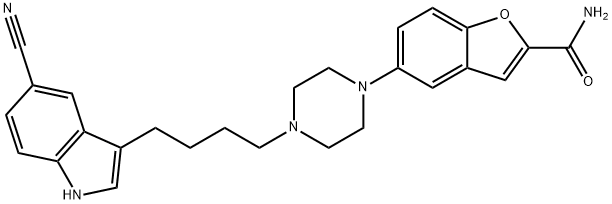
Mirabegron
Synonym(s):2-(2-Amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-N-[4-[2-[((2R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino]ethyl]phenyl]acetamide;2-Amino-N-[4-[2-[[(2R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]-4-thiazoleacetamide;YM 178;YM178(R)-Mirabegron
- CAS NO.:223673-61-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H24N4O2S
- Molecular Weight: 396.51
- MDL number: MFCD11100356
- EINECS: 800-126-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-06 10:15:11
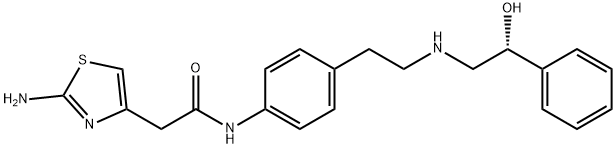
What is Mirabegron?
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of orally administered mirabegron ranges from 29% at a dose of 25 mg to 35% at a dose of 50 mg. The Tmax for the extended-release tablet and suspension formulations are approximately 3.5 hours, while the Tmax for the granule formulation is 4-5 hours. Both Cmax and AUC increase more than dose proportionally - an increase in dose from 50mg to 100mg results in a 2.9- and 2.6-fold increase in Cmax and AUC, respectively, whereas an increase from 50mg to 200mg results in a 8.4- and 6.5-fold increase in Cmax and AUC, respectively.
Steady-state concentrations of mirabegron are achieved after approximately 7 days of once-daily administration.
Toxicity
At doses of up to 400mg in healthy volunteers (~8x the recommended maximum), reported symptoms of overdose included palpitations and increased heart rate. Symptoms of chronic overdosage are similar in presentation and may also include a rise in systolic blood pressure. In cases of overdosage, employ standard symptomatic and supportive measures in addition to ECG monitoring.
Description
Betanis (Mirabegron) was approved in July 2011 by the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare for the treatment of urgency, urinary frequency, and urinary urge urinary incontinence associated with overactive bladder (OAB). Mirabegron is synthesized by coupling 4-nitrophenethyl amine to (R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid. The resulting amide is reduced to an amine. The nitro group is then reduced and the resulting aniline is coupled to 2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl) acetic acid to give mirabegron. Mirabegron has an EC50 of 22 nM (intrinsic activity=0.8) for β3-AR with no detectable activity for β1- andβ2-AR (EC50>10,000 nM). In an anesthetized rat rhythmic bladder contraction model in which bladder contractions are induced by saline, mirabegron at 3 mg/kg iv decreased the frequency of rhythmic bladder contraction without suppressing contraction amplitude. These data suggest that the activation of β3-AR increases bladder capacity without influencing the frequency of bladder contraction.
Description
Mirabegron, a compound with multiple functional groups, is the active ingredient of drugs used for treating an overactive bladder. It is sold under the trade names Myrbetriq and Betmiga, both marketed by Astellas Pharma (Tokyo).
Mirabegron activates the β3 adrenergic receptor in the detrusor muscle of the bladder. Activating the receptor relaxes the muscle, allowing the bladder to accommodate a greater quantity of urine.
The drug, however, is not without adverse side effects. The most common is elevated blood pressure; but there are many others, including dry mouth, susceptibility to colds, and urinary tract infection.
Although mirabegron is taken orally, one of the hazards listed in its safety data sheets (see hazard information box) is oral toxicity. But the medicine is not toxic unless the patient consumes 5–10 times the normally prescribed dosage.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Astellas Pharma Inc. (Japan)
The Uses of Mirabegron
Mirabegron is a selective β3-adrenoceptor agonist with EC50 of 22.4 nM.
The Uses of Mirabegron
A potent bladder relaxant compound
The Uses of Mirabegron
Potent bladder relaxant and reagent for diabetes remedy.;Labeled Mirabegron, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Mirabegron by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
Background
Mirabegron is a sympathomimetic beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonist used to relax the smooth muscle of the bladder in the treatment of urinary frequency and incontinence. It is unique amongst overactive bladder treatment options in that, unlike other treatments such as solifenacin and darifenacin, it lacks significant antimuscarinic activity, which is responsible both for the therapeutic effects of these medications and their broad range of adverse effects. Mirabegron has a comparatively favorable adverse effect profile as compared to other available treatment options, and its complementary mechanism to the antimuscarinics that came before it allows for its use alongside solifenacin in refractory cases.
Mirabegron first received FDA approval in 2012, under the brand name Myrbetriq, for the treatment of adults with overactive bladder. An extended-release granule formulation was subsequently granted approval in March 2021 for the treatment of pediatric patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Mirabegron is also used in other jurisdictions across the globe, including Canada, the EU, and Japan.
Indications
Mirabegron is indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB) - with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency - either alone or in combination with solifenacin. It is also indicated for the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older and weighing 35kg or more.
What are the applications of Application
Mirabegron is a β3-AR (β3 adrenergic receptor) agonist of bladder muscles
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-ylacetic acid with the anilino group of (1R)-2-{[2-(4-aminophenyl)ethyl]amino}-1-phenylethanol. Used for the treatment of overactive ladder syndrome.
brand name
Betanis
Pharmacokinetics
Mirabegron exerts its pharmacologic effects by inducing relaxation of bladder smooth muscle, consequently expanding its capacity and alleviating urgency in patients with overactive bladder syndrome. Although it does not seem to adversely affect the mean maximum flow rate or mean detrusor pressure at maximum flow rate in individuals with lower urinary tract symptoms and bladder outlet obstruction (BOO), caution is advised when administering mirabegron to patients with BOO due to reported cases of significant urinary retention. Moreover, mirabegron demonstrates a dose-dependent increase in both blood pressure and heart rate, necessitating careful consideration when prescribing to patients with severely uncontrolled hypertension or those vulnerable to the potential risks associated with such physiological changes.
Clinical Use
Mirabegron is an orally active β3-adrenoceptor agonist currently in development by Astellas Pharma for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB). The drug is a nanomolar EC50 antagonist against human β3-AR biochemical assays with good selectivity over b1- and β2-ARs. Mirabegron demonstrates a novel mechanism by targeting the β3-AR for bladder relaxation to help manage OAB symptoms such as increased urinary urgency and frequency and urgency incontinence. However, mirabegron is a cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitor, and it raises a concern for drug–drug interaction with concomitant administration of other cytochrome P450 2D6 substrates.
Synthesis
The synthesis of mirabegron began with a condensation reaction between (R)-styrene oxide (182) and 4-nitrophenylethylamine (183) in refluxing isopropanol to yield corresponding aminoalcohol 184 in 22% yield. Aminoalcohol 184 was protected as its N-Boc derivative with t-butyl dicarbonate in THF in 96% yield, and this was followed by nitro group hydrogenative reduction with 10% Pd/C to give free amine 185 in 96% yield. Aniline 185 was coupled with 2-amino-4-thiazolyl acetic acid 186 in the presence of EDCI and HOBt to give amide 187 in 85% yield. Removal of the Boc group was affected with 4 N HCl solution in a 2:1 volume ratio in ethyl acetate to obtain mirabegron HCl in 52% yield. The HCl salt was neutralized with 1 N NaOH to deliver mirabegron (XVII).

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous
interactions with other drugs
None known
Metabolism
Mirabegron is extensively metabolized via a number of mechanisms, although unchanged parent drug is still the major circulating component following oral administration. Presumed metabolic pathways and their resultant metabolites include amide hydrolysis (M5, M16, M17), glucuronidation (mirabegron O-glucuronide, N-glucuronide, N-carbamoylglucuronide, M12), and secondary amine oxidation or dealkylation (M8, M9, M15), amongst others. The enzymes responsible for the oxidative metabolism of mirabegron are thought to be CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, while the UDP-glucuronosyltransferases responsible for conjugation reactions have been identified as UGT2B7, UGT1A3, and UGT1A8. Other enzymes that may be involved in the metabolism of mirabegron include butylcholinesterase and possibly alcohol dehydrogenase.
Metabolism
Metabolised via multiple pathways involving dealkylation, oxidation, (direct) glucuronidation, and amide hydrolysis. Renal elimination of mirabegron is primarily through active tubular secretion along with glomerular filtration.
Storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of Mirabegron
| Melting point: | 138-140°C |
| Boiling point: | 690.0±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.313 |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly, Heated), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| appearance | white to off-white crystals or powder |
| pka | 13.51±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Pale Yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 223673-61-8 |
Safety information for Mirabegron
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Mirabegron
| InChIKey | PBAPPPCECJKMCM-IBGZPJMESA-N |
| SMILES | S1C=C(CC(NC2=CC=C(CCNC[C@H](O)C3=CC=CC=C3)C=C2)=O)N=C1N |
Mirabegron manufacturer
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Mirabegron 99%View Details
Mirabegron 99%View Details -
 Mirabegron Intermediates 98%View Details
Mirabegron Intermediates 98%View Details -
 Mirabegron 97%View Details
Mirabegron 97%View Details -
 MIRABEGRON 98%View Details
MIRABEGRON 98%View Details -
 Mirabegron 98%View Details
Mirabegron 98%View Details -
 Mirabegron 99%View Details
Mirabegron 99%View Details -
 Mirabegron 99%View Details
Mirabegron 99%View Details -
 Mirabegron 98%View Details
Mirabegron 98%View Details
