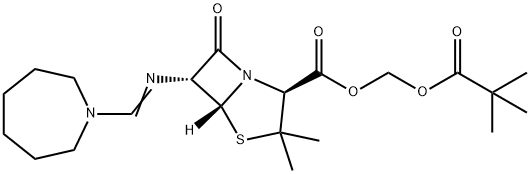
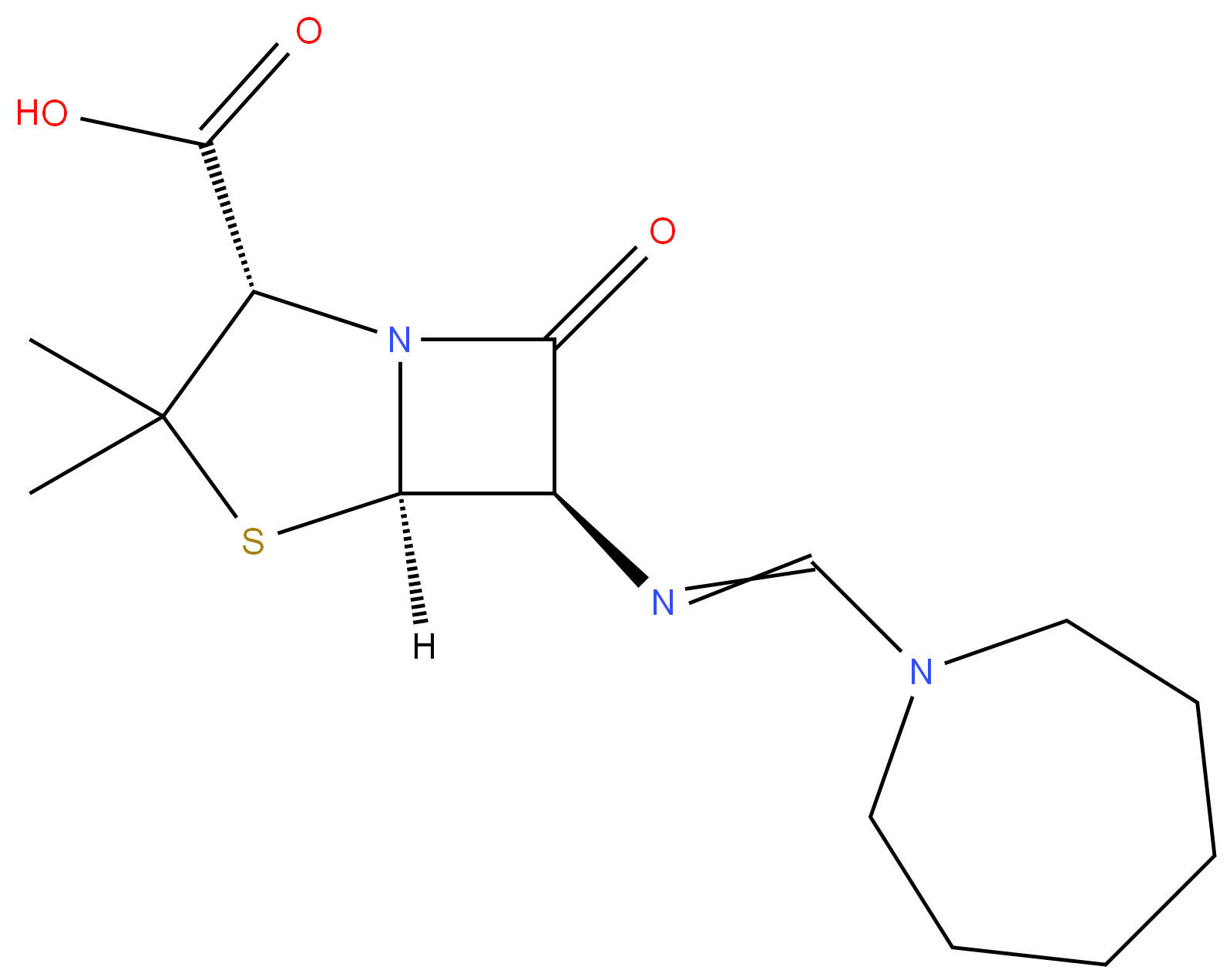
Mecillinam
- CAS NO.:32887-01-7
- Empirical Formula: C15H23N3O3S
- Molecular Weight: 325.43
- MDL number: MFCD00056869
- EINECS: 251-277-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
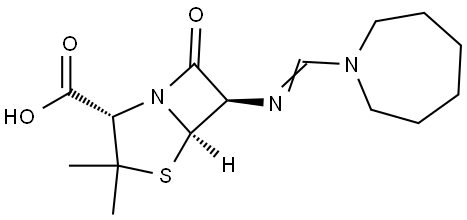
What is Mecillinam?
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Selexidin,Leo,UK,1979
The Uses of Mecillinam
Mecillinam (amidinocillin) is a penicillin nucleus (6 APA) derivative, active in vitro against most aerobic and anaerobic Gram-negative bacilli, including E. coli and B. fraglis, but not active against Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus, or Pseudomonas. Mecillinam is synergistic with other beta-lactam drugs and therefore can be used in combination to treat severe Gram-negative infections. Although its in vitro efficacy is convincing, there are not enough clinical trials to support its use for intra-abdominal infections.
The Uses of Mecillinam
Active antibacterial against gram-negative bacteria
The Uses of Mecillinam
Effective against Gram-negative bacteria
What are the applications of Application
Amdinocillin is an antibacterial compound
Definition
ChEBI: Mecillinam is a penicillin in which the 6beta substituent is [(azepan-1-yl)methylidene]amino; an extended-spectrum penicillin antibiotic that binds specifically to penicillin binding protein 2 (PBP2), and is only considered to be active against Gram-negative bacteria. It has a role as an antibacterial drug and an antiinfective agent.
Manufacturing Process
The starting material N-formylhexamethyleneimine was prepared from hexamethyleneimine and chloral.
12.7 g of N-formylhexamethyleneimine were dissolved in 250 ml of dry ether.
While stirring and cooling, 8.5 ml of oxalyl chloride in 50 ml of dry ether were
added dropwise, whereafter the mixture was stirred overnight at room
temperature. The precipitated amide chloride was filtered off and washed with
dry ether, and was placed in an exsiccator.
A solution of the amide chloride (4.6 g) in dry, alcohol-free chloroform (20 ml)
was added slowly to a solution of trimethylsilyl 6-amino-penicillanate (7.2 g)
and triethylamine (3.5 ml) in dry, alcohol-free chloroform (50 ml) with stirring
and cooling to -70°C. The temperature was raised to 0°C during 1.5 hours.
The solution was evaporated to dryness in vacuo and the residue was
triturated with dry ether (200 ml). The precipitate was filtered off and washed
with dry ether. The filtrate was diluted with ether (200 ml). 2-Butanol (2.8 ml)
was added dropwise with stirring and cooling to 0°C. The stirring was
continued for 1/4 hour at 0°C, whereupon the precipitate was filtered off,
washed with ether and dried. It was a white, amorphous powder, soluble in
water.
brand name
Coactin (Roche).
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Antimicrobial activity
The antibacterial spectrum differs greatly from that of the
aminopenicillins in that the compound displays high activity
against many Gram-negative bacteria but limited activity
against Gram-positive organisms.
Mecillinam is active against many Enterobacteriaceae due to
its selective binding to PBP 2, although the susceptibility of
Proteus and Providencia spp. is variable. H. influenzae is less susceptible
than enteric bacilli, and Acinetobacter spp., B. fragilis
and Ps. aeruginosa are resistant.
It is readily inactivated by many β-lactamases, although it
is more stable than ampicillin.
Acquired resistance
Intrinsic resistance in susceptible species of enterobacteria is uncommon and many ampicillin-resistant strains are susceptible. Bacteria that are resistant to both ampicillin and mecillinam are usually those producing large amounts of β-lactamase, most commonly plasmid-mediated enzymes.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption (pivmecillinam): c. 75%
Cmax 200 mg intravenous infusion: 12 mg/L end infusion
200 mg intramuscular: c. 6 mg/L after 45 min
400 mg oral (pivmecillinam): 2–5 mg/L after c. 1 h
Plasma half-life: 50 min
Volume of distribution: 0.2–0.4 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: 5–10%
Absorption
Oral absorption is very poor, with conventional doses producing plasma levels of <1 mg/L and recovery of only about 5% in the urine. A 400 mg dose of the pivaloyl ester is equivalent to 273 mg mecillinam. It is relatively well absorbed and rapidly liberates the parent compound. Metabolism and excretion
The amidino side chain undergoes spontaneous aqueous hydrolysis to the N-formyl derivative, which retains some antibacterial activity. Hydrolysis of the β-lactam ring also occurs.
Approximately 60% is excreted unchanged in the urine in the first 6 h, achieving concentrations exceeding 1 g/L. The concentration in bile can reach 40 or 50 mg/L in patients with normally functioning gallbladders treated with 800 mg intramuscularly.
Clinical Use
Urinary tract infection (pivmecillinam)
Other infections with susceptible Gram-negative bacilli (usually in
combination with other agents)
Side Effects
It is generally well tolerated, and serious anaphylactic responses are said to be rare. Nausea and vomiting, which may be persistent, occur with diarrhea in some patients treated with pivmecillinam.
Properties of Mecillinam
| Melting point: | 156°C |
| Boiling point: | 551℃ |
| alpha | D20 +285° (c = 1 in 0.1N HCl) |
| Density | 1.44±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| pka | pKa 3.40 (Uncertain) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water at approximately 1mg/ml |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 32887-01-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Mecillinam
Computed Descriptors for Mecillinam
Mecillinam manufacturer
VIVAN Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Medec Dragon Private Limited
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Amdinocillin 98%View Details
Amdinocillin 98%View Details -
 32887-01-7 Amdinocillin 99%View Details
32887-01-7 Amdinocillin 99%View Details
32887-01-7 -
 Mecillinam CAS 32887-01-7View Details
Mecillinam CAS 32887-01-7View Details
32887-01-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1