Magnesium stearate
Synonym(s):Stearic acid magnesium salt
- CAS NO.:557-04-0
- Empirical Formula: C36H70MgO4
- Molecular Weight: 591.24
- MDL number: MFCD00036391
- EINECS: 209-150-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:52
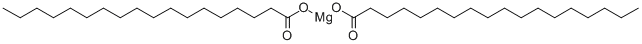
What is Magnesium stearate ?
Description
Magnesium stearate (MgSt), a magnesium salt composed of stearic acid and magnesium, is a common food additive and inactive ingredient (excipient) in pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements, such as capsules, tablets, and powders. In foods, it prevents powders from clumping and emulsifies ingredients. In cosmetics, it provides a smooth texture and improves product adhesion and spreadability.
Chemical properties
Magnesium stearate is a fine, off-white precipitate or ground powder with a light, thin texture and low bulk density. It has a faint stearic acid odor and characteristic taste. The powder has a greasy feel and adheres easily to the skin. It is insoluble in water, alcohol, and ether and is non-flammable.
The Uses of Magnesium stearate
Magnesium stearate is widely used in food supplements, pharmaceutical excipients, and cosmetic emulsifiers. It functions as a lubricant, binder, emulsifier, and anti-caking agent. It is commonly used as an anti-adhesive agent in medical tablets, capsules, and powders; as a lubricant or release agent in compressed candies; and as a common ingredient in infant formula. In cosmetics, it can be used to prevent clumping in pressed powder and mascara and improve product color and texture. It can also be used in combination with calcium soap as a stabilizer for polyvinyl chloride.
Definition
Mg(C18H35O2)2 or with one H2O. Technical grade contains small amounts of the oleate and 7% magnesium oxide, MgO.
Production Methods
Magnesium stearate is prepared either by the interaction of aqueous solutions of magnesium chloride with sodium stearate or by the interaction of magnesium oxide, hydroxide, or carbonate with stearic acid at elevated temperatures.
Preparation
Magnesium stearate is created by the reaction of sodium stearate with magnesium sulfate.
General Description
Magnesium stearate (Mg-St) is the magnesium salt of stearic acid. Its anhydrate, dihydrate and trihydrate forms have been prepared. The tabletting of the blends of magnesium stearate and lactose granules has been described. The influence of mixing time on hardness, disintegration time and ejection force on the compressed tablets was examined. Mg-St is widely used lubricant in pharmaceutical industry. It also plays a role in delaying the process of dissolution. Its detection in tablets by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy has been proposed.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Magnesium stearate is widely used in cosmetics, foods, and pharmaceutical formulations. It is primarily used as a lubricant in capsule and tablet manufacture at concentrations between 0.25% and 5.0% w/w. It is also used in barrier creams.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Magnesium stearate is the magnesium salt of stearic acid that possess lubricating properties and hence prevents ingredients from sticking to manufacturing equipment during the compression of chemical powders into solid tablets. Dry coating of drugs with magnesium stearate leads to flow improvement, flow-aid and lubrication effects, tabletability as well as non-inhibited dissolution rate.
Safety Profile
Slightly toxic by ingestion. Spontaneously combustible. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and toxic fumes.
Safety
Magnesium stearate is widely used as a pharmaceutical excipient
and is generally regarded as being nontoxic following oral
administration. However, oral consumption of large quantities
may produce a laxative effect or mucosal irritation.
No toxicity information is available relating to normal routes of
occupational exposure. Limits for heavy metals in magnesium
stearate have been evaluated in terms of magnesium stearate worstcase
daily intake and heavy metal composition.
Toxicity assessments of magnesium stearate in rats have
indicated that it is not irritating to the skin, and is nontoxic when
administered orally or inhaled.
Magnesium stearate has not been shown to be carcinogenic
when implanted into the bladder of mice.
LD50 (rat, inhalation): >2 mg/L
LD50 (rat, oral): >10 g/kg
Storage
Magnesium stearate is stable and should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong acids, alkalis, and iron salts. Avoid mixing with strong oxidizing materials. Magnesium stearate cannot be used in products containing aspirin, some vitamins, and most alkaloidal salts.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in the USA and UK. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral capsules, powders, and tablets; buccal and vaginal tablets; topical preparapreparations; intravitreal implants and injections). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. Listed on the US TSCA inventory.
Properties of Magnesium stearate
| Melting point: | 200 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.028g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | alcohol: insoluble |
| form | Fine Powder |
| color | White |
| PH | 7 (H2O) (slurry) |
| Odor | wh. soft oily powd., tasteless, odorless |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| Merck | 14,5690 |
| BRN | 3919702 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 3 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 557-04-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Magnesium stearate (557-04-0) |
Safety information for Magnesium stearate
Computed Descriptors for Magnesium stearate
| InChIKey | DRJIJXNWSSRTTE-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Magnesium stearate manufacturer
Shanpar Industries Private Limited
Vasa Pharmachem Pvt Ltd. (VPPL)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Magnesium Stearate 98%View Details
Magnesium Stearate 98%View Details -
 MAGNESIUM STEARATE 99%View Details
MAGNESIUM STEARATE 99%View Details -
 Magnesium Stearate 99%View Details
Magnesium Stearate 99%View Details -
 Magnesium Stearate 99%View Details
Magnesium Stearate 99%View Details -
 Magnesium Stearate 99%View Details
Magnesium Stearate 99%View Details -
 Magnesium stearate 98%View Details
Magnesium stearate 98%View Details -
 Magnesium stearate 98%View Details
Magnesium stearate 98%View Details -
 Magnesium Stearate CASView Details
Magnesium Stearate CASView Details
