Magnesium bromide
- CAS NO.:7789-48-2
- Empirical Formula: Br2Mg
- Molecular Weight: 184.11
- MDL number: MFCD00011105
- EINECS: 232-170-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
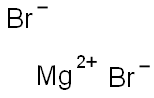
What is Magnesium bromide?
Chemical properties
Magnesium Bromide is a colorless, very deliquescent crystals or white solid; bitter taste. Soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol. It formed by reaction of magnesium carbonate and hydrobromic acid.
Physical properties
The anhydrous MgBr2 is a white crystalline substance; hexagonal crystals; deliquescent; density 3.72 g/cm3; melts at 700°C; highly soluble in water (101.5g/100mL at 20°C); moderately soluble in methanol and ethanol (21.8 and 6.9 g/mL at 20°C, respectively).
The hexahydrate, MgBr2.6H2O consists of colorless monoclinic crystals; bitter taste; hygroscopic; fluoresce in x-rays; density 2.07 g/cm3; melts at 172.4°C; intensely soluble in water, 316 g/100 mL at 0°C; dissolves in methanol and ethanol; slightly soluble in ammonia solution.
Occurrence
Magnesium bromide occurs in seawater, some mineral springs, natural brines, inland seas and lakes such as the Dead Sea and the Great Salt Lake, and salt deposits such as the Stassfurt deposits. In seawater, it is the primary source of bromine. By the action of chlorine gas upon seawater or seawater bitterns, bromine is formed. It is an electrolyte component in certain dry cells. In medicine, it is a sedative and anticonvulsant for treatment of nervous disorder. It also is used in organic synthesis forming several addition compounds.
The Uses of Magnesium bromide
Magnesium Bromide is an inorganic salt used in the synthesis of superconductors and nanowires. Also present in polymer nanocomposites to improve conductivity.
What are the applications of Application
The major use of Magnesium bromide has been in the commercial production of bromine. The Dow process is an electrolytic method of bromine extraction from brine, and was Herbert Dow’s second revolutionary process for generating bromine commercially (1889).
Magnesium bromide has also been used in organic syntheses. An efficient and environmentally friendly procedure for the one-pot synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidines from aldehydes, a-diketones and urea/thiourea by using magnesium bromide as an inexpensive and easily available catalyst under solvent-free conditions has been described. Compared with the classical Biginelli reaction conditions, this new method has the advantage of good to excellent yields (74%–94%) and short reaction times (45–90 min). The structure of the Biginelli reaction product from a-diketone, salicylaldehyde and urea has been proposed to possess an oxygen bridge by cyclization (intramolecular Michael addition).
Preparation
Magnesium bromide is prepared by treating MgO
with hydrobromic acid and then crystallization
above 0.0°C in solution. The product is the hexahydrate
salt:
MgO+2HBr→MgBr2+H2O→MgBr2·6H2O
The anhydrous form may also be prepared by heating
the hexahydrate with dry HBr gas. This compound can
also be formed directly from the elements:
Mg+Br2→MgBr2
Synthesis
Magnesium bromide is prepared by treating magnesium oxide with hydrobromic acid and subsequent crystallization above 0°C. The product is hexahydrate, MgBr2.6H2O:
MgO + 2HBr → MgBr2 + H2O
The anhydrous MgBr2 may be obtained by heating the hexahydrate with dry hydrogen bromide gas. Magnesium bromide also can be made from its elements. Heating magnesium metal with bromine vapor yields the salt:
Mg + Br2 → MgBr2
Magnesium bromide, like the chloride salt, is obtained from sea water (see Magnesium and Magnesium chloride). In this process, magnesium hydroxide precipitated from sea water is neutralized with hydrobromic acid, and MgBr2 is obtained by crystallization.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from EtOH or H2O (3.3g/mL). Dry it in a vacuum at ~150o, or heat the hydrate in a stream of HCl. It is very deliquescent. [Ehrlich in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 909 1963.]
Properties of Magnesium bromide
| Melting point: | 711 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1248.47°C (estimate) |
| Density | 3.72 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly, Heated), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | Powder |
| color | off-white |
| Specific Gravity | 3.72 |
| Water Solubility | g/100g H2O: 100.6 (25°C), 125.4 (100°C); solid phase, MgBr2 ·6H2O [KRU93] |
| Merck | 13,5681 |
| Stability: | hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7789-48-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Magnesium dibromide(7789-48-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Magnesium bromide (MgBr2) (7789-48-2) |
Safety information for Magnesium bromide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Magnesium bromide
Magnesium bromide manufacturer
Faluck International
Parad Corporation Pvt Ltd
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 7789-48-2 Magnesium bromide 98%View Details
7789-48-2 Magnesium bromide 98%View Details
7789-48-2 -
 7789-48-2 98%View Details
7789-48-2 98%View Details
7789-48-2 -
 Magnesium bromide 99%View Details
Magnesium bromide 99%View Details
7789-48-2 -
 7789-48-2 MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 99%View Details
7789-48-2 MAGNESIUM BROMIDE 99%View Details
7789-48-2 -
 Magnesium bromide CAS 7789-48-2View Details
Magnesium bromide CAS 7789-48-2View Details
7789-48-2 -
 Magnesium bromide CAS 7789-48-2View Details
Magnesium bromide CAS 7789-48-2View Details
7789-48-2 -
 Magnesium bromide CAS 7789-48-2View Details
Magnesium bromide CAS 7789-48-2View Details
7789-48-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1