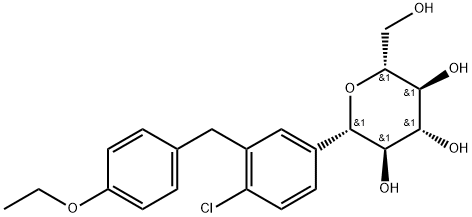
LX-4211
- CAS NO.:1018899-04-1
- Empirical Formula: C21H25ClO5S
- Molecular Weight: 424.94
- MDL number: MFCD22493506
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 17:20:10
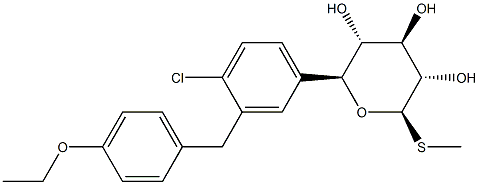
What is LX-4211?
Absorption
Following a single dose, the Tmax of sotagliflozin ranged from 1.25 to 3 hours. Following multiple doses, the Tmax ranged from 2.5 to 4 hours. The estimated oral bioavailability of sotagliflozin is 71%.
Toxicity
Multiple doses of 800mg once daily (double the maximum recommended dose) have been administered to healthy volunteers without evidence of overdose symptoms. In the event of a suspected overdose, administer supportive treatment as clinically indicated.
The Uses of LX-4211
Sotagliflozin is used for the treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Background
Sotagliflozin is a dual inhibitor of SGLT1 and SGLT2, the first of its kind, which is approved for use in the EU, in combination with insulin, to improve glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and a BMI ≥27 kg/m2. Its potency in inhibiting SGLT2 is similar to that of other SGLT2 inhibitors, such as canagliflozin and dapagliflozin, but its potency in inhibiting SGLT1 is >10-fold higher than its predecessors. The added inhibition of intestinal SGLT1 delays glucose absorption in the distal small intestine and colon, thereby reducing post-prandial glucose levels.
Sotagliflozin was approved by the EMA under the brand name "Zynquista" on April 26, 2019, for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. A similar approval has also been sought in the US, but the FDA has since published a proposal to refuse the approval because the data submitted did not show that it was safe under the proposed conditions of use. On March 22, 2022, the marketing authorization of sotagliflozin for the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus was withdrawn by the EMA due to commercial reasons.
In May 2023, sotagliflozin was approved by the FDA to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure in patients with high risk factors.[]
Indications
In the US, sotagliflozin is indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure in adults with heart failure, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, and other cardiovascular risk factors.
Pharmacokinetics
Sotagliflozin exerts its pharmacologic effects by slowing glucose absorption in the gastrointestinal tract and increasing the excretion of glucose in the urine. It is administered by mouth once daily before the first meal of the day.
The use of SGLT2 inhibitors, including sotagliflozin, can cause diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Patients, especially those with a higher baseline risk of DKA, should be instructed on how and when to monitor for ketoacidosis and what actions to take when DKA is suspected.
SGLT2 inhibitors, including sotagliflozin, also increase the risk of genital infections. This is due to the increase in urinary glucose excretion, which provides a relatively glucose-rich environment in which infectious agents may establish themselves.
Clinical Use
Two of the current SGLT-2 inhibitors (canagliflozin and LX-4211) have effects on SGLT-1. LX-4211 is a dual SGLT1/2 inhibitor and higher doses of canagliflozin transiently inhibit SGLT-1 in the gut due to high canagliflozin concentrations within the intestinal lumen during the period of drug absorption.
Synthesis
Sotagliflozin is a dual SGLT-1/SGLT-2 inhibitor which is currently under development by Lexicon Pharmaceuticals (phase III). It follows a similar strategy to ertugliflozin, i.e. aryl addition on an acyclic precursor. The synthesis starts from L-xylose 53, and the aryl moiety (same aryl moiety as for dapagliflozin) is introduced on an amide derivative (morpholine amide 54) via Grignard addition. A subsequent transformation leads to the sotagliflozin (Scheme 10). The overall yield of the synthesis is around 30%.

Sotagliflozin synthesis
Metabolism
The major metabolite of sotagliflozin is a 3-O-glucuronide (M19), which comprised ~94% of of the radioactivity in plasma following the oral administration of a radiolabeled dose of sotagliflozin. The M19 metabolite is effectively inactive, with >275-fold less activity at SGLT1 and SGLT2 compared to the parent drug.
The primary route of metabolism is via glucuronidation by UGT1A9 (and both UGT1A1 and UGT2B7, to a lesser extent) as well as oxidation via CYP3A4.
Properties of LX-4211
| Boiling point: | 607.9±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.37±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO:84.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);197.67(Max Conc. mM) Ethanol:17.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);40.01(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 12.87±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for LX-4211
Computed Descriptors for LX-4211
LX-4211 manufacturer
New Products
1-Amino-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid N-Boc-2-bromoethylamine 2-Hydroxy-N-methylacetamide ELECTROLYTIC IRON POWDER 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride Decanonitrile tert-butyl 4-(1H-benzo[d]iMidazol-2-yl)piperidine-1-carboxylate N,N'-diallyl-1,3-diaminopropanedihydrochloride 3-Iodo-6-nitroindazole Cyclopropanamine hydrochloride 4-methoxybenzylbromide (3,5-dibromophenyl)methanamine 2-chloro-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 6-bromo-5-cyano quinoline 5-Bromo-2-chloro-3-methoxypyridine 2,5-dibromopyridine terephthalonitrile 5-Bromo-4-chloro-2(1h)-pyridinone, 5-Fluoro-2-Oxindole N-Vinylformamide 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSU Chloro UracilRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![D-Glucitol, 1,5-dideoxy-1,5-epithio-1-C-[5-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)Methyl]-2-Methoxy-4-Methylphenyl]-, (1S)-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/898537-18-3.gif)
You may like
-
 615-42-9 1,2-Diiodobenzene 98%View Details
615-42-9 1,2-Diiodobenzene 98%View Details
615-42-9 -
 3-Fluoro-4-nitroaniline 2369-13-3 98%View Details
3-Fluoro-4-nitroaniline 2369-13-3 98%View Details
2369-13-3 -
 195434-34-5 Boc-Glu(OBzl)-ol 98%View Details
195434-34-5 Boc-Glu(OBzl)-ol 98%View Details
195434-34-5 -
 6-bromo-4-chloro-N-methylquinolin-3-amine 98%View Details
6-bromo-4-chloro-N-methylquinolin-3-amine 98%View Details -
 mPEG12-OH 98%View Details
mPEG12-OH 98%View Details
5702-16-9 -
 1,2-dibromo-4,5-difluorobenzene 64695-78-9 98%View Details
1,2-dibromo-4,5-difluorobenzene 64695-78-9 98%View Details
64695-78-9 -
 2-chloro-4-nitro-toluene 121-86-8 98%View Details
2-chloro-4-nitro-toluene 121-86-8 98%View Details
121-86-8 -
 602-00-6 3-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid 98%View Details
602-00-6 3-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid 98%View Details
602-00-6