LOXO-101
- CAS NO.:1223403-58-4
- Empirical Formula: C21H22F2N6O2
- Molecular Weight: 428.44
- MDL number: MFCD28902192
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
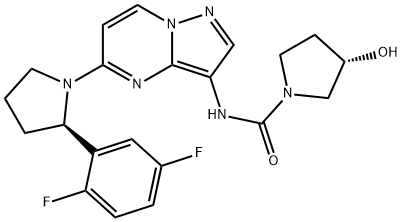
What is LOXO-101?
Absorption
The mean absolute bioavailability of larotrectinib capsules has been recorded as 34%, from a range spanning 32% to 37% . In adult patients who received larotrectinib capsules 100 mg twice daily, peak plasma levels Cmax were achieved at about one hour after dosing and steady-state was reached within the time span of three days . The mean steady-state of these administered larotrectinib capsules was Cmax 788 ng/mL and the AUC(0-24hr) was 4351 ng*h/mL . Concurrently, in healthy subjects, the AUC of the administered larotrectinib oral solution formulation was similar to that of the capsules and the particular Cmax was 36% greater with the oral solution .
The AUC of larotrectinib was similar but the Cmax was reduced by 35% after oral administration of a single 100 mg capsule of larotrectinib to healthy subjects taken with a high-fat meal (approximately 900 calories, 58 grams carbohydrate, 56 grams fat and 43 grams protein) compared to the Cmax and AUC in the fasted state .
Toxicity
Although there is no available data on larotrectinib use in pregnant women, based on literature reports in human subjects with congenital mutations leading to changes in TRK signaling, findings from animal studies, and the agent's mechanism of action it is believed that larotrectinib can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman . Published reports of individuals with congenital mutations in TRK pathway proteins suggest that decreases in TRK-mediated signaling are correlated with obesity, developmental delays, cognitive impairment, insensitivity to pain, and anhidrosis . Furthermore, animal studies data note that lacrotrectinib can cross the placenta in animals . Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus .
There are no data on the presence of larotrectinib or its metabolites in human milk and no data on its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production . Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with larotrectinib and for 1 week after the final dose .
Female patients of reproductive potential who are being treated with larotrectinib are advised to use effective contraception during larotrectinib treatment and for at least one week after the final dose . Males with female partners of reproductive potential are also advised to use effective contraception during larotrectinib therapy and for one week after the final dose .
Based on histopathological findings in the reproductive tracts of female rats in a 1-month repeated-dose study, larotrectinib use may reduce fertility in females .
The safety and effectiveness of larotrectinib in pediatric patients was established based upon data from clinical trials in adult or pediatric patients 28 days and older . The pharmacokinetics of larotrectinib in the pediatric population have also been determined to be similar to those seen in adults .
Clinical studies of larotrectinib did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects .
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A). Larotrectinib clearance was reduced in subjects with moderate (Child-Pugh B) to severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment .
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment of any severity .
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with larotrectinib . Larotrectinib was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assays, with or without metabolic activation, or in the in vitro mammalian mutagenesis assays, with or without metabolic activation . In vivo, larotrectinib was negative in the mouse micronucleus test .
Fertility studies with larotrectinib have not been conducted. In a 3-month repeat-dose toxicity study in the rat, larotrectinib had no effects on spermatogenesis at 75 mg/kg/day (approximately 7 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily dose) [FDA
Label. Additionally, larotrectinib had no histological effects on the male reproductive tract in rats or monkeys at doses resulting in exposures up to 10 times the human exposure (AUC0-24hr) at the 100 mg twice daily clinical dose .
In a 1-month repeat-dose study in the rat, decreased uterine weight and uterine atrophy were seen at 200 mg/kg/day [approximately 45 times the human exposure (AUC) at the 100 mg twice daily dose] . Fewer corpora lutea and increased incidence of anestrus were also noted at doses ≥ 60 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily dose] . There were no findings in female reproductive organs in repeat-dose studies in monkeys at exposures up to 22 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily dose .
In a 1-month repeat-dose study in the rat, decreased uterine weight and uterine atrophy were seen at 200 mg/kg/day [approximately 45 times the human exposure (AUC) at the 100 mg twice daily dose] . Fewer corpora lutea and increased incidence of anestrus were also noted at doses ≥ 60 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily dose) . Decreased fertility occurred in a juvenile animal study . There were no findings in female reproductive organs in repeat-dose studies in monkeys at exposures up to 22 times the human exposure at the 100 mg twice daily dose .
Description
LOXO-101 is an inhibitor of the tropomyosin-related kinases TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC (IC50s = 2-20 nM). It is selective for TrkA, -B, and -C over a panel of 226 kinases at 1 μM. LOXO-101 inhibits the growth of CUTO-3.29, KM12, and MO-91 patient-derived cancer cell lines (IC50s = <100, <10, and <10 nM, respectively). In vivo, LOXO-101 (60 and 200 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth in a KM12 mouse xenograft model.
Description
Larotrectinib (tradename Vitrakvi) is a cancer drug that was discovered by Array BioPharma (Boulder, CO) in the 2000s. In 2013, Array licensed it to Loxo Oncology (Stamford, CT, and South San Francisco, CA). The drug was jointly developed by Loxo (now part of Eli Lilly [Indianapolis]) and Bayer AG (Leverkusen, Germany). In 2018, the US Food and Drug Administration approved larotrectinib for treating cancer patients with a certain genetic marker.
Larotrectinib is the second drug (after Merck’s Keytruda), and the first small molecule, to be approved as a “tissue-agnostic” drug by the FDA. Tissue-agnostic means that the drug is not directed at cancers in specific organs, but rather at cancers caused by particular genetic mutations.
One type of gene mutation produces tumors resulting from the fusion of enzymes in the tropomyosin kinase (TRK) family. Larotrectinib inhibits TRK fusions and shrinks tumors produced by many types of cancer.
As always, there’s a catch. Vitrakvi is outrageously expensive. The Loxo–Bayer partnership has set the monthly wholesale acquisition cost of Vitrakvi pills at US$32,800. The price of the liquid formulation (primarily for children) is somewhat lower at $11,000. The companies justify these prices because of the rarity of patients with TRK fusion mutations.
Description
Larotrectinib, also known as LOXO-101 and ARRY-470, is a small molecule that was designed to block the ATP-binding site of the TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC, serving as a highly specific and potent inhibitor of all of the three tropomyosin kinase receptors.
The Uses of LOXO-101
Larotrectinib is a TRK Inhibitor (Tyrosine kinase inhibitor).
Background
Larotrectinib is an orally administered tropomyosin receptor kinase (Trk) inhibitor with demonstrated antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, larotrectinib binds to Trk, thereby preventing neurotrophin-Trk interaction and Trk activation, which results in both the induction of cellular apoptosis and the inhibition of cell growth in tumors that overexpress Trk. Trk, a receptor tyrosine kinase activated by neurotrophins, is mutated in a variety of cancer cell types and plays an important role in tumor cell growth and survival.
Originally discovered by Array BioPharma, the agent was ultimately licensed to Loxo Oncology in 2013. Larotrectinib is another example of innovative new cancer therapy medications that target key, specific genetic biomarker drivers of cancer rather than particular types of tumors .
Indications
Larotrectinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is currently indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with solid tumors that either a) have a neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase (NTRK) gene fusion without a known acquired resistance mutation, b) are metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and c) have no satisfactory alternative treatments or that have progressed following treatment .
At the moment, these uses of larotrectinib are only approved under the auspices of an accelerated approval by the US FDA based on overall response rate and duration of response and continuation of support for these indications may be contingent upon the verification and description of continued clinical benefit in confirmatory trials .
brand name
Vitrakvi
General Description
Class: receptor tyrosine kinase; Treatment: NTRK-altered solid tumors; Other name: ARRY-407, LOXO-101; Oral bioavailability = 25%; Elimination half-life = 2.9 h; Protein binding = 70%
Pharmacokinetics
At doses that are nine-fold greater than the recommended adult dose, larotrectinib does not elicit any QTc interval prolongation that is clinically relevant .
Clinical Use
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval to larotrectinib (Vitrakvi?) on November 26th, 2018, as a treatment for adult and pediatric patients with solid tumors that have NTRK gene fusions without a known acquired resistance mutation, are metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and have no satisfactory alternative treatments or that have progressed following treatment on. In the approval statement by FDA, a complete response rate of 22% and partial response rate of 53% were cited.
Metabolism
Larotrectinib is metabolized predominantly by the CYP3A4 isoenzymes . Following oral administration of a single [14C] radiolabeled 100 mg dose of larotrectinib to healthy subjects, unchanged larotrectinib constituted 19% and an O-linked glucuronide constituted 26% of the major circulating radioactive drug components in plasma .
References
1) Ghilardi?et al.?(2010),?Administration of a tropomyosin receptor kinase inhibitor attenuates sarcoma-induced nerve sprouting, neuroma formation, and bone cancer pain; Mol. Pain,?6?87 2) Doebele?et al.?(2015),?An Oncogenic NTRK Fusion in a Patient with Soft-Tissue Sarcoma with Response to the Tropomyosin-Related Kinase Inhibitor LOXO-101; Cancer Discov.,?5?1049 3) Landman?et al.?(2018),?Rapid response to Larotrectinib (LOXO-101) in Adult Chemotherapy-Na?ve Patients With Advanced Triple-Negative Secretory Breast Cancer Expressing ETV6-NTRK3 Fusion; Clin. Breast Cancer,?18?e267 4) Drilon?et al.?(2018),?Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion-Positive Cancers in Adults and Children; N. Engl. J. Med.,?378?731
Properties of LOXO-101
| Melting point: | unavailable |
| Density | 1.55±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | RT |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 5 mg/ml). |
| form | solid |
| pka | 8.41±0.40(Predicted) |
| appearance | yellow powder |
| color | Yellow |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 2 months. |
Safety information for LOXO-101
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for LOXO-101
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
