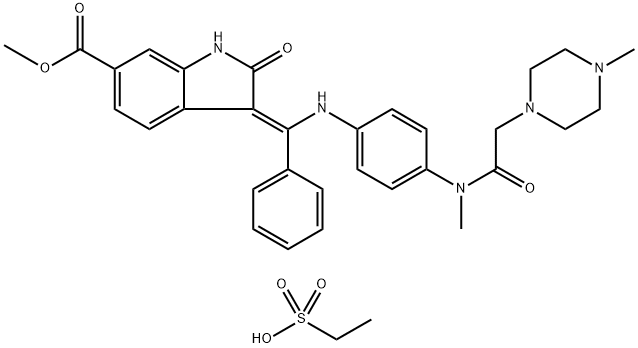
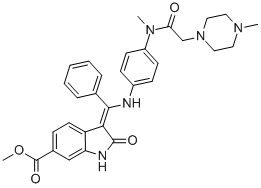
Nintedanib esylate
- CAS NO.:656247-18-6
- Empirical Formula: C33H39N5O7S
- Molecular Weight: 649.76
- MDL number: MFCD26142360
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
What is Nintedanib esylate?
Description
Nintedanib esylate is a potent, oral triple angiokinase inhibitor developed by Boehringer Ingelheim that targets proangiogenic and pro-fibrotic pathways mediated by the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, fibroblast growth factor receptor and plateletderived growth factor receptor families, as well as Src and Flt-3 kinases. It was approved for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a condition in which the lungs become progressively scarred over time, by the US FDA in October 2014 and by the EMA in January 2015. The FDA granted nintedanib esylate fast-track, priority review, orphan product, and breakthrough designations. The drug was also approved by the EMA in November 2014 for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer in combination with docetaxel after first-line chemotherapy.
The Uses of Nintedanib esylate
Nintedanib Esylate is the salt form of Nintedanib, which is angiokinase inhibitor and is used in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Also inhibits the process blood vessel formation which may be used to assist in cancer therapy.
What are the applications of Application
Nintedanib esylate is the ethanesulfonate salt form of BIBF1120
Definition
ChEBI: An organosulfonate salt obtained by combining nintedanib with one molar equivalent of ethanesulfonic acid. A kinase inhibitor used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and cancer.
Synthesis
The synthesis of indolinone 197 commenced with commercial
4-chloro-3-nitro-benzoic acid (194)?aesterification of which preceded
displacement of the chloride by dimethyl malonate (195)
in the presence of base to generate nitrobenzene 196. Hydrogenation
of 196 under acidic conditions furnished 6-methyoxycarbonyl-
substituted oxindole 197 by decarboxylative cyclization in
87% yield. Acylation of indolinone 197 with chloroacetic anhydride
in refluxing toluene and subsequent condensation with trimethyl
orthobenzoate resulted in indolone 198, which was isolated in
86% yield over the two-step sequence. While these two steps could
reportedly be combined into a one-pot protocol using acetic anhydride
as the solvent, the stepwise procedure was found to be more
amenable for large-scale synthesis due to fewer complications
with undesired side products. Subjection of 198 to methanolic
potassium hydroxide followed by condensation with aniline
fragment 199
in refluxing methanol and then exposure to aqueous ethanesulfonic
acid in methanol provided nintedanib esylate (XXIII) in 82%
over the three-step sequence.
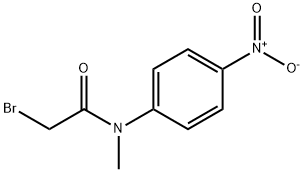
Aniline fragment 199 was prepared in three steps
and 82% overall yield via initial acylation of N-methyl-4-nitroaniline
200 with chloro acetylchloride followed by displacement of
the a-amidochloride with N-methylpiperazine and hydrogenative
reduction of the nitro group gave the desired aniline.183,184

Properties and Applications
Nintedanib esylate (NE) is used in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and in diverse cancers, including nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). NE has a pH-dependent solubility profile with low aqueous solubility under neutral pH and increased solubility at acidic pH. The oral bioavailability of NE is 4.7% because it is a P-gp substrate and also undergoes first-pass metabolism in the liver by esterases. However, the administration of NE along with food increases the area under the curve (AUC) and maximum concentration (Cmax) when the drug is taken with food; hence, it has a positive food effect[1].
References
[1] Priyanshi Patel, Mitali Patel. “Enhanced oral bioavailability of nintedanib esylate with nanostructured lipid carriers by lymphatic targeting: In vitro, cell line and in vivo evaluation.” European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 159 (2021): Article 105715.
[2] Veerareddy Arava, Surendrareddy Gogireddy. “An improved process for the synthesis of nintedanib esylate.” Synthetic Communications 47 10 (2017): Pages 975-981.
[3] Esylate, Nintedanib. “Nintedanib Esylate.” Definitions 10 1 (2020).
[4] Shabari Girinath Kala, Santhivardhan Chinni. “Bioavailability enhancement of vitamin E TPGS liposomes of nintedanib esylate: formulation optimization, cytotoxicity and pharmacokinetic studies.” Drug Delivery and Translational Research 12 11 (2022): 2856–2864.
Properties of Nintedanib esylate
| Melting point: | >233°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Yellow solid. |
| color | Light Yellow to Yellow |
Safety information for Nintedanib esylate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Nintedanib esylate
Nintedanib esylate manufacturer
LUPA PHARMACEUTICALS
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![1,3-DiMethyl 2-[4-(Methoxycarbonyl)-2-nitrophenyl]propanedioate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/1160293-27-5.gif)


You may like
-
 656247-18-6 Nintedanib esylate 98%View Details
656247-18-6 Nintedanib esylate 98%View Details
656247-18-6 -
 656247-18-6 98%View Details
656247-18-6 98%View Details
656247-18-6 -
 656247-18-6 Nintedanib esylate 98%View Details
656247-18-6 Nintedanib esylate 98%View Details
656247-18-6 -
 NINTEDANIB ESYLATE 656247-18-6 95-99 %View Details
NINTEDANIB ESYLATE 656247-18-6 95-99 %View Details
656247-18-6 -
 Nintedanib Ethanesulfonate 656247-18-6 98+View Details
Nintedanib Ethanesulfonate 656247-18-6 98+View Details
656247-18-6 -
 Nintedanib ethanesulphonate CAS 656247-18-6View Details
Nintedanib ethanesulphonate CAS 656247-18-6View Details
656247-18-6 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
