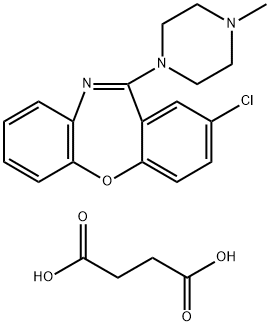
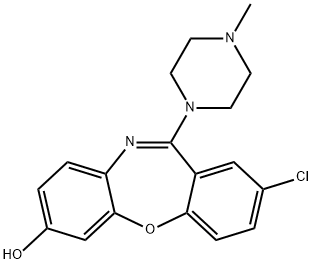
loxapine
- CAS NO.:1977-10-2
- Empirical Formula: C18H18ClN3O
- Molecular Weight: 327.81
- EINECS: 217-835-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-20 11:41:24
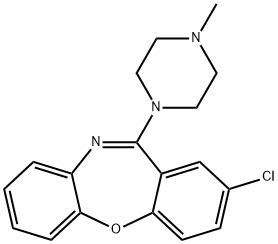
What is loxapine?
Absorption
Systemic bioavailability of the parent drug was only about one third that after an equivalent intramuscular dose (25 mg base) in male volunteers
Toxicity
LD50=65 mg/kg (Orally in mice)
Originator
Loxitane,Lederle,US,1976
The Uses of loxapine
Tranquilizer (minor).
Background
An antipsychotic agent used in schizophrenia. [PubChem]
Indications
For the management of the manifestations of psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia
Definition
ChEBI: Loxapine is a dibenzooxazepine. It has a role as an antipsychotic agent and a dopaminergic antagonist.
Manufacturing Process
One route is described in US Patent 3,412,193 as follows. To a mixture of o-
(p-chlorophenoxy)aniline hydrochloride (prepared from 32 g of the base) in 50
ml of pyridine is added gradually while heating under reflux, 25 ml of ethyl
chloroformate. After the addition is completed, the mixture is heated under
reflux for one hour longer, and then evaporated under reduced pressure to an
oily residue. The residue is taken up in 300 ml of water, and extracted with
ether (approximately 200 ml).
The ether extract is separated, dried over sodium sulfate, and evaporated to
an oily residue (40 g) which contains ethyl o-(p-chlorophenoxy)carbanilate
and is used without further purification. The crude ethyl o-(p-chlorophenoxy)
carbanilate is dissolved in 20 ml of benzene, and 20 ml of 1I-methylpiperazine
and a small amount of sodium methylate (approximately 25 to 50 mg) are
added. Benzene is then removed by slow distillation; and the mixture is
heated overnight under reflux (approximately 16 hours).
Evaporation under reduced pressure then gives a solid residue which is
dissolved in 400 ml of ether with heating. Concentration to half-volume under
reduced pressure produces a precipitate which is collected, washed with
petroleum ether and dried (36 g). A second crop of product is isolated from
the filtrate. This product is dissolved in 200 ml of chloroform and treated with
an excess of anhydrous hydrogen chloride. The resulting precipitate is
collected and dried at 50°C (in vacuo), and 4-methyl-2'-(p-chlorophenoxy)-1-piperazinecarboxanilide hydrochloride, MP 210° to 213°C, is thereby obtained.
A mixture of 4-methyl-2'-(p-chlorophenoxy)-1-piperazinecarboxanilide
hydrochloride (6 g), 50 ml of phosphorus oxychloride and 10 g of phosphorus
pentoxide is heated under reflux for about 24 hours, and then concentrated to
a gummy residue by evaporation under reduced pressure. This residue is
taken up in 150 ml of ether, 200 g of ice is added, and the mixture is made
basic with concentrated aqueous ammonium hydroxide. The ether layer is
separated, dried over potassium hydroxide pellets and evaporated to a solid
residue (approximately 4 g).
This crude product is dissolved in 100 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid, the acid
solution is extracted with ether, and the aqueous layer is made basic with
sodium hydroxide solution (3N) in the presence of ether (approximately 250
ml). The ether layer is separated, dried over potassium hydroxide and
evaporated to a white solid. Additional purification by repeating the formation
of the hydrochloric acid salt and reprecipitation of the base is carried out.
When purified in this manner, followed by drying at 80°C in vacuo over
phosphorus pentoxide, 2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)dibenz[b,f]
[1,4]oxazepine, MP 109° to 111°C, is obtained.
brand name
Loxitane-C Oral Suspension [as hydrochloride] (Wyeth-Ayerst); Loxitane Intramuscular [as hydrochloride] (Wyeth-Ayerst).
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
Biological Activity
loxapine succinate is a d2dr and d4dr inhibitor, serotonergic receptor antagonist and also a dibenzoxazepine anti-psychotic agent [1].
Pharmacokinetics
Loxapine, a dibenzoxazepine compound, represents a subclass of tricyclic antipsychotic agents, chemically distinct from the thioxanthenes, butyrophenones, and phenothiazines. Pharmacologically, Loxapine is a tranquilizer for which the exact mode of action has not been established, however, it is believed that by antagonising dopamine and serotonin receptors, there is a marked cortical inhibition which can manifest as tranquilization and suppression of aggression.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. A tranquilizer. Many dbenz-azepine compounds have central nervous system effects. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cl and NOx.
in vitro
loxapine was a typical neuroleptic that showed great structural and functional homology to the atypical antipsychotic clozapine. chronic loxapine treatment was usually associated with extrapyramidal symptoms (eps). loxapineexihibited an extremely strong binding affinity fordopamined4 andserotonin5-ht2receptors, suggesting that both serotonergic and dopaminergic mechanisms contributed to the antipsychotic drug action and eps associated with loxapine in the treatment of schizophrenia [1]. in frontal cortex of brain in human and bovine, in the presence of loxapine, [3h]ketanserin bound to 5-ht2 receptor with ki value of 6.2 nm and 6.6 nm, respectively. in comparing competition experiments involving the human membranes, loxapine exihibited the rank order of potency for the various receptors as follows: 5-ht2≥d4>>>d1>d2 [1]. loxapine administration at 0.2, 2 and 20 μmafter 1 and 3 days of exposure reduced il-1βand il-2 secretion by lps-activated mixed glia cultures. loxapine also decreased il-1βand il-2 secretion in lps-induced microglia cultures [2].
in vivo
chronic administration of loxapine(5 mg/kg) in rats for 4 weeks or 10 weeks significantly reduced more than 50% of serotonin (s2) receptor density. loxapine (5 mg/kg) didn’t change dopamine receptor density but greatly reduced serotonin receptor density by 47% in the brain of rats [3].
Metabolism
Hepatic
References
[1]. singh an1,barlas c,singh s,franks p,mishra rk. a neurochemical basis for the antipsychotic activity of loxapine: interactions withdopamined1,d2, d4 andserotonin5-ht2receptorsubtypes.j psychiatry neurosci.1996 jan;21(1):29-35.
[2]. labuzek k1,kowalski j,gabryel b,herman zs. chlorpromazine and loxapine reduce interleukin-1beta and interleukin-2 release by rat mixed glial and microglial cell cultures.eur neuropsychopharmacol.2005 jan;15(1):23-30.
[3]. lee t,tang sw. loxapine and clozapine decreaseserotonin(s2) but do not elevatedopamine(d2)receptornumbers in the rat brain.psychiatry res.1984 aug;12(4):277-85.
Properties of loxapine
| Melting point: | 109-110° |
| Density | 1.2299 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| form | Powder |
| color | Light yellow to yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1977-10-2 |
Safety information for loxapine
Computed Descriptors for loxapine
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1