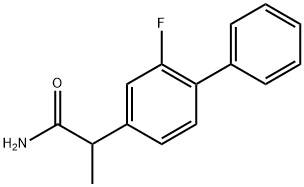
Flurbiprofen
Synonym(s):(±)-2-Fluoro-α-methyl[1,1ʹ-biphenyl]-4-acetic Acid, U-27182;(±)-2-Fluoro-α-methyl-4-biphenylacetic acid;Flurbiprofen;Flurbiprofen - CAS 5104-49-4 - Calbiochem;L-790,330
- CAS NO.:5104-49-4
- Empirical Formula: C15H13FO2
- Molecular Weight: 244.26
- MDL number: MFCD00079303
- EINECS: 225-827-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
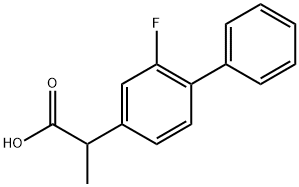
What is Flurbiprofen?
Absorption
Fluribiprofen is rapidly and almost completely absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are reached 0.5 - 4 hours after oral administration.
Toxicity
LD50=10 mg/kg (orally in dogs).
Selective COX-2 inhibitors have been associated with increased risk of serious cardiovascular events (e.g. myocardial infarction, stroke) in some patients. Current data is insufficient to assess the cardiovascular risk of flurbiprofen. Flurbiprofen may increase blood pressure and/or cause fluid retention and edema. Use caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure. Risk of GI toxicity including bleeding, ulceration and perforation. Risk of direct renal injury, including renal papillary necrosis. Anaphylactoid and serious skin reactions (e.g. exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) may occur. Common adverse events include abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, GI bleeding, GI perforation, nausea, peptic ulcer, vomiting, renal function abnormalities, anemia, dizziness, edema, liver function test abnormalities, headache, prolonged bleeding time, pruritus, rash, tinnitus. Although rarely documented in the case of flurbiprofen, oral propionic acid derivatives have been associated with a relatively high frequency of allergic reactions.
Description
Flurbiprofen synthesis was originally reported in 1974. During a study of the pharmacological properties of a large number of substituted phenylalkanoic acids, including ibuprofen and ibufenac, the most potent were found to be substituted 2-(4-biphenyl)propionic acids. Further toxicological and pharmacological studies indicated that flurbiprofen possessed the most favorable therapeutic profile, so it was selected for further clinical development. It was not marketed until 1987, when it was introduced as the sodium salt as Ocufen, the first topical NSAID indicated for ophthalmic use in the United States. The indication for Ocufen is the same as that for Profenal—that is, to inhibit intraoperative miosis induced by prostaglandins in cataract surgery.
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Froben, Boots,UK ,1977
The Uses of Flurbiprofen
An anti-inflammatory used as an analgesic.
The Uses of Flurbiprofen
antiinflammatory, analgesic
The Uses of Flurbiprofen
A cyclooxygenase inhibitor
Background
Flurbiprofen, a propionic acid derivative, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAIA) with antipyretic and analgesic activity. Oral formulations of flurbiprofen may be used for the symptomatic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and anklylosing spondylitis. Flurbiprofen may also be used topically prior to ocular surgery to prevent or reduce intraoperative miosis. Flurbiprofen is structurally and pharmacologically related to fenoprofen, ibuprofen, and ketoprofen.
Indications
Flurbiprofen tablets are indicated for the acute or long-term symptomatic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteorarthritis and anklosing spondylitis. It may also be used to treat pain associated with dysmenorrhea and mild to moderate pain accompanied by inflammation (e.g. bursitis, tendonitis, soft tissue trauma). Topical ophthalmic formulations may be used pre-operatively to prevent intraoperative miosis.
What are the applications of Application
Flurbiprofen is a potent inhibitor of Cox-1 and Cox-2
Indications
Flurbiprofen (Ansaid) is indicated for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Its half-life, longer than that of many of the NSAIDs, allows for twice daily dosing.The most common adverse effects of flurbiprofen are similar to those of the other acidic NSAIDs. Flurbiprofen inhibits both COX isoforms about equally.
Definition
ChEBI: Flurbiprofen is a monocarboxylic acid that is a 2-fluoro-[1,1'-biphenyl-4-yl] moiety linked to C-2 of propionic acid. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic, it is used as a pre-operative anti-miotic as well as orally for arthritis or dental pain. It has a role as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a non-narcotic analgesic, an antipyretic and an EC 1.14.99.1 (prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase) inhibitor. It is a fluorobiphenyl and a monocarboxylic acid. It is functionally related to a propionic acid. It derives from a hydride of a biphenyl.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 3-acetyl-2-fluorobiphenyl, MP 95°C to 96°C, (73.5 g) [prepared from 4.bromo-3-nitroacetophenone (Oelschlage, Ann., 1961, 641, 81) via-4acetyl-2-nitrobiphenyl, MP 106°C to 108°C (Ullman reaction), 4-acetyl-2aminobiphenyl, MP 124°C to 125°C (reduction), and finally the Schiemann reaction], sulfur (17.4 g) and morpholine (87 ml) was refluxed for 16.5 hr, and then the resulting thiomorpholide was hydrolyzed by refluxing with glacial acetic acid (340 ml) concentrated sulfuric acid (54 ml) and water (78 ml) for 24 hr. The cooled solution was diluted with water, and the precipitated crude 2-fluoro-4-biphenylylacetic acid was collected. (A sample was purified by recrystallization to give MP 143°C to 144.5°C; Found (%): C, 73.2; H, 4.8. C14H11FO2 requires C, 73.1; H, 4.8.)
A sodium carbonate solution of the crude acetic acid was washed with ether and then acidified with hydrochloric acid; the required acid was isolated via an ether extraction and was esterified by refluxing for 6 hr with ethanol (370 ml) and concentrated sulfuric acid (15 ml). Excess alcohol was distilled, the residue diluted with water and the required ester isolated in ether. Distillation finally gave ethyl 2-fluoro-4-biphenylacetate, BP 134°C to 136°C/0.25 mm.
This ester (70g) and diethyl carbonate (250 mg) were stirred at 90°C to 100°C while a solution of sodium ethoxide [from sodium (7.8 g) and ethanol (154 ml)] was added over 1 hr. During addition, ethanol was allowed to distill and after addition distillation was continued until the column heat temperature reached 124°C. After cooling the solution to 90°C, dimethyl sulfate (33 ml) was followed by a further 85 ml of diethyl carbonate. This solution was stirred and refluxed for 1 hr and then, when ice cool, was diluted with water and acetic acid (10 ml). The malonate was isolated in ether and fractionally distilled to yield a fraction boiling at 148°C to 153°C/0.075 mm, identified as the alpha-methyl malonate. This was hydrolyzed by refluxing for 1 hr at 2.5 N sodium hydroxide (350 ml) and alcohol (175 ml), excess alcohol was distilled and the residual suspension of sodium salt was acidified with hydrochloric acidto give a precipitate of the alpha-methyl malonic acid. This was decarboxylated by heating at 180°C to 200°C for 30 minutes and recrystallized from petroleum ether (BP 80°C to 100°C) to give 2-(2-fluoro-4biphenylyl)propionic acid, MP 110°C to 111°C
brand name
Ansaid (Pharmacia & Upjohn).
Therapeutic Function
Antiinflammatory
General Description
Flurbiprofen (Ansaid, Ocufen, Froben), is another drug inthis class indicated for both acute and long-term managementof RA and OA but with a more complex mechanism ofaction. Unlike the other drugs in this class, it does not undergochiral inversion (i.e., the conversion of the “inactive”[R]-enantiomer to the active, [S]-enantiomer). Similar to aspirinand other salicylates, both flurbiprofen enantiomersblock COX-2 induction as well as inhibiting the nuclearfactor-κB-mediated polymorphonuclear leukocyte apoptosissignaling; therefore, both enantiomers are believed to contributeequally to its overall anti-inflammatory action.
(R)-flurbiprofen is actually a strong clinical candidate forthe treatment of Alzheimer disease, because it has beenshown to reduce Aβ42 production by human cells.
Biological Activity
Potent inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (IC 50 values are 0.1 and 0.4 μ M for inhibition of human COX-1 and COX-2 respectively). Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic in vivo . Inhibits tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo . Also inhibits fibroblast proliferation in vitro .
Pharmacokinetics
Flurbiprofen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAIA) of the propionic acid class, is structually and pharmacologically related to fenoprofen, ibuprofen, and ketoprofen, and has similar pharmacological actions to other prototypica NSAIAs. Flurbiprofen exhibits antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities. The commercially available flurbiprofen is a racemic mixture of (+)S- and (-) R-enantiomers. The S-enantiomer appears to possess most of the anti-inflammatory, while both enantiomers may possess analgesic activity.
Pharmacokinetics
Flurbiprofen is well absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma levels being attained within 1.5 hours. Food alters the rate of absorption but not the extent of its bioavailability. It is extensively bound to plasma proteins (99%).and has a plasma half-life of 2 to 4 hours. Metabolism is extensive, with 60 to 70% of flurbiprofen and its metabolites being excreted as sulfate and glucuronide conjugates. Flurbiprofen shows some interesting metabolic patterns, with 40 to 47% as the 4′-hydroxy metabolite, 5% as the 3′,4′-dihydroxy metabolite, 20 to 30% as the 3′-hydroxy- 4′-methoxy metabolite, and the remaining 20 to 25% of the drug being excreted unchanged. None of these metabolites demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory activity.
Clinical Use
Flurbiprofen is indicated as an oral formulation for the acute or long-term treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis and as an ophthalmic solution for the inhibition of intraoperative miosis.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists: antagonism of hypotensive effect; increased risk of nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemia. Analgesics: avoid concomitant use with other NSAIDs or aspirin; avoid concomitant use with ketorolac (increased side effects and haemorrhage). Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of convulsions with quinolones. Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of bleeding with heparin, dabigatran and edoxaban - avoid long term use with edoxaban. Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with SSRIs or venlafaxine. Antidiabetics: effects of sulphonylureas enhanced. Antiepileptics: possibly enhanced effect of phenytoin. Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by ritonavir; increased risk of haematological toxicity with zidovudine. Ciclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicity. Cytotoxics: reduced excretion of methotrexate; increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib. Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity; antagonism of diuretic effect; hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics. Lithium: excretion reduced (risk of lithium toxicity). Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleeding. Tacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity
Metabolism
Hepatic. Cytochrome P450 2C9 plays an important role in the metabolism of flurbiprofen to its major metabolite, 4’-hydroxy-flurbiprofen. The 4’-hydroxy-flurbiprofen metabolite showed little anti-inflammatory activity in animal models of inflammation.
Metabolism
Flurbiprofen is metabolised mainly by hydroxylation (via the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP2C9) and conjugation in the liver and excreted in the urine. The rate of urinary excretion of flurbiprofen and its two major metabolites ([2-(2-fluoro-4′-hydroxy-4-biphenylyl) propionic acid] and [2-(2-fluoro-3′-hydroxy-4′-methoxy-4-biphenylyl) propionic acid]) in both free and conjugated states is similar for both the oral and rectal routes of administration.
Storage
Room temperature
Properties of Flurbiprofen
| Melting point: | 110-112 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 376.2±30.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.1795 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | methanol: soluble50mg/mL |
| form | White solid |
| pka | pKa 3.80(H2O) (Uncertain) |
| color | white to off-white |
| Water Solubility | 8mg/L(room temperature) |
| Merck | 14,4199 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 5104-49-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | [1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-acetic acid, 2-fluoro-?-methyl- (5104-49-4) |
Safety information for Flurbiprofen
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Flurbiprofen
| InChIKey | SYTBZMRGLBWNTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Flurbiprofen manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 FLURBIPROFEN 99%View Details
FLURBIPROFEN 99%View Details -
 5104-49-4 Flurbiprofen 98%View Details
5104-49-4 Flurbiprofen 98%View Details
5104-49-4 -
 Flurbiprofen 99%View Details
Flurbiprofen 99%View Details -
 FLURBIPROFEN 5104-49-4 95-99 %View Details
FLURBIPROFEN 5104-49-4 95-99 %View Details
5104-49-4 -
 Flurbiprofen CAS 5104-49-4View Details
Flurbiprofen CAS 5104-49-4View Details
5104-49-4 -
 Flurbiprofen 95% CAS 5104-49-4View Details
Flurbiprofen 95% CAS 5104-49-4View Details
5104-49-4 -
 Flurbiprofen >98% (HPLC) CAS 5104-49-4View Details
Flurbiprofen >98% (HPLC) CAS 5104-49-4View Details
5104-49-4 -
 Pure Flurbiprofen api powder, 5104-49-4View Details
Pure Flurbiprofen api powder, 5104-49-4View Details
5104-49-4
